



This is for the simple text copy pasting formate template for work file
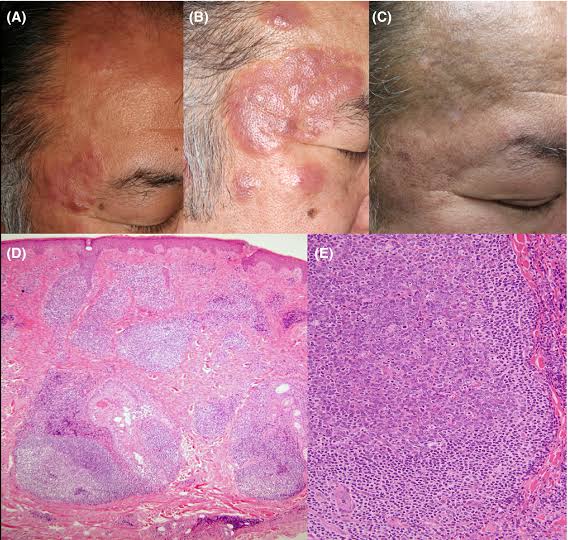
2️⃣ PITYRIASIS LICHENOIDES
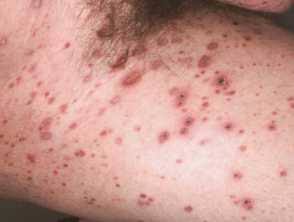

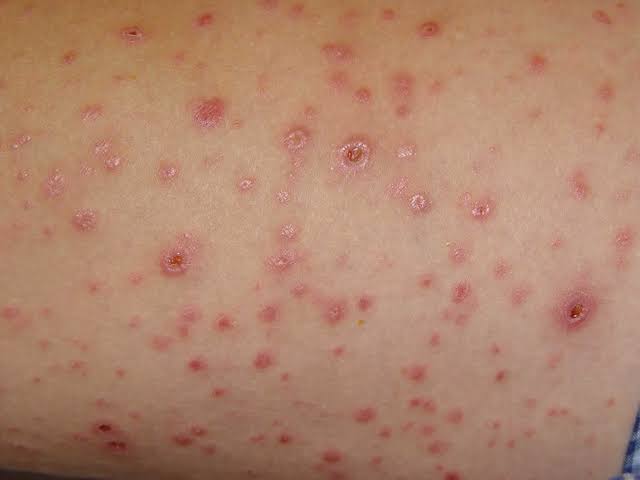
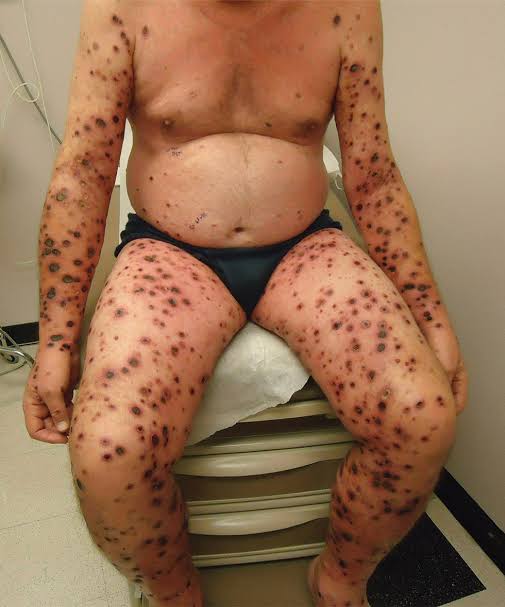
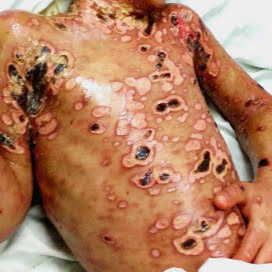
Febrile ulceronecrotic Mucha Habermann disease👇🏻

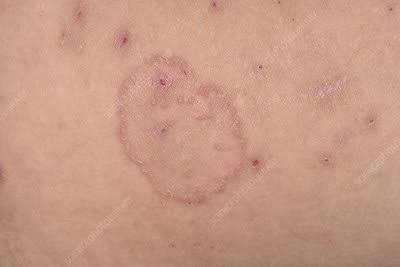
3️⃣ PARAPSORIASIS
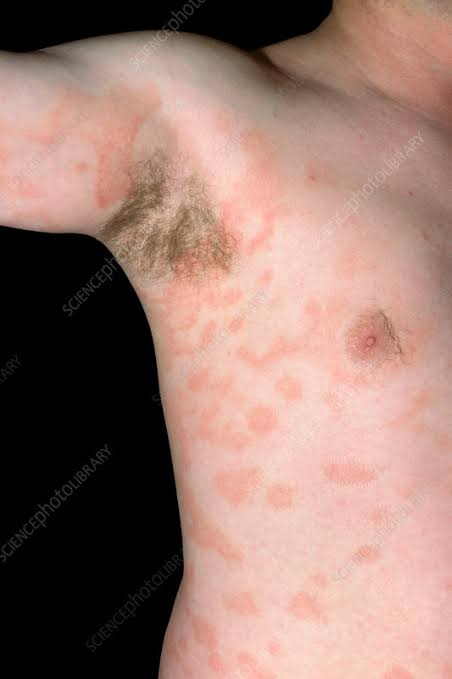
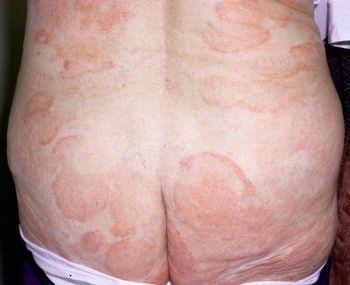
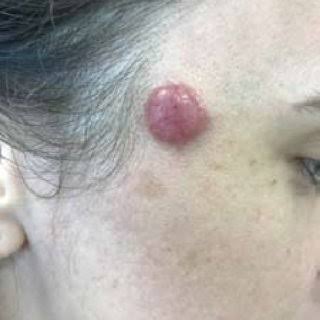
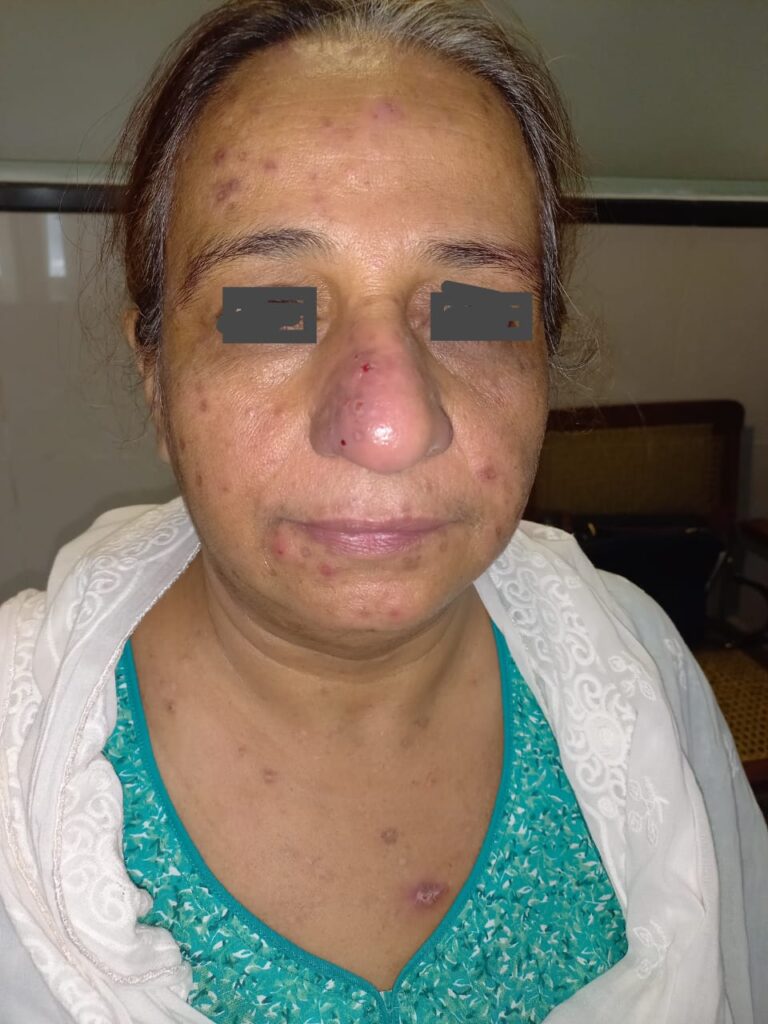
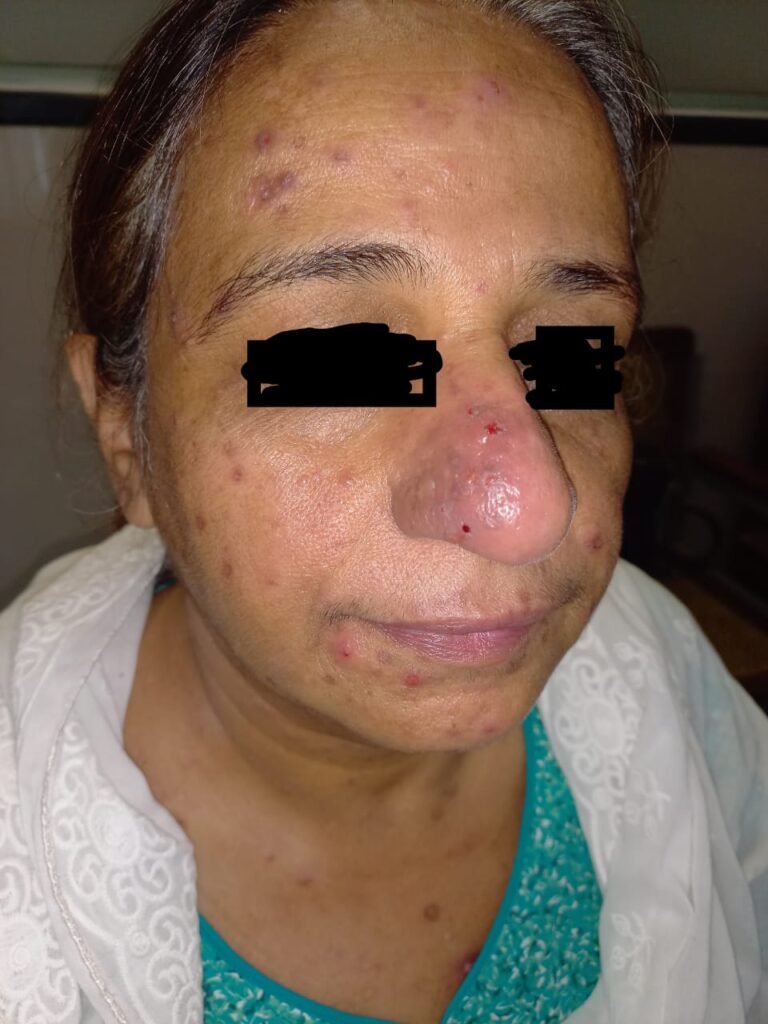
4️⃣ LYMPHOCYTOMA CUTIS
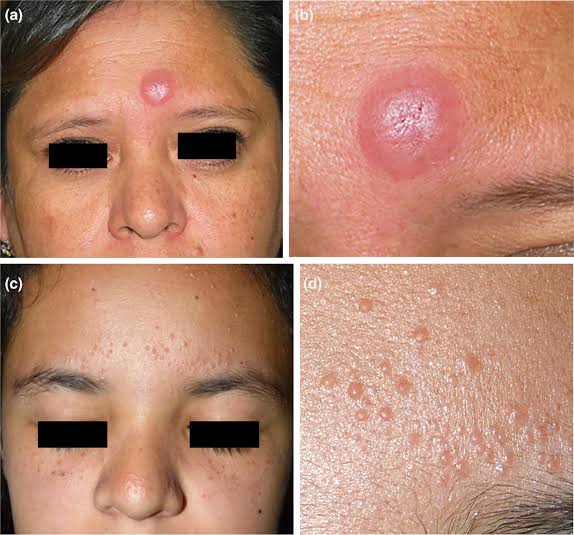
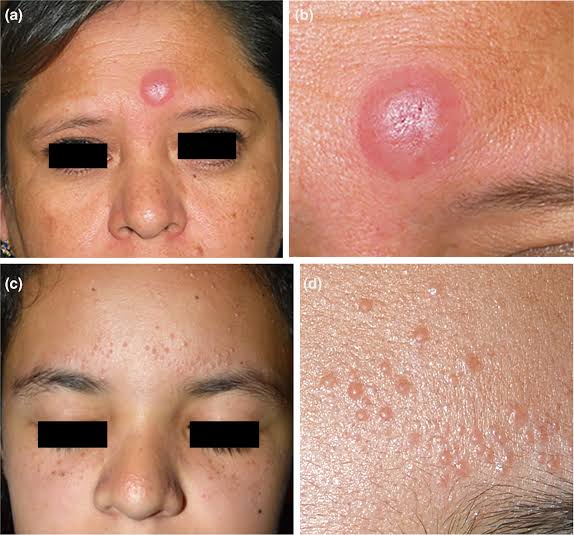
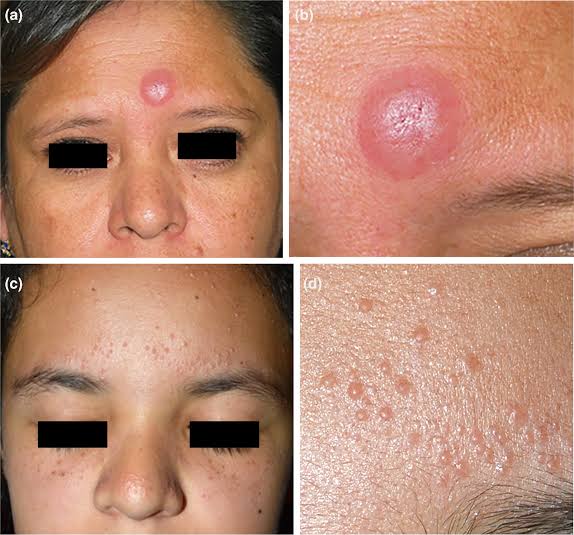

5️⃣ JESSNER’S LYMPHOCYTIC INFILTRATE


Epidermal melanin unit
Distribution of melanocytes
Melanoblast migration and differentiation
Melanosome transport
Melanosome transfer to keratinocytes
Melanocyte culture
Biochemistry of melanogenesis
Regulation of human pigmentation
Melanocyte regulation by endocrine factors
Melanocyte regulation by paracrine and autocrine
Biological significance of melanin
Constitutive pigmentation
Classification of disorders of melanin pigmentation
Physiological Hypermelanosis
Facial melanosis
Melasma

Photocontact melanosis
Poikiloderma of Civatte
Erythromelanosis follicularis of the face and neck
Peribuccal pigmentation of Brocq
Ephelides
Lentiginosis
🔰 Hypermelanosis due to endocrine disorders
1️⃣ Addison disease
2️⃣ Acromegaly
3️⃣ Cushing syndrome
4️⃣ ACTH administration
5️⃣ Hyperthyroidism
🔰 *Hyperpigmentation in other systemic disorders*
🔰 Neoplastic disease
Hyperpigmentation in rheumatoid disease
Systemic sclerosis and morphea
SLE and dermatomyositis
Neurological disorders
Multiple organ failure
Renal failure
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Hemochromatosis
Cutaneous amyloidosis
Nutritional deficiency
POEMS syndrome
🔰 Hypermelanosis of drug origin
✅ Very important👆🏻
Fixed drug eruption
Pigmentation resulting from acute photodynamic and phototoxic reactions
Post inflammatory hypermelanosis
Ashy dermatosis and erythema dyschromicum perstans
Treatment of hypermelanosis
1️⃣ Vitiligo
2️⃣ Halo naevus

🔰 Acquired syndromic hypomelanosis
1️⃣ Vogt- koyanagi- Harada syndrome
2️⃣ Alezzandrini syndrome
Post inflammatory hypomelanosis
Chemical depigmentation
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis
Punctate leukoderma
Endogenous non melanin pigmentation
Cutaneous hemosiderosis
Jaundice and bronze baby syndrome
Carotenoderma
Ochronosis
🔰 Important tip for this chap.👇🏻
Dun waste too much time on reading this chap from rooks.
Just listen to above voice notes and solve mcqs
Happy learning😊
🔰 Table 91.1 in rooks 9th edition is a summary of the whole topic Rosacea.


🔰 Summary of rosacea👆🏻
ETTR
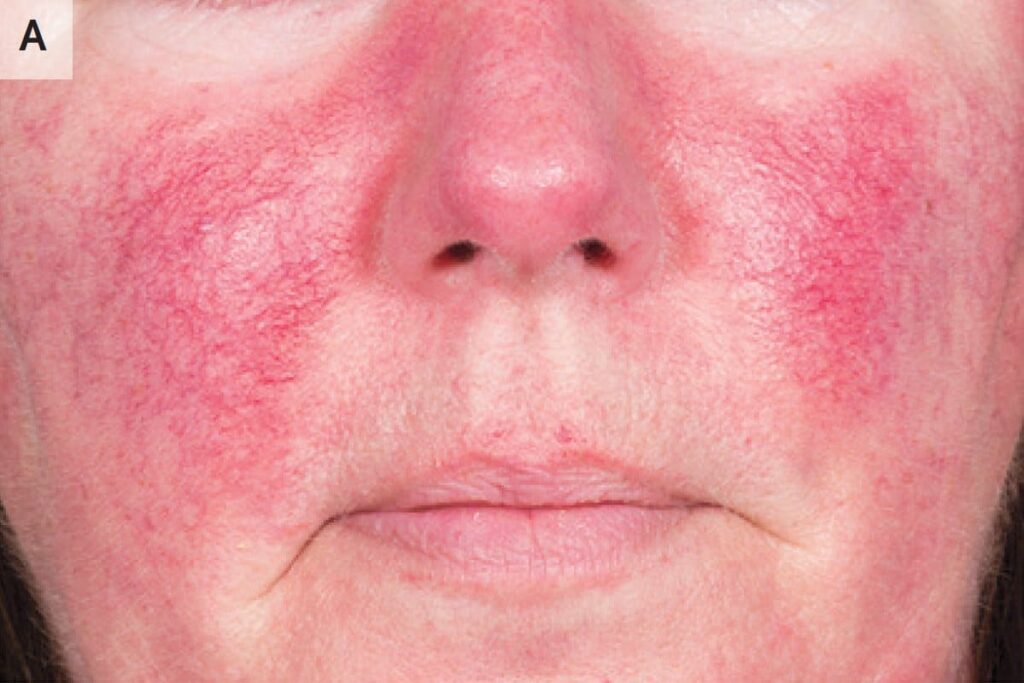


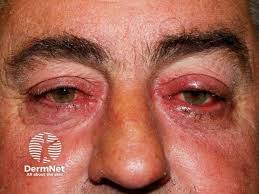
Pathophysiology👇🏻
Pathology👇🏻
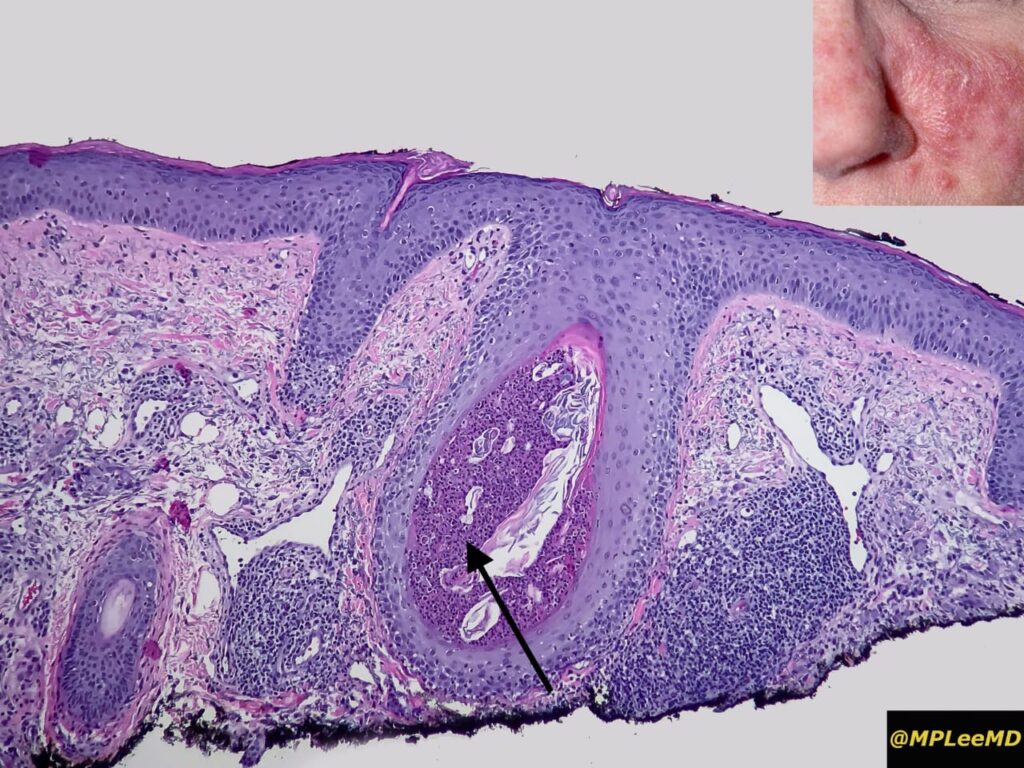
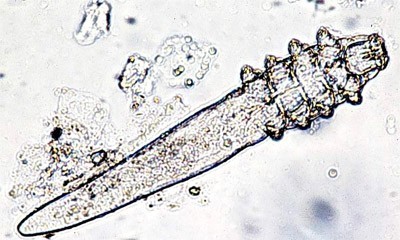
Causative organisms 👇🏻
Demodex mite
Clinical features
Clinical variants 👇🏻
Granulomatous rosacea

Differential diagnosis👇🏻
Only read this table for DDs

Complications👇🏻
Disease course and prognosis👇🏻
Investigations
Management👇🏻



Only revise tables for management👆🏻
🔰 *Important note*👇🏻
For Rosacea, only listen to above voice notes, revise tables from rooks and practice mcqs.
Its more than enough for this chap
Associations 👇🏻
Pathophysiology👇🏻
Pathology👇🏻

Diagnostic criteria👇🏻
All 3 must be fulfilled

Clinical features👇🏻
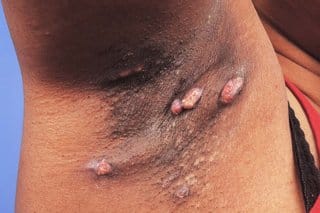
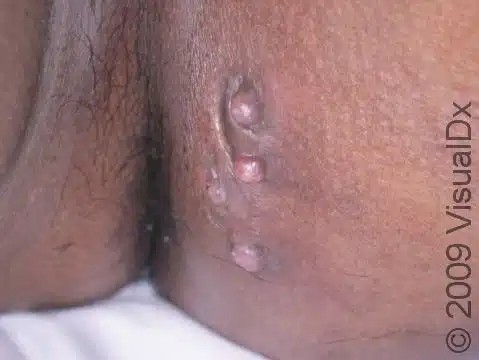
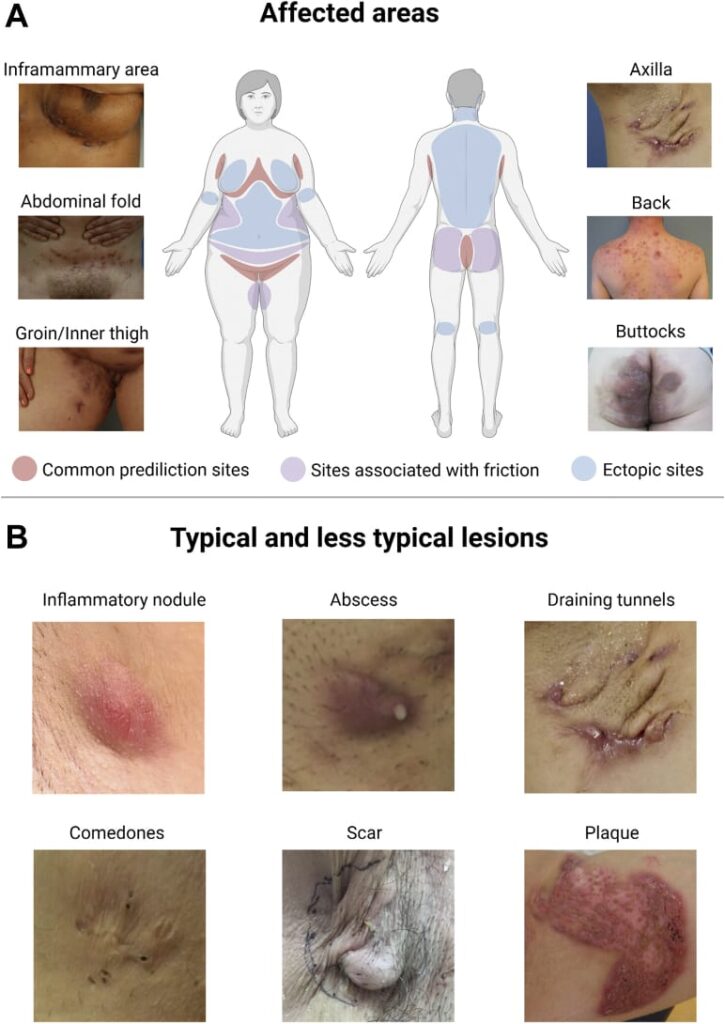
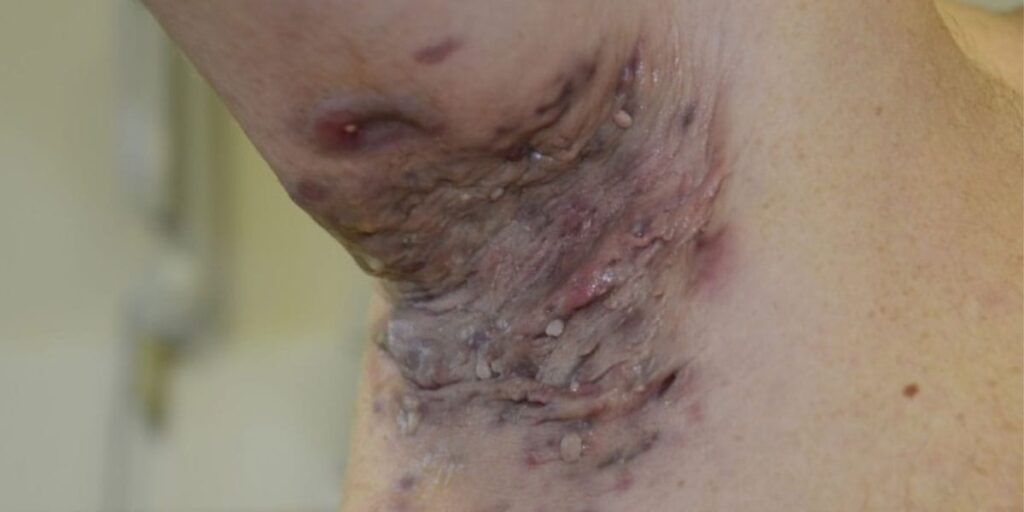
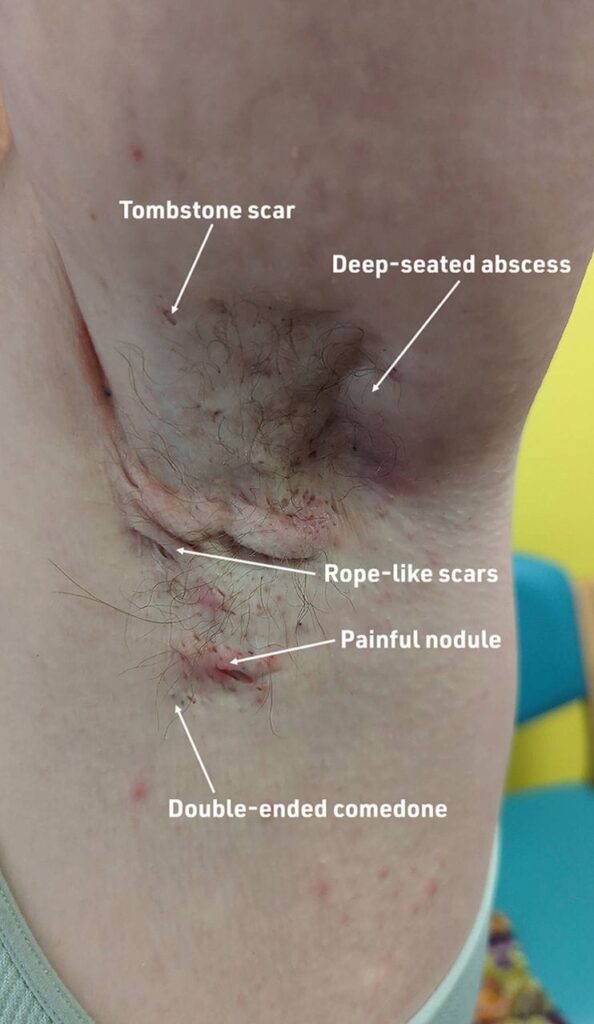
Classification of severity👇🏻
*Hurley staging system*

Hurley stage 1
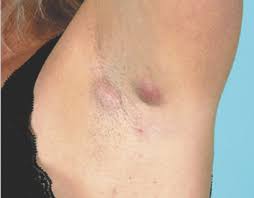
Hurley stage 2

Hurley stage 3
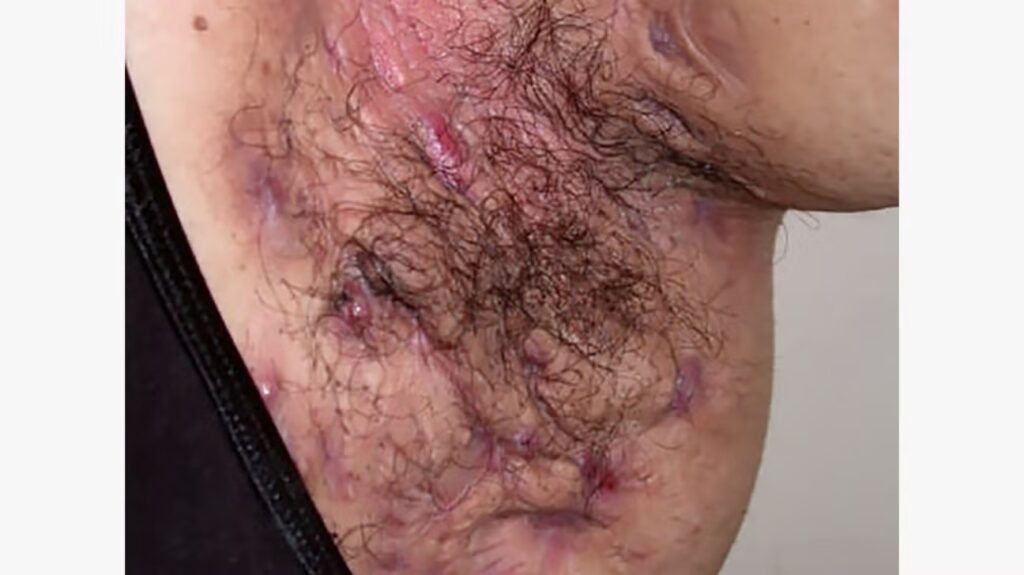
Differential diagnosis👇🏻
Complications 👇🏻
Disease course and prognosis👇🏻
Investigations 👇🏻
Management👇🏻

🔰 *Important note*👇🏻
For HS, above voice notes are enough. Reading from rooks can be done for self satisfaction.
Practice from mcqs later on.
🔰 Disorders of pilosebaceous unit and disorders of sweat glands can be covered from mcqs.
Dun waste ua time reading it from rooks.


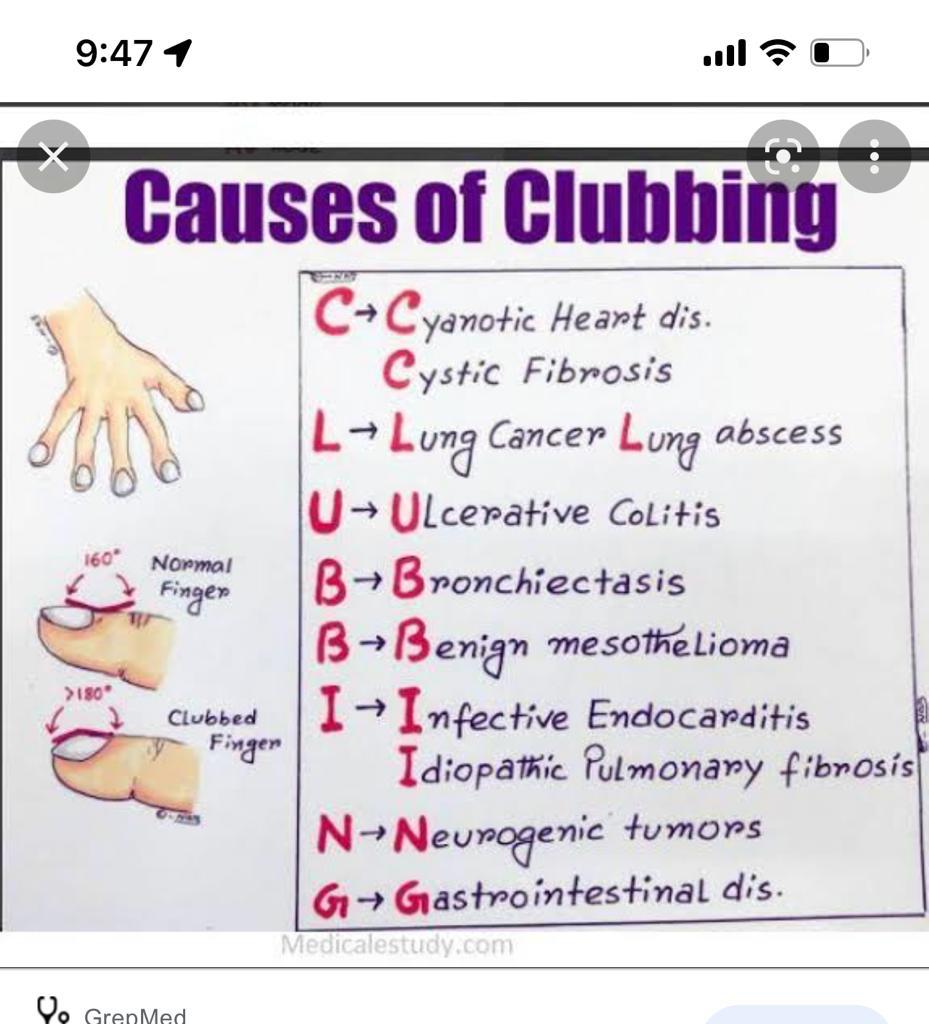
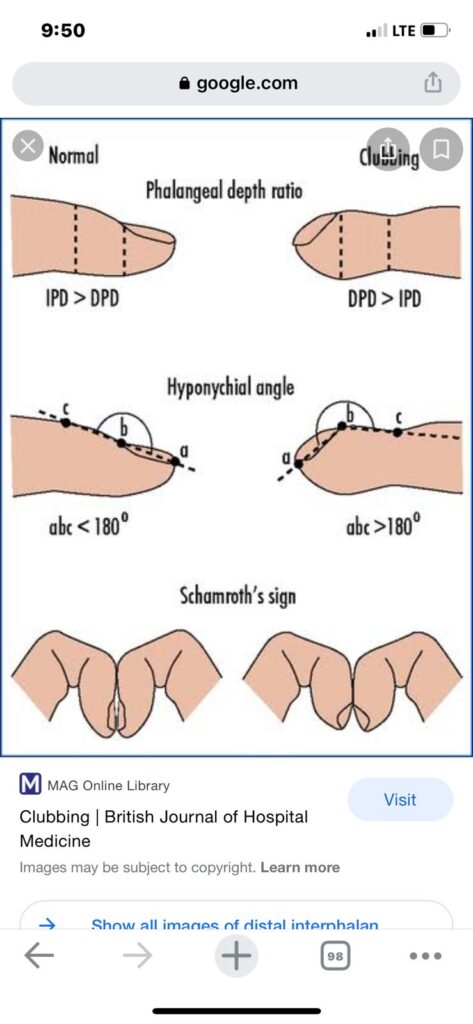
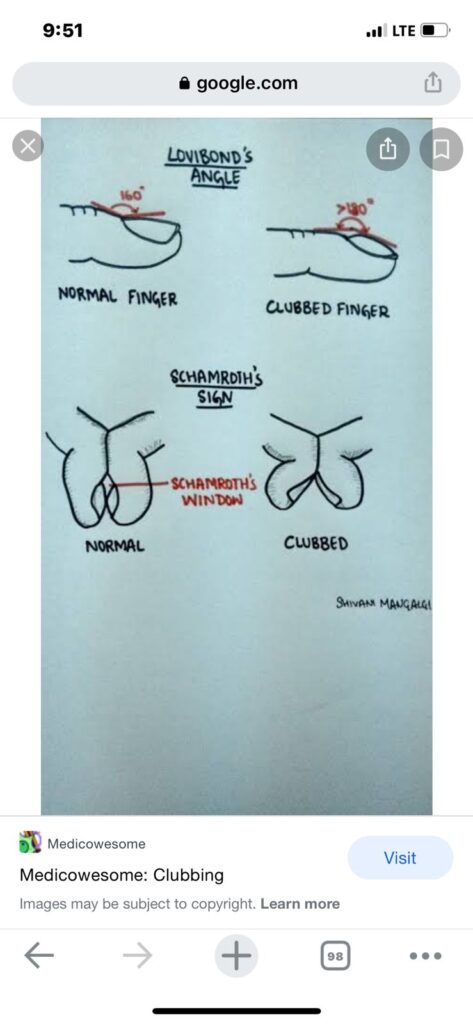
Clubbing👇🏻👇🏻

Koilonychia
Pincer nail
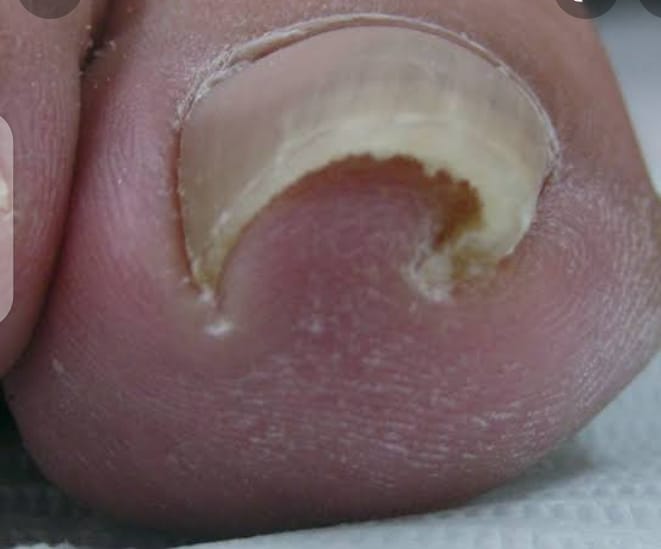
Nail shedding
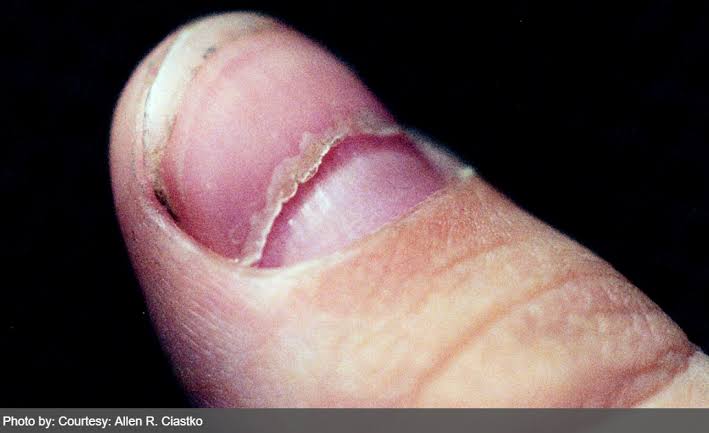
Onycholysis
Pterygium
Longitudinal grooves👇🏻
Transverse grooves and beau’s lines
Trachyonychia
Onychoschizia/ lamellar dystrophy
Nail plate pigmentation
Subungual disturbances
Nail bed changes
Leuconychia
Colour changes due to drugs and chemicals
YELLOW NAIL SYNDROME
Red lanulae
Longitudinal erythronychia
Splinter hemorrhage
🔰 *Causes of Splinter hemorrhage*
Liver disease
Endocarditis
Connective tissue disease
Meningococcal disease
Psittacosis
Disseminated histoplasmosis.
*Skin disease*
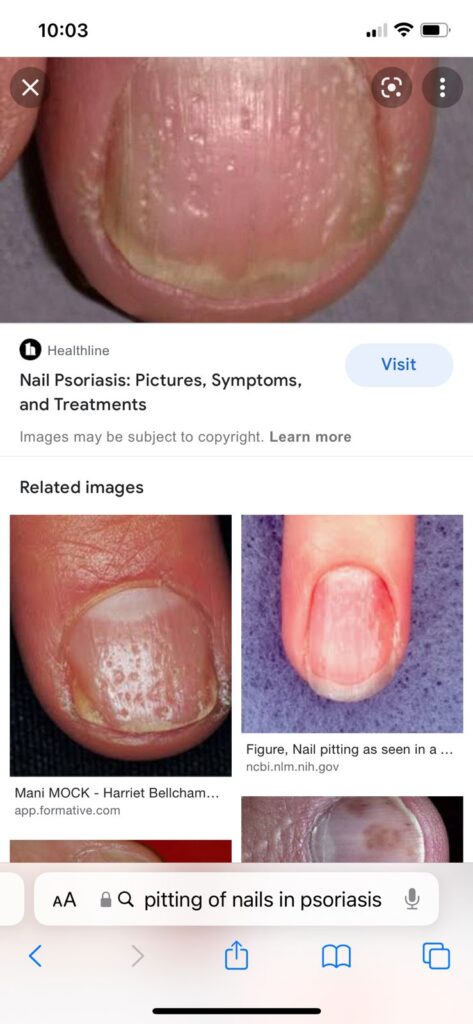
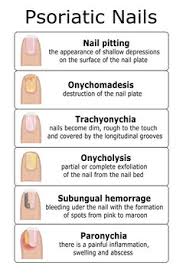
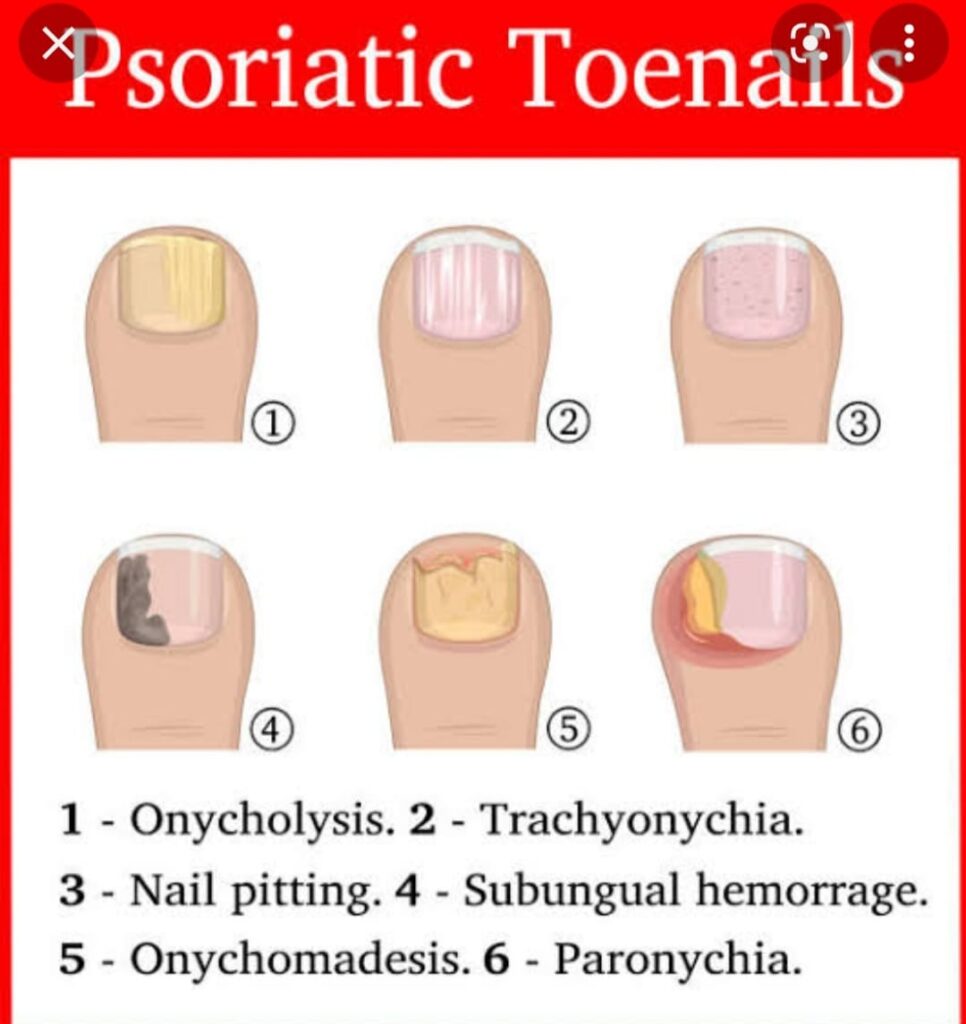
psoriatic nail disease
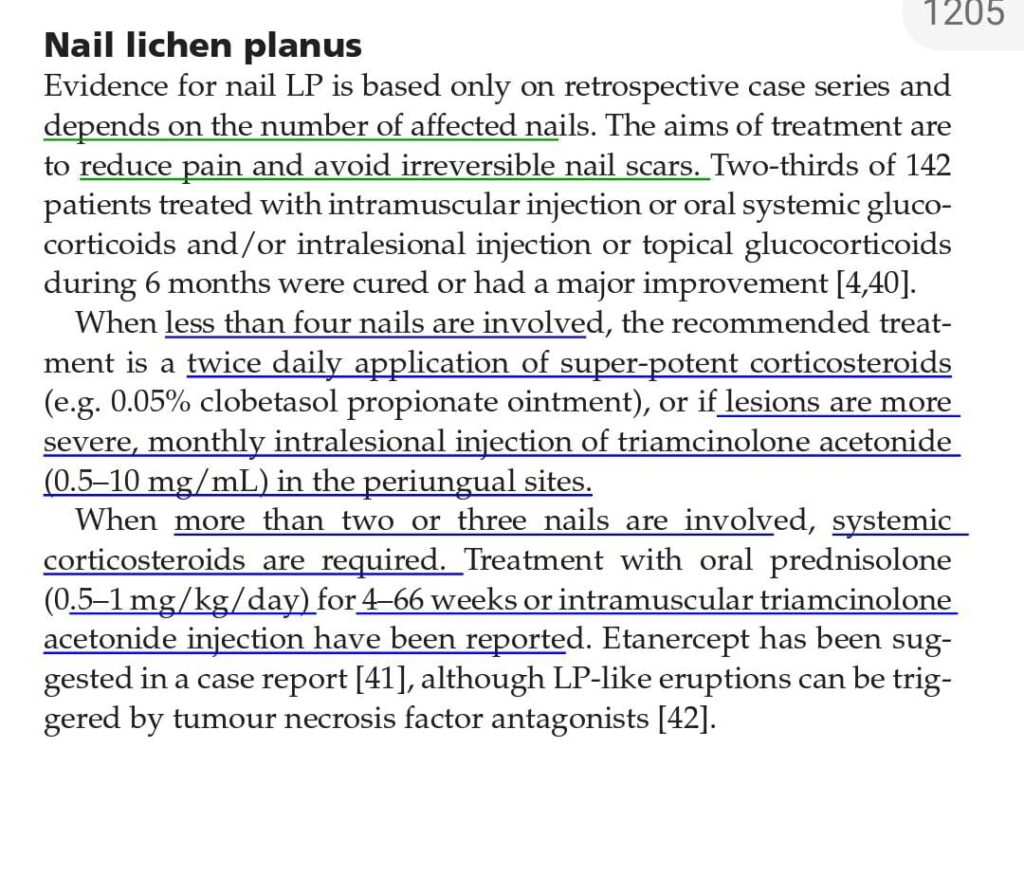
lichen planus
*Systemic diseases*
microemboli or injury to vessel walls associated with vasculitis
Primary antiphospholipid syndrome
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Raynaud disease
Behcet disease
Cutaneous vasculitis
Scurvy.
chronic kidney disease on haemodialysis or post-renal transplant
*Drugs*
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (seen in 60–70% of patients taking sunitinib and sorafenib)
Nitrofurantoin
Ganciclovir
Terbinafine
Tetracyclines.
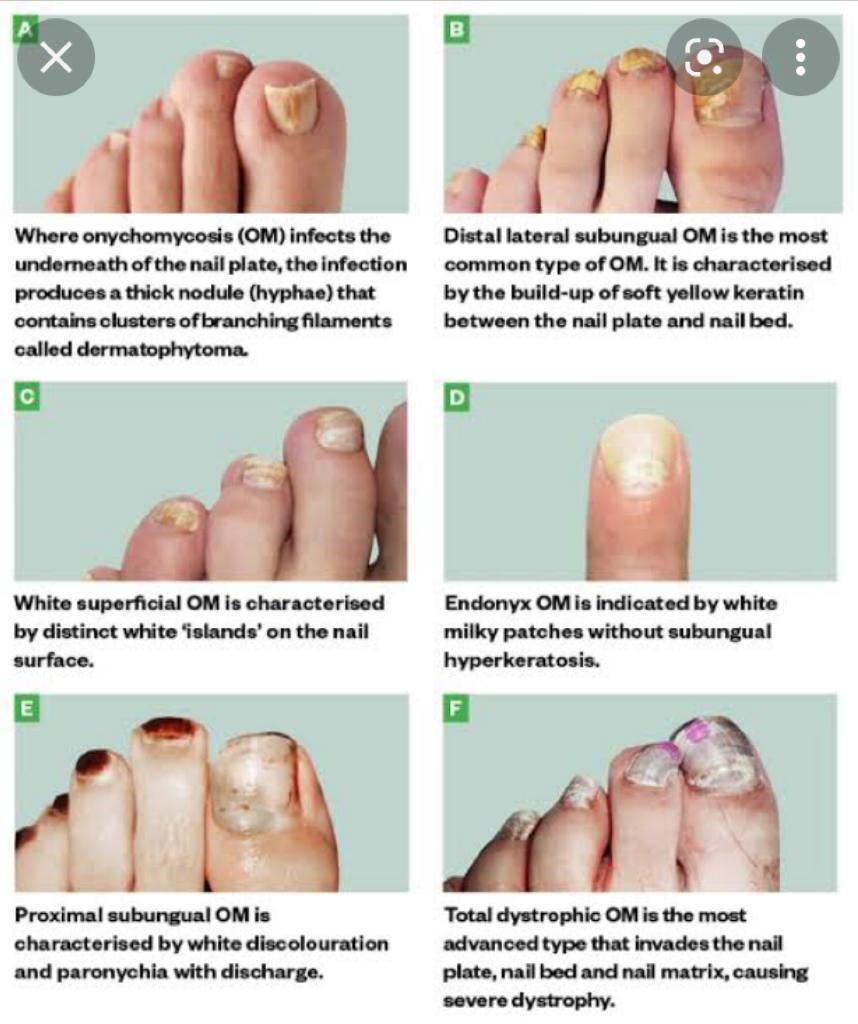
Mneumonic of painful tumours

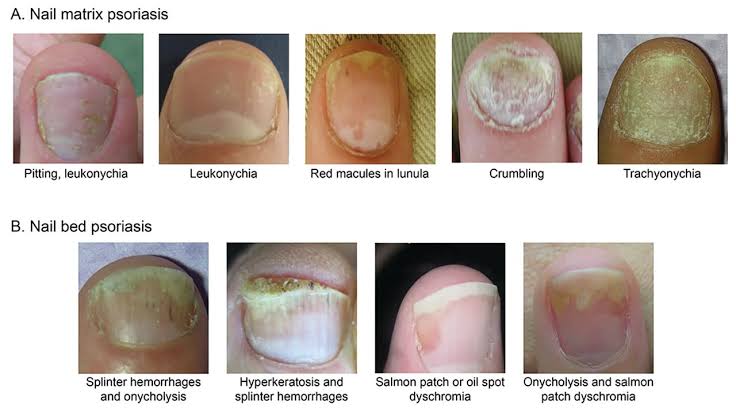





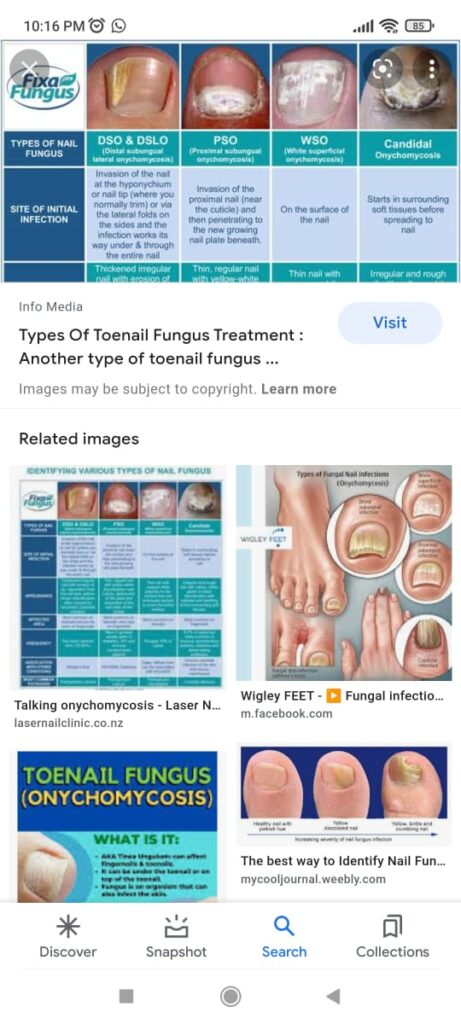
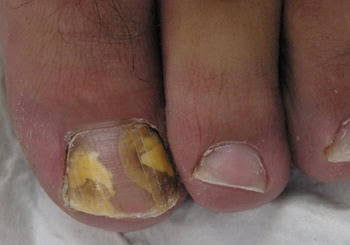
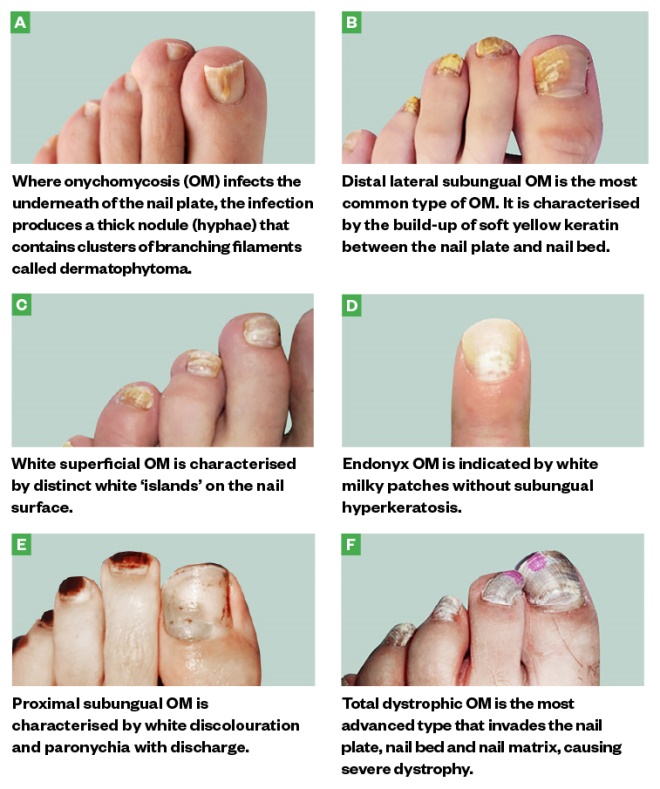

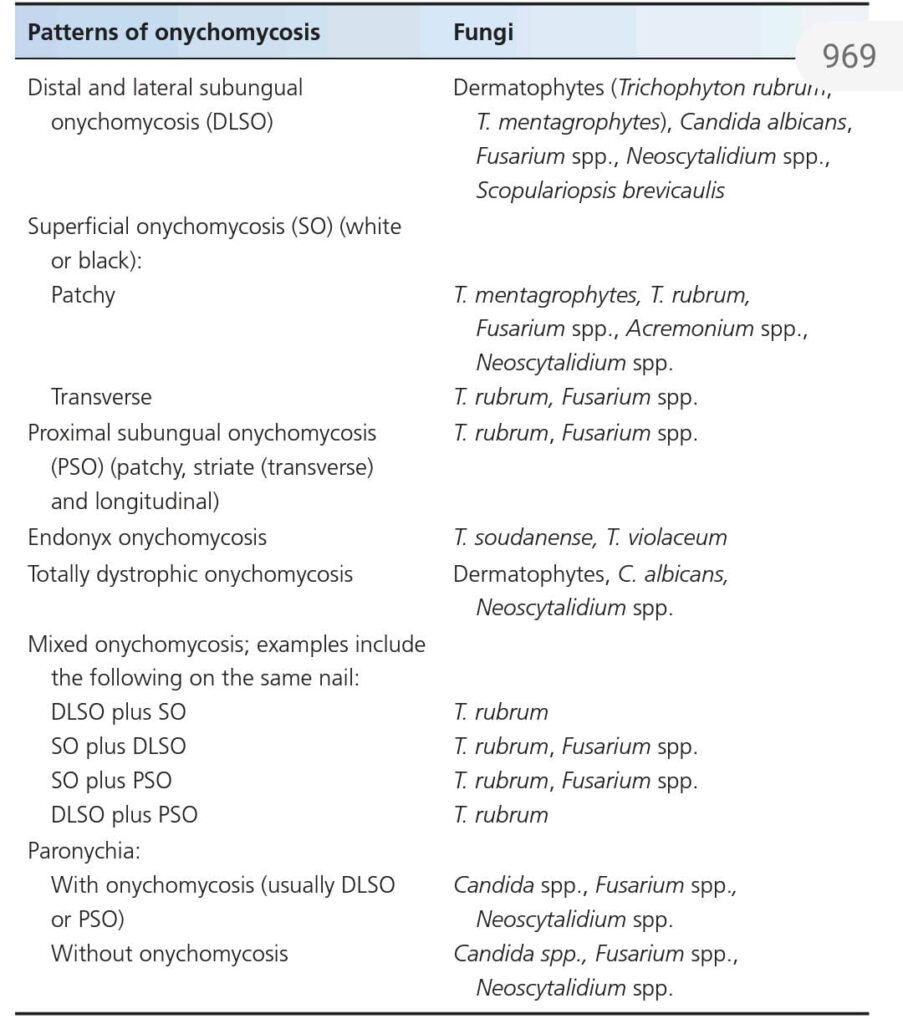

7 types
Superficial
Dystrophic
Proximal
Endonyx
Paronychia
Mixed
Dlso







📝 Hutchinson eye sign …in herpes zoster ..
Hutchinson nail sign.. melanoma.. ( others are pseudo Hutchinson and micro Hutchinson)
Hutchinson triad in congenital syphilis ..
Hutchinson summer prurigo which is actinic prurigo.
Hutchinson malignant freckle which is lentigo maligna
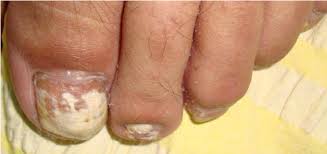
What is the significance of this… Black streak…
*Melanonychia*
Here there can be the following *possibilities*
*1.functionsl melanonychia* ( melanocyte activation,common in dark individuals, can be due to trauma ,)
*2.melanocytic nevi*
*3.inflammatory skin conditions* like lp and other pigmentary disorders which can be correlated clinically)
The pigmentation varies from brown dark brown to black
Pseudo Hutchinson can be seen too.
Most commonly involves thumb but other nails can be involved as well
*_Mostly a naevi in matrix !*_
mostly these are *matrix naevi* leading to band, so focal matrix ablation might lead a nail plate dystophy lateron which might look uglier than this
Would the nail appearance be normal after this procedure and complete healing?
*Yes only the transverse lenght* *will be shortened* , rest it will be perfact
Grabbing this opportunity to revise *ABCDEFGHI* , to R/O *subungual melanoma* in such cases
*A: Age (* 50–70 years old); African, Japanese, Chinese, and Native American heritage
*B: Brown-black* pigmented band ≥3mm with blurred borders
*C: Change or lack of change* despite treatment in the nail band or nail morphology
*D: Digit most* commonly involved (thumb, big toe, or index finger)
*E: Extension* of pigment into the skin surrounding the nail (Hutchinson sign)
*F: Family or personal history* of melanoma or dysplastic nevus (atypical mole)
*G – Geometry* of lesion like triangular band
*H – Hyponychial involvement*
*I – irregular pigment pattern* (like different color bands) , irregular spaces , irregular thickness

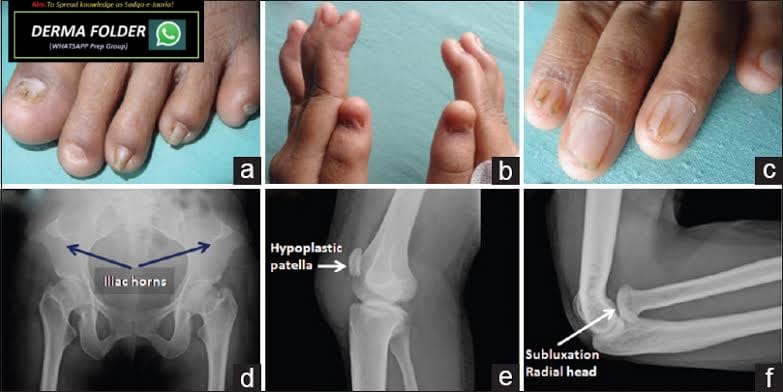

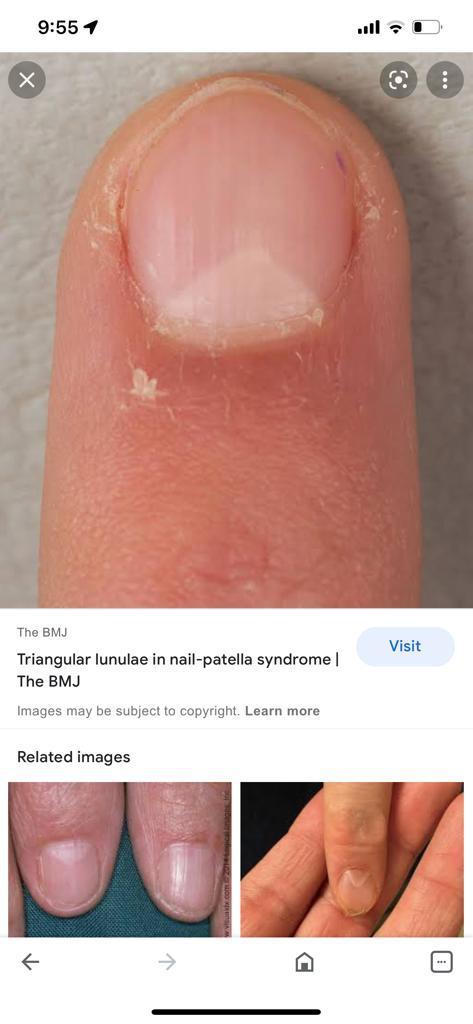

🔑 🗝 🔐 Pincer nails deformity
*hereditary disease*
▪️autosomal dominant Mendelian
▪️Clouston
*acquired pincer nails*
▪️gastrointestinal malignancies,
▪️renal failure,
▪️Kawasaki disease,
▪️amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and
▪️systemic lupus erythematosus
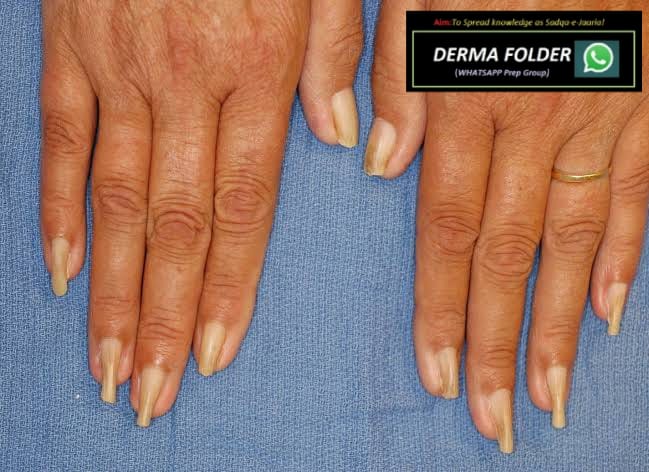
🔰 Racquet nails
🟥 *causes?* 🔑
*Genetic disorders*
▪️Larsen syndrome,
▪️Brooke–Spiegler syndrome,
▪️Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome,
▪️Hajdu–Cheney syndrome,
▪️cartilage–hair hypoplasia,
▪️pycnodysostosis,
▪️acrodysostosis,
▪️brachydactyly type D.
*Acquired racquet nail*
associated with
▪️acroosteolysis and
▪️psoriatic arthropathy.
▪️diagnostic of bone resorption in hyperparathyroidism.

Anonychia


🔰 Important tip for this chap👇🏻
Pathogenesis👇🏻
Pathology👇🏻
Basophilic fibrinous sheath

🔰 Imp tip for histopathology👆🏻
Differential diagnosis 👇🏻
Triggers👇🏻
Clinical features👇🏻
1️⃣ Cutaneous sarcoidosis
🔯 Specific forms of Cutaneous sarcoidosis
✅Maculopapular sarcoidosis
Typical appearance of lesions of sarcoidosis
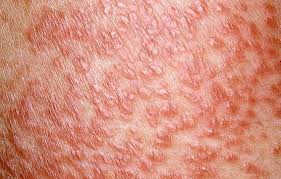
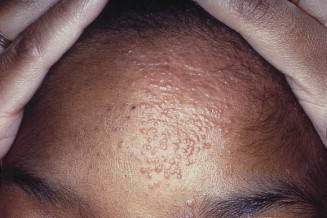
✅ Nodular and Plaque sarcoidosis

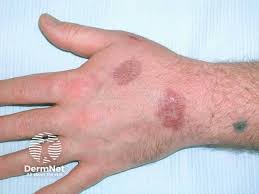
✅ Lupus pernio
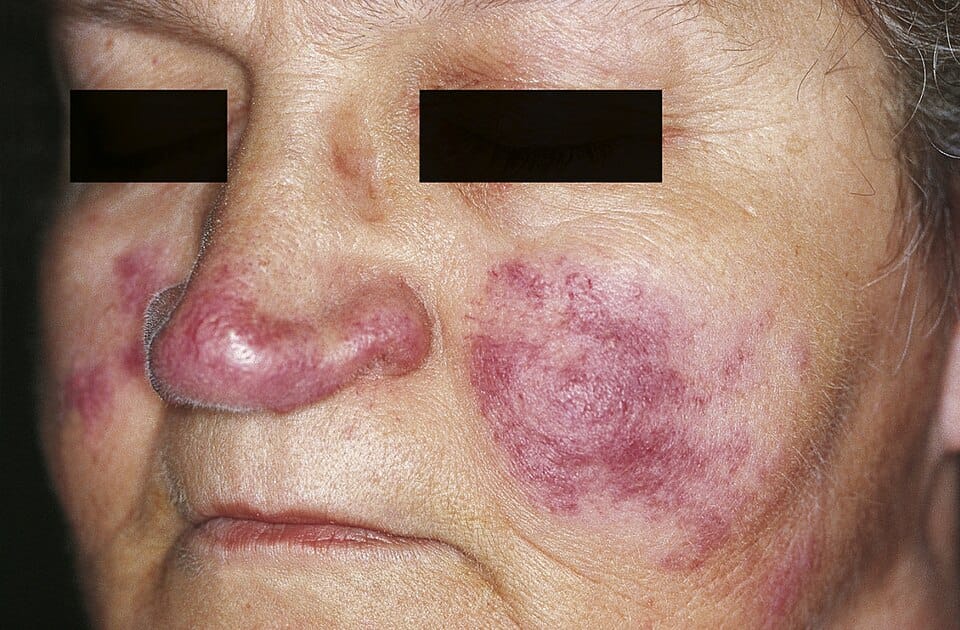
✅ Scar sarcoidosis
Scar sarcoidosis

✅ Subcutaneous sarcoidosis
Sarcoid dactylitis

🔯 Less common forms of cutaneous sarcoidosis

Heerfordt syndrome 👇🏻

Heerfordt syndrome

Mneumonic
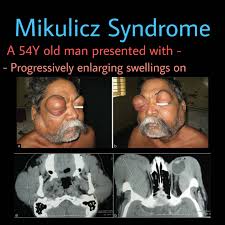
Mikulicz syndrome 👇🏻
2️⃣ Pulmonary sarcoidosis
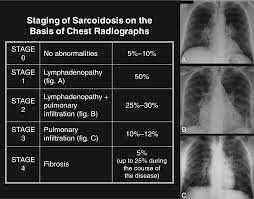
3️⃣ Ocular sarcoidosis
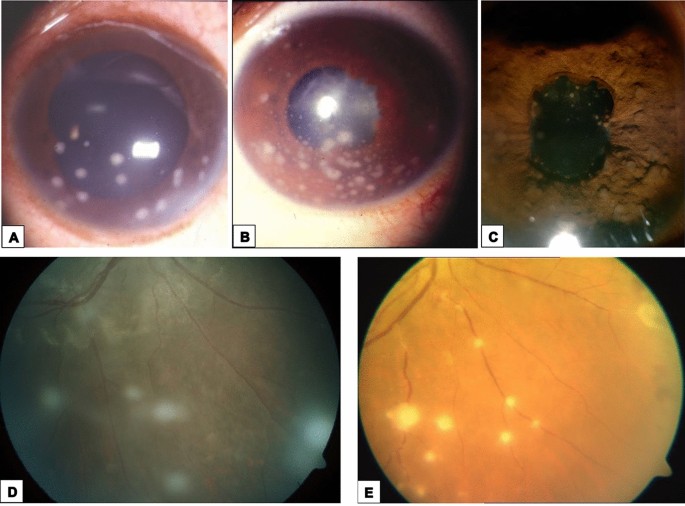
4️⃣ Reticuloendothelial system
5️⃣ Liver
6️⃣ Neurosarcoidosis
7️⃣ Others
🔰 Course and prognosis 👇🏻
🔰 Investigations 👇🏻

🔰 Management
🔰 *IMPORTANT TIP*
Above voice notes covers all imp aspects of Sarcoidosis.
So if u skip reading it from the book and only listen to these voice notes + practice with mcqs will be sufficient.
🔰 IMPORTANT TIP FOR THIS CHAP👇🏻
Septal Panniculitis

Basophilic fibrinous sheath

Imp points to remember👆🏻
Stains used in biopsy specimens of Panniculitis
🔰 SEPTAL PANNICULITIS
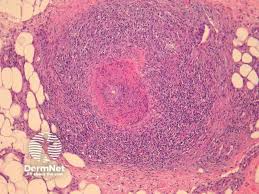
1️⃣ Cutaneous PAN👇🏻

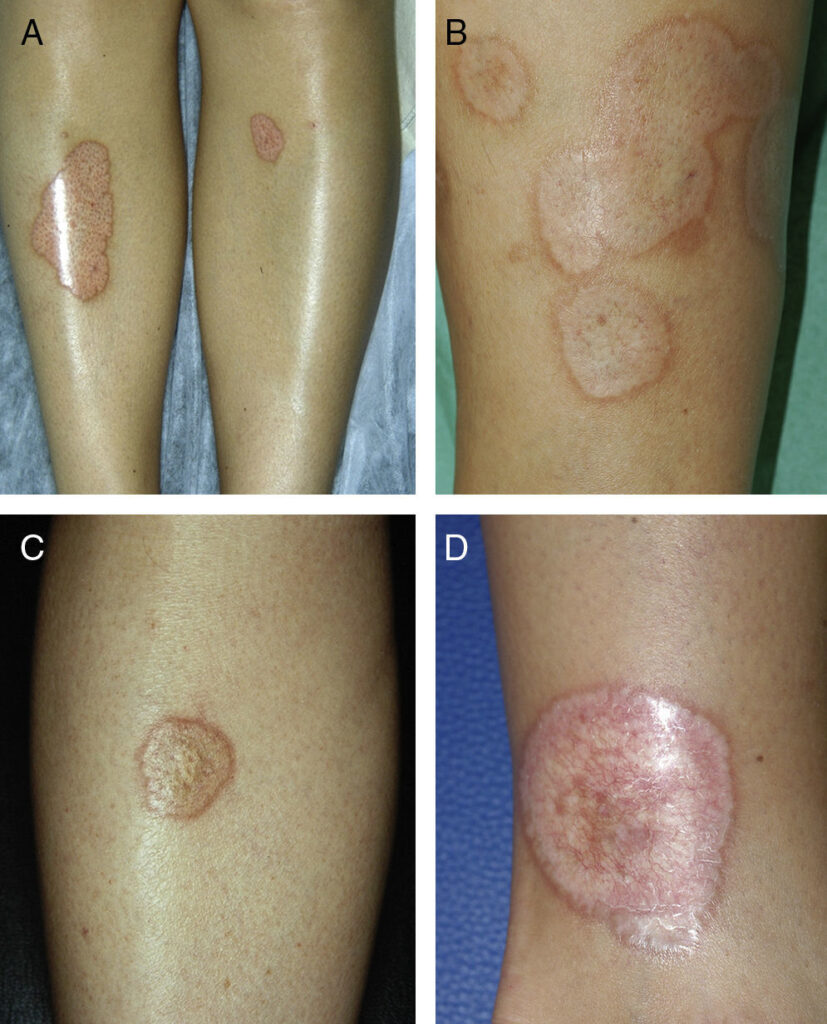
2️⃣ Necrobiosis lipoidica 👇🏻

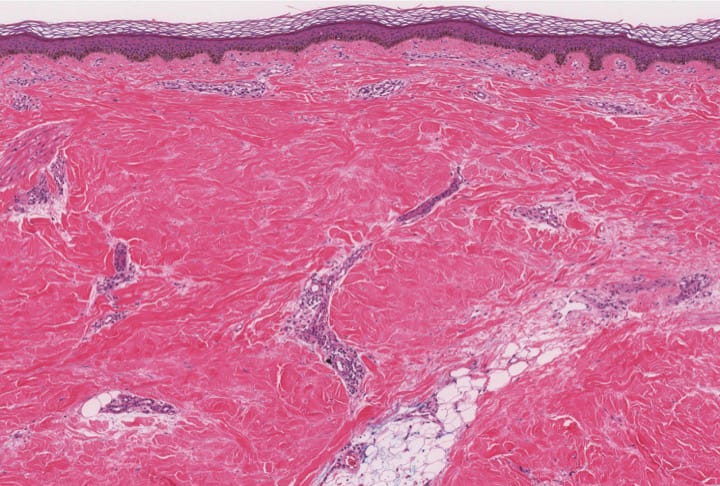
3️⃣ Deep morphea👇🏻

4️⃣ Subcutaneous granuloma annulare👇🏻

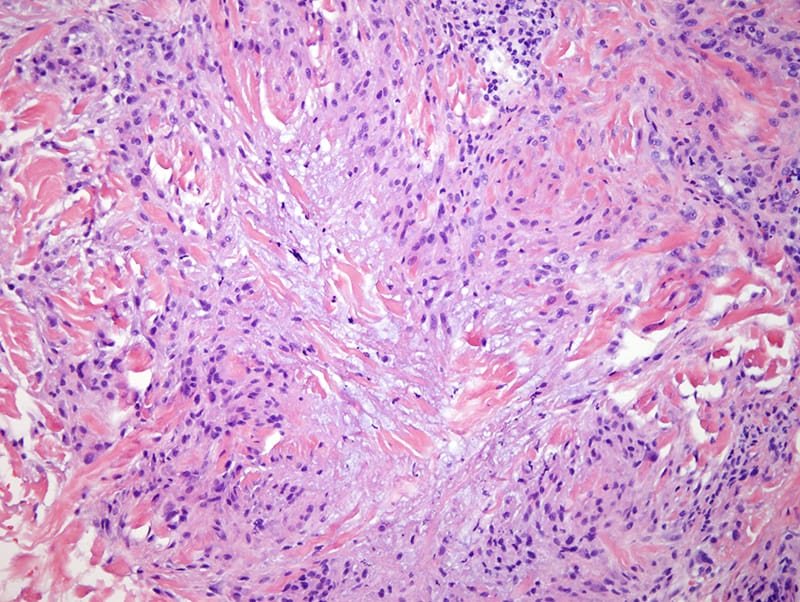
5️⃣ Rheumatoid nodule👇🏻



6️⃣ Necrobiotic xanthogranuloma👇🏻
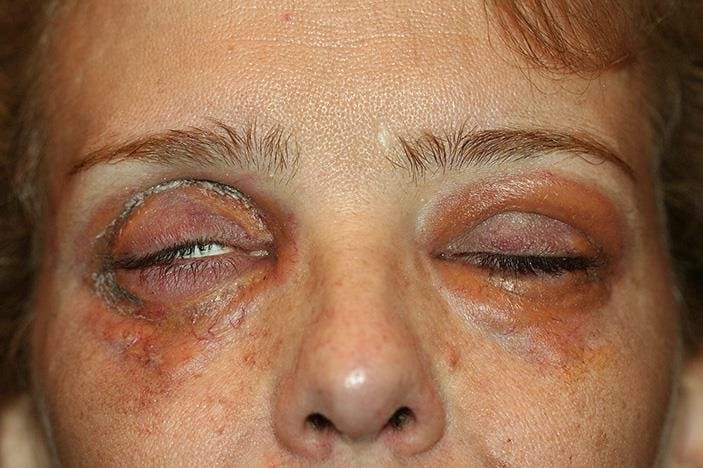
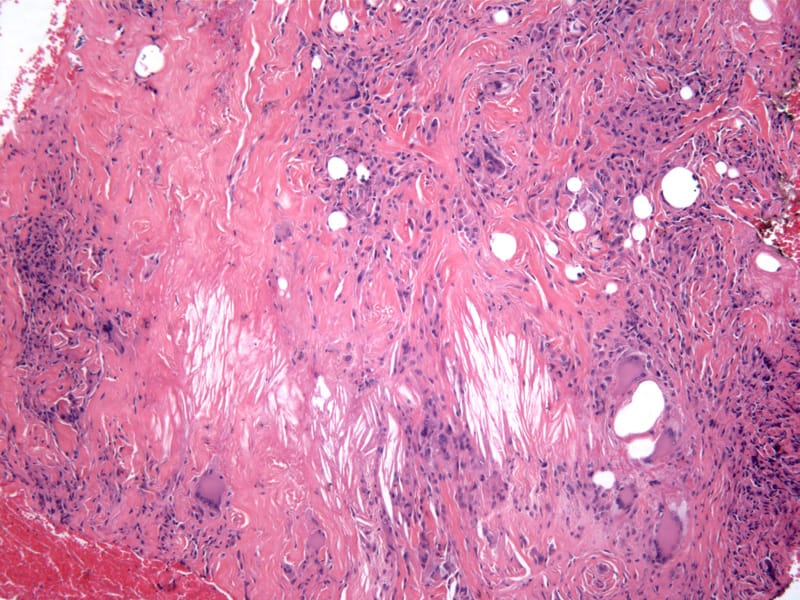
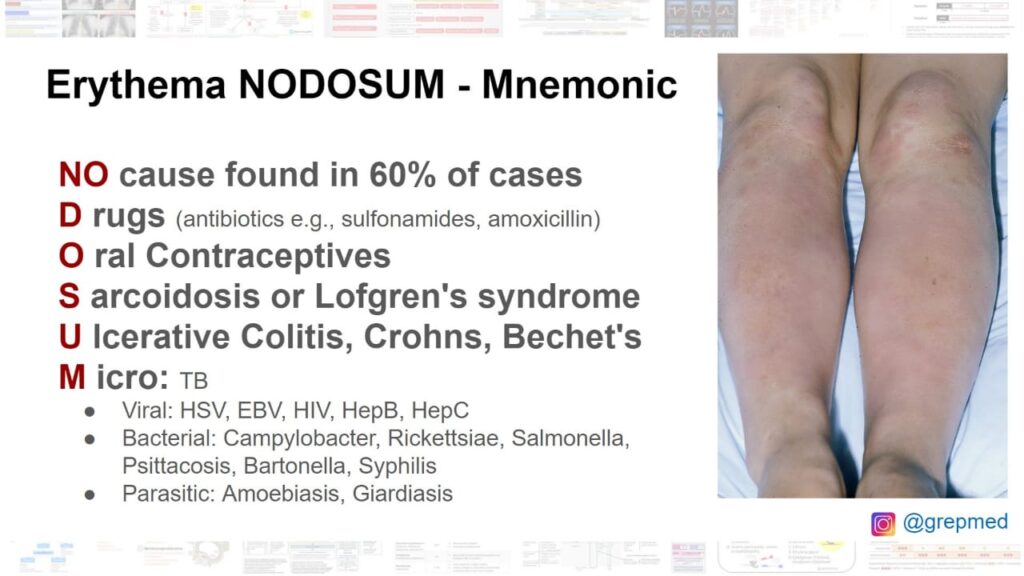
7️⃣ *Erythema nodosum*👇🏻
Zoom in




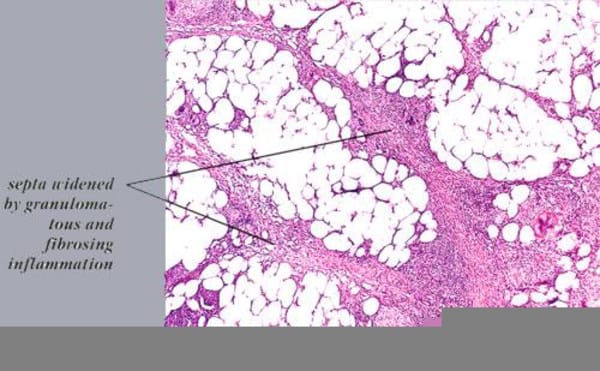
1️⃣ Erythema nodosum leprosum 👇🏻
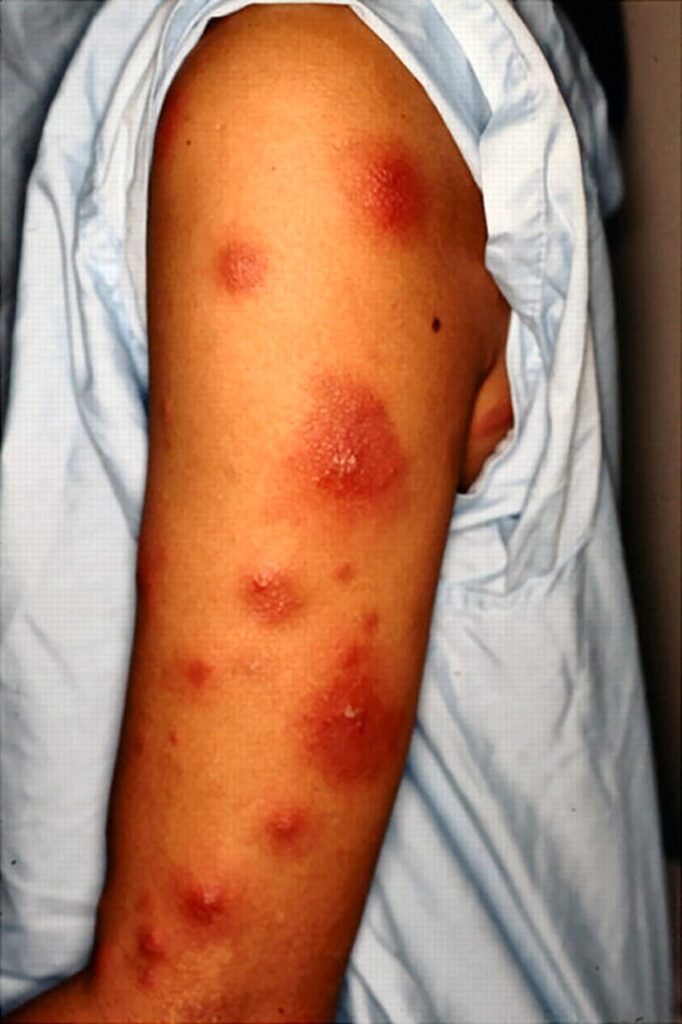
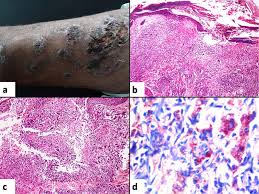
2️⃣ Erythema induratum of Bazin

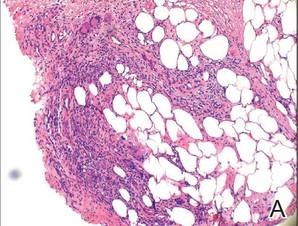
2️⃣ Erythema induratum of Bazin
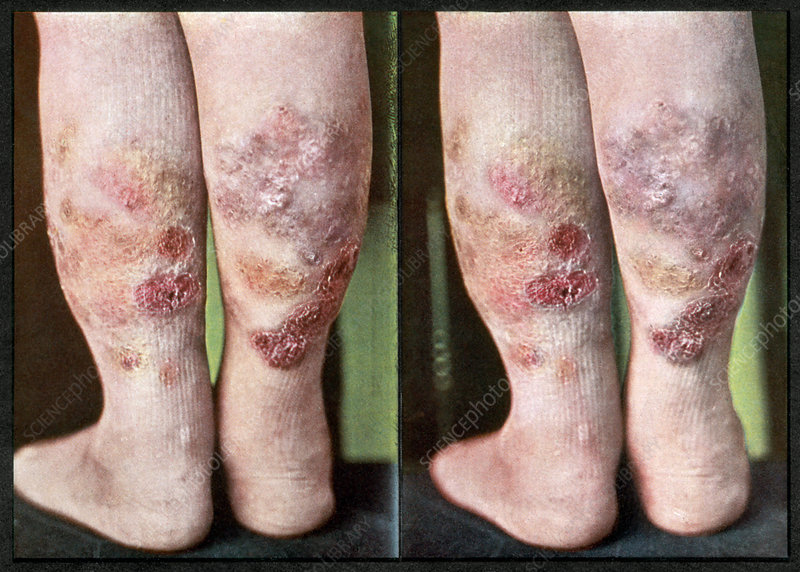

3️⃣ Calciphylaxis👇🏻
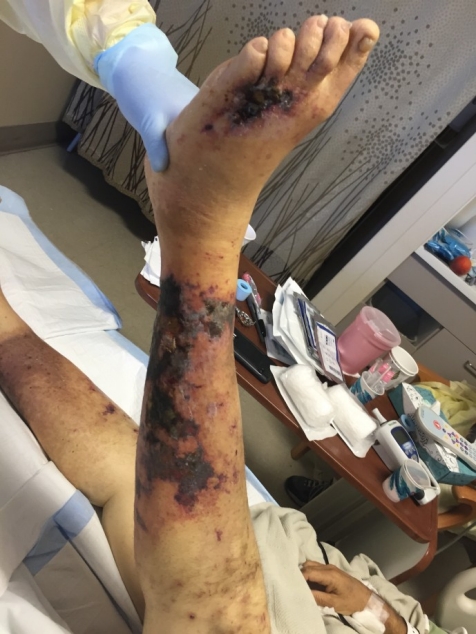
4️⃣ Cold panniculitis
Horse rider’s pernio

5️⃣ *Lupus panniculitis/ lupus erythematosus profundus*

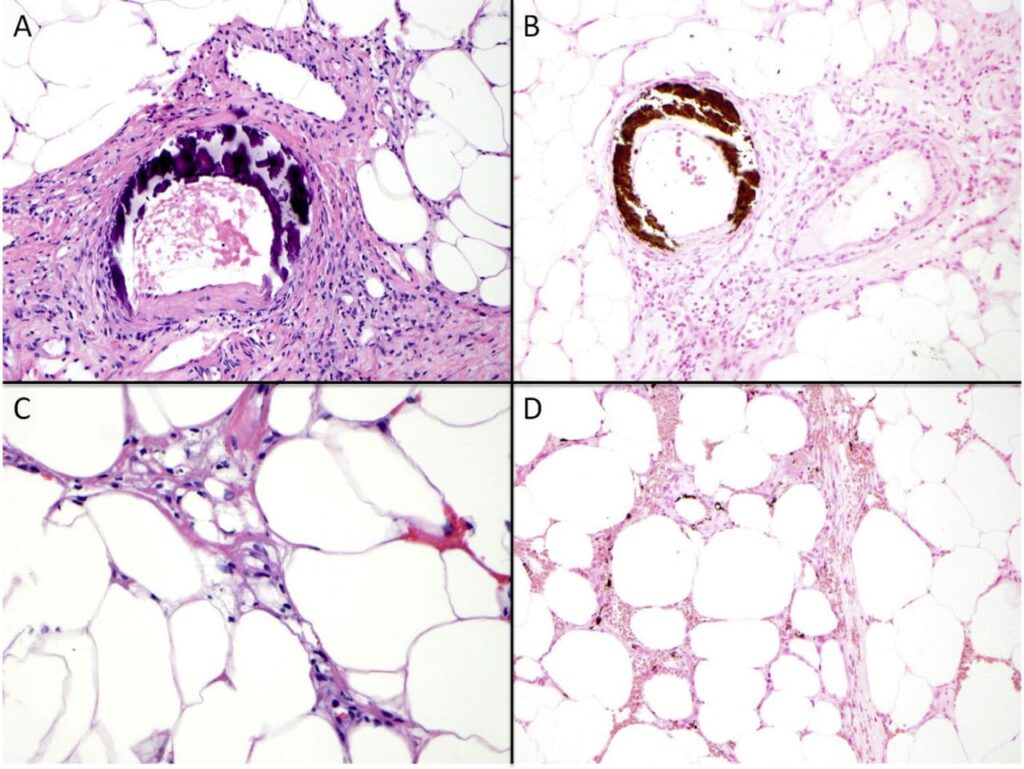
6️⃣ Pancreatic panniculitis👇🏻

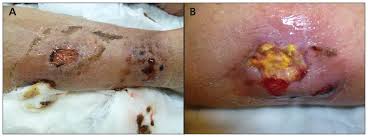
7️⃣ Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency panniculitis

8️⃣ Infective panniculitis
🔰 *Important mneumonic* 👇🏻
Ghost adipocytes can be seen in pancreatic panniculitis, mucormycosis and aspergillosis
MAP – mneumonic
Follow the map to reach the ghost
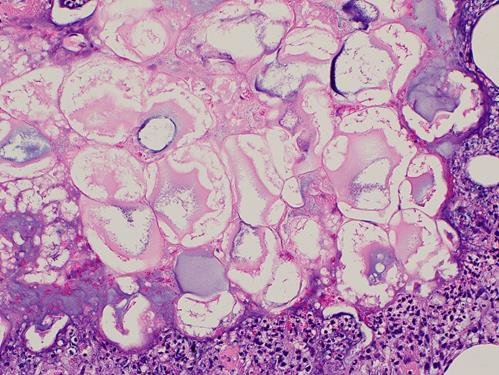
9️⃣ *Subcutaneous fat necrosis of newborn*
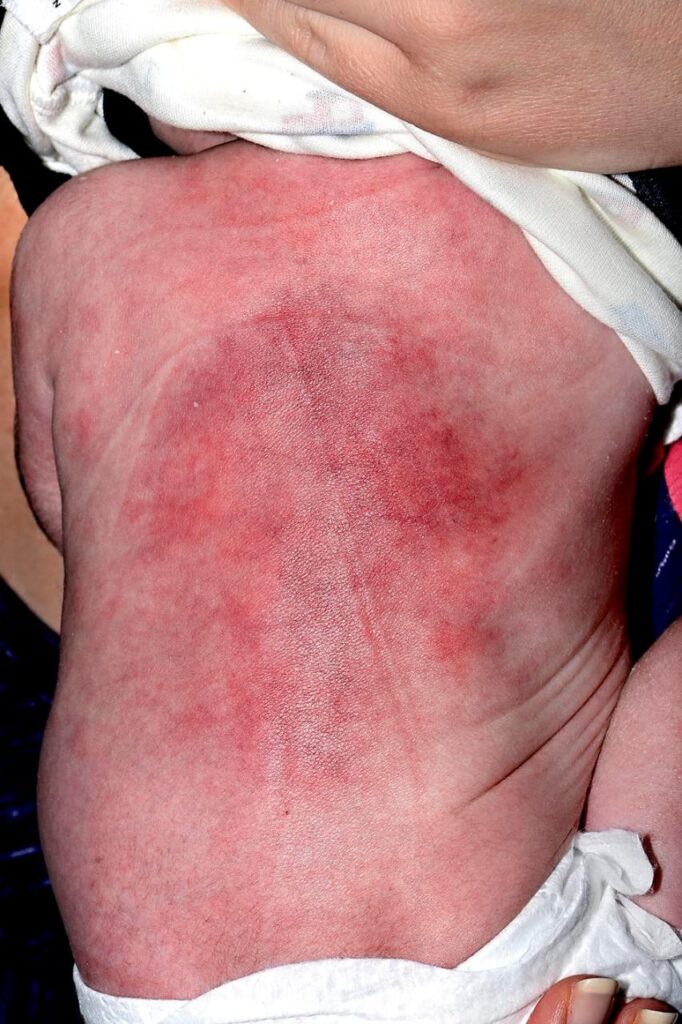

🔟 Sclerema neonatorum👇🏻
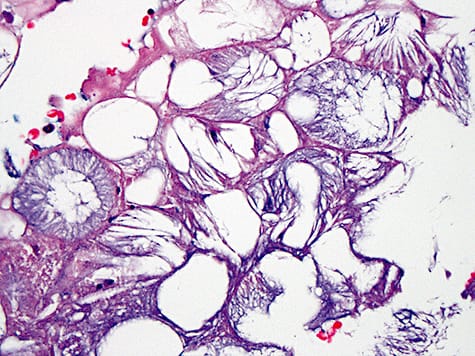
🔰 *IMPORTANT TIP*
Panniculitis is an imp chap for theory and viva exam.
They imp topics and tips mentioned here are the most useful and now onwards u l never find this chap difficult in sha Allah.
Simply remember the table in the beginning of the chapter and imp histopath findings
Topics which arent covered are less likely asked but must practice them from mcqs
Happy learning😊
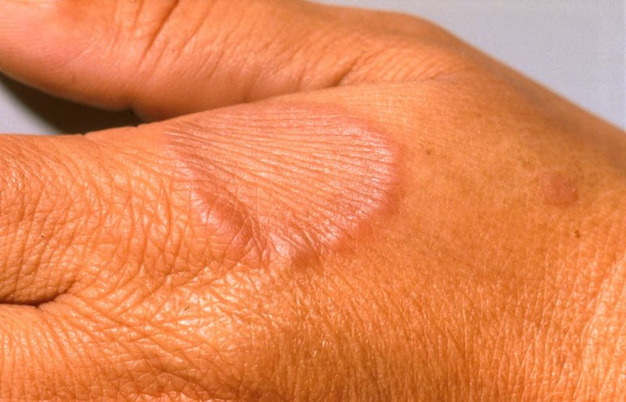
1️⃣ Granuloma annulare
*Clinical features*👇🏻
Localized granuloma annulare
Generalized GA

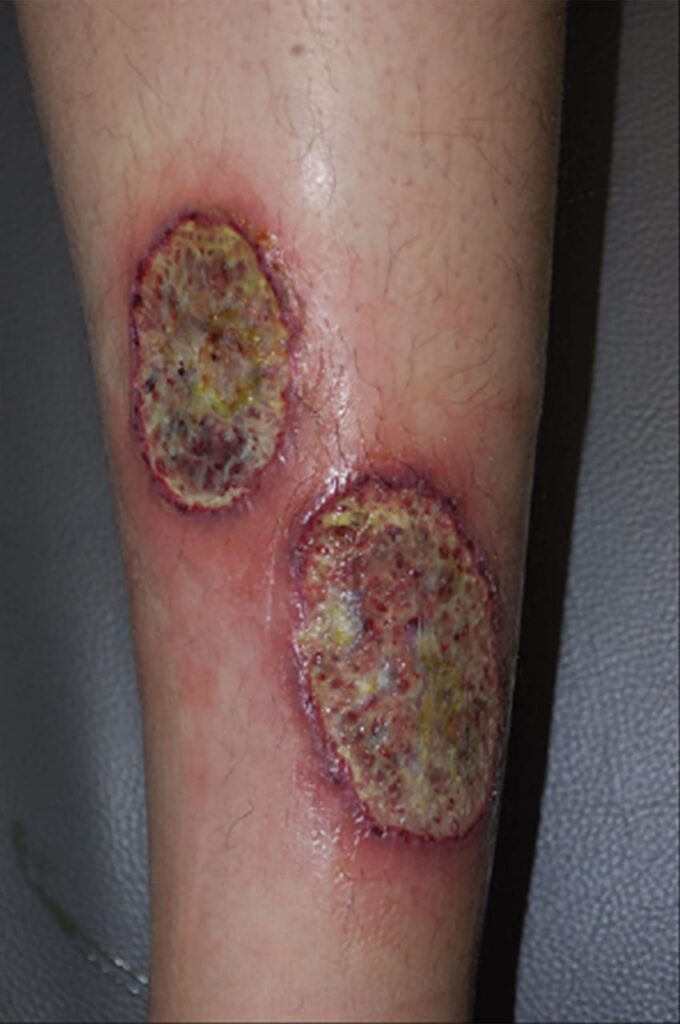
Perforating GA
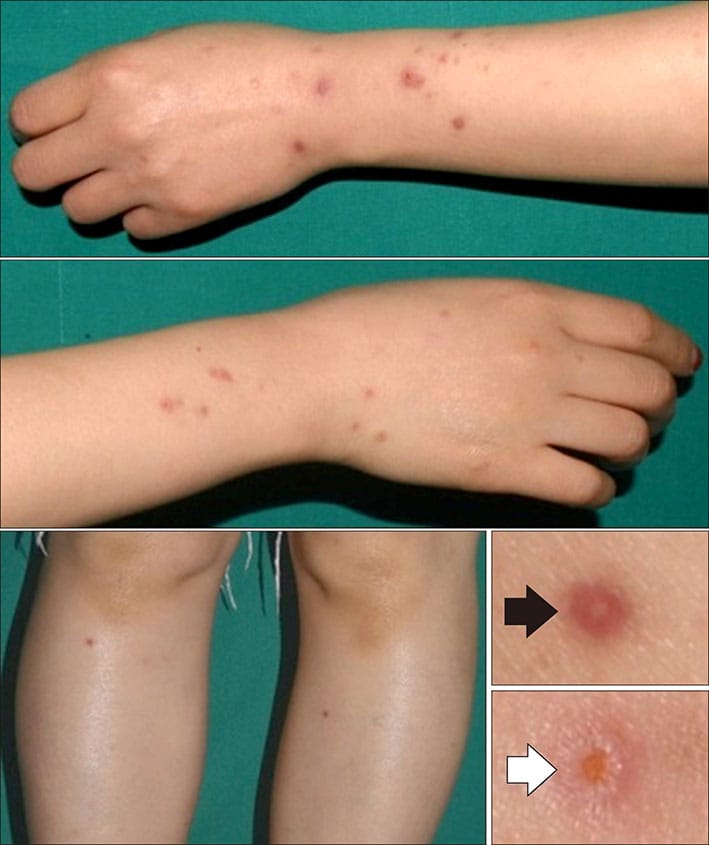
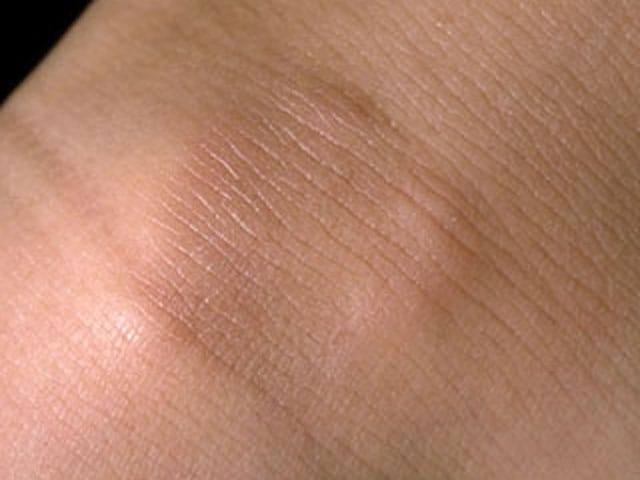
Subcutaneous GA
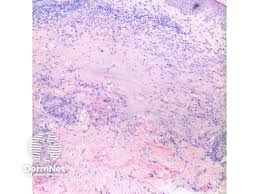
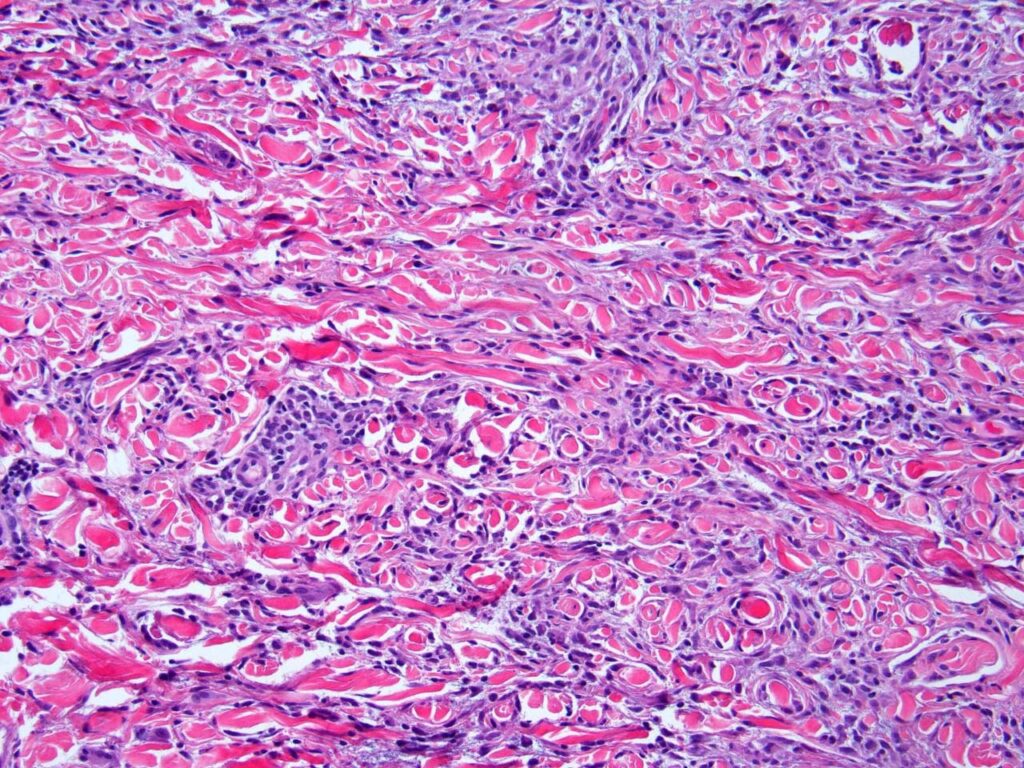
Histopathology👇🏻
- Necrobiotic palisading granulomas
- Interstitial form
- Granulomas of tuberculoid or sarcoidal type
*Differential diagnosis*👇🏻
Complications
*Disease course and prognosis*
Benign self resolving lesions
40% patients may show recurrence
*Investigations*
*Management*

🔰 *IMPORTANT NOTE*
For this chap, listen to above notes and solve mcqs for practice.


*Drugs causing abnormal platelet function*👇🏻
- NSAIDs
- Penicillin and beta lactam antibiotics
- Prostacyclin and iloprost
- Alteplase and other fibrinolytic drugs
- Ticlopidine and clopidogrel
- Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonist
- CCBs, nitrates, quinidine
- Streptokinase
🔰 *NON THROMBOCYTOPENIC VASCULAR CAUSES OF PURPURA* 👇🏻

1️⃣ *Gravitational purpura*
2️⃣ *Acroangiodermatitis*
3️⃣ *Exercise induced purpura*


🔰 *IMPORTANT NOTE*
For this chap, listen to above notes and solve mcqs for practice.

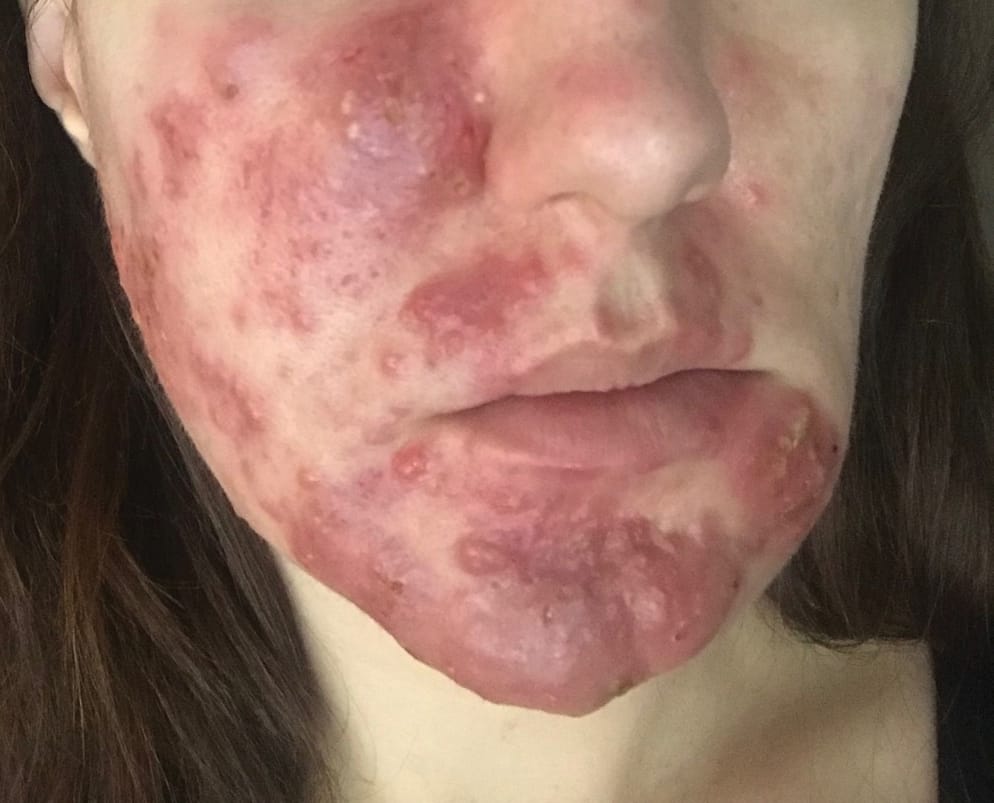


 *SARCOIDOSIS*
*SARCOIDOSIS*