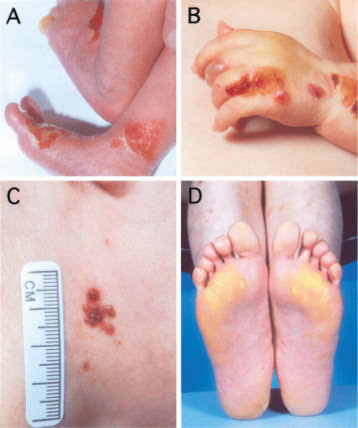
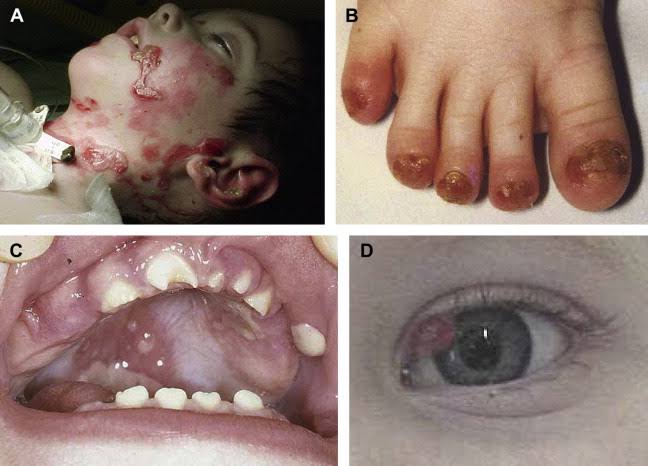
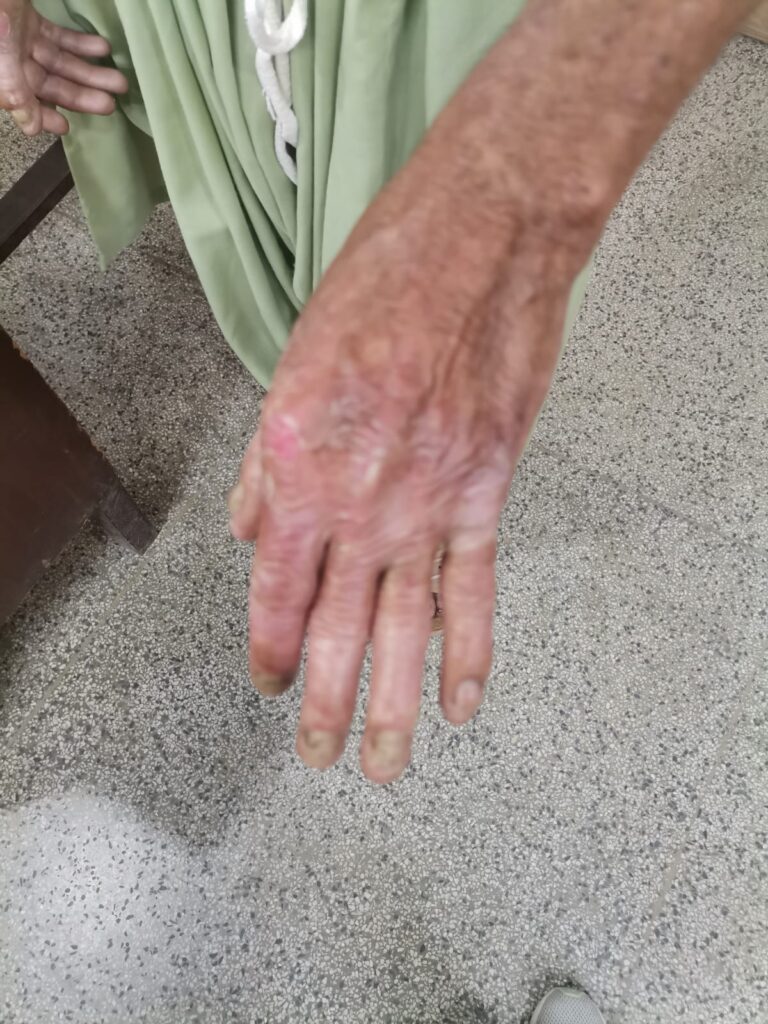
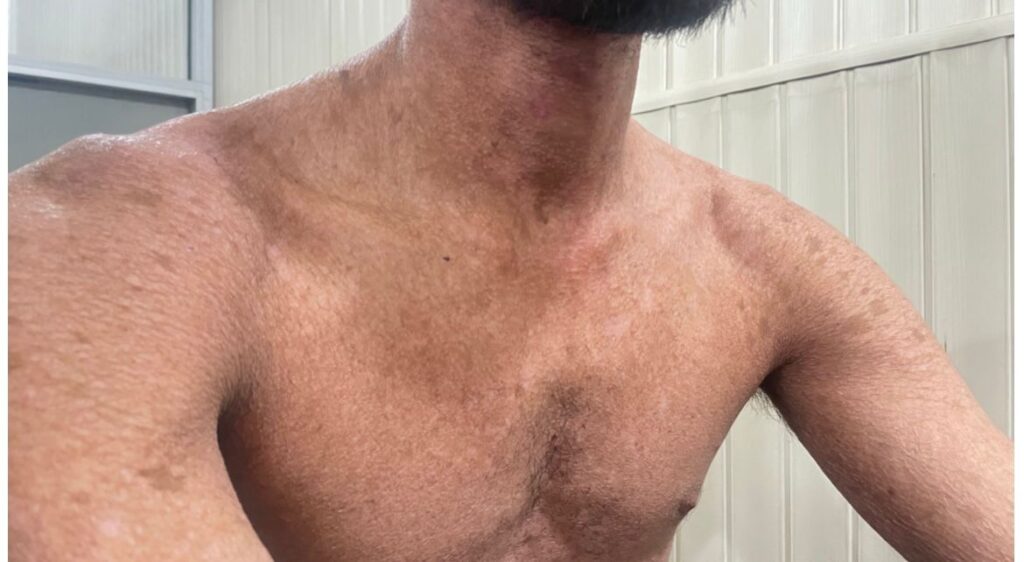
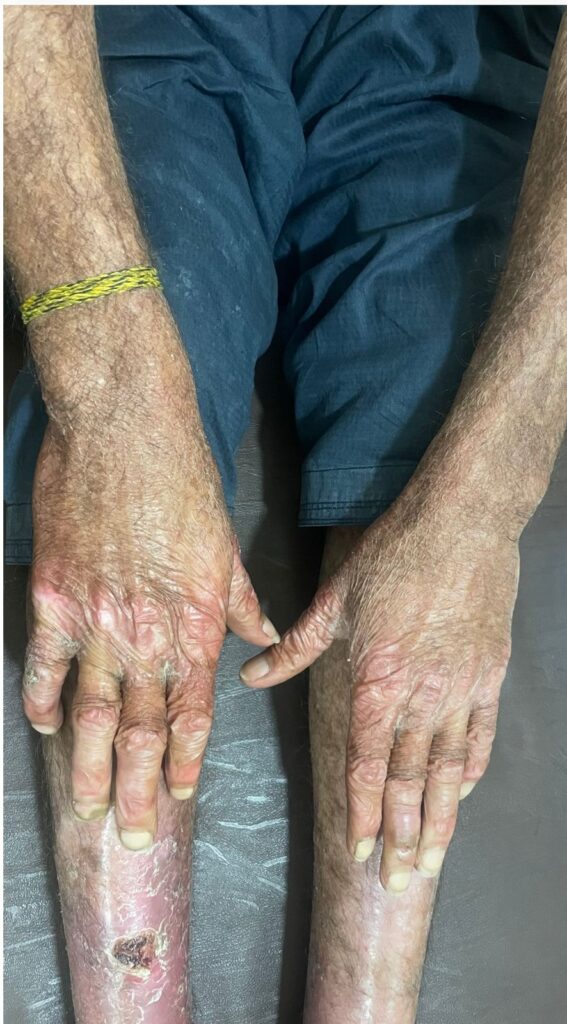
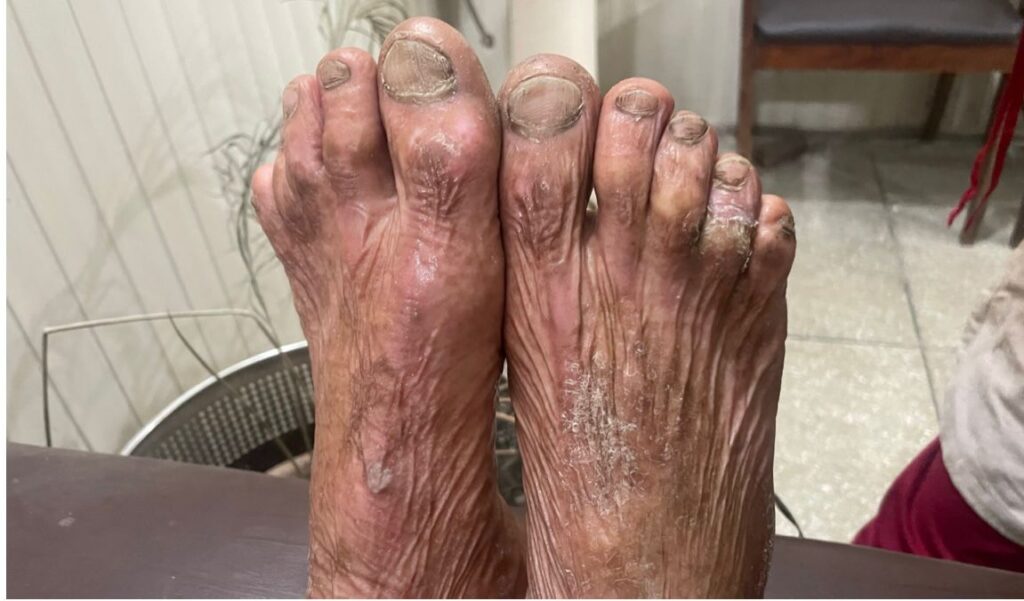
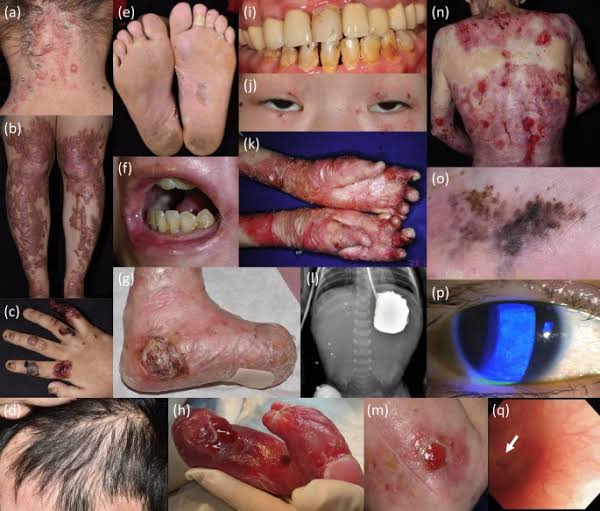
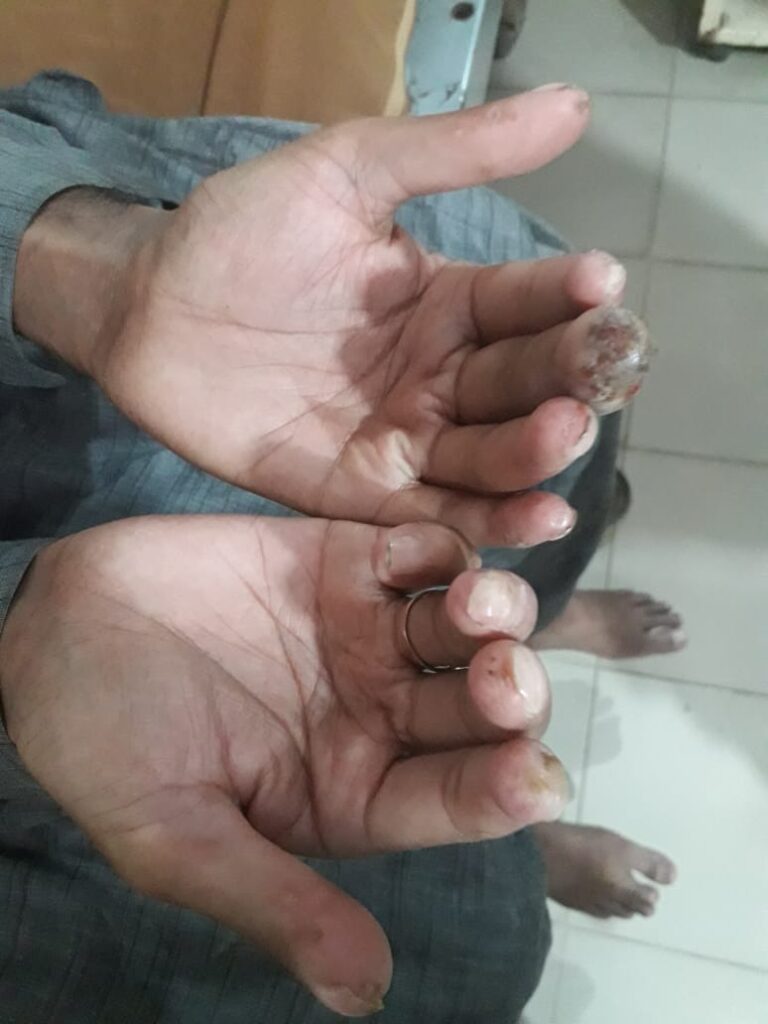
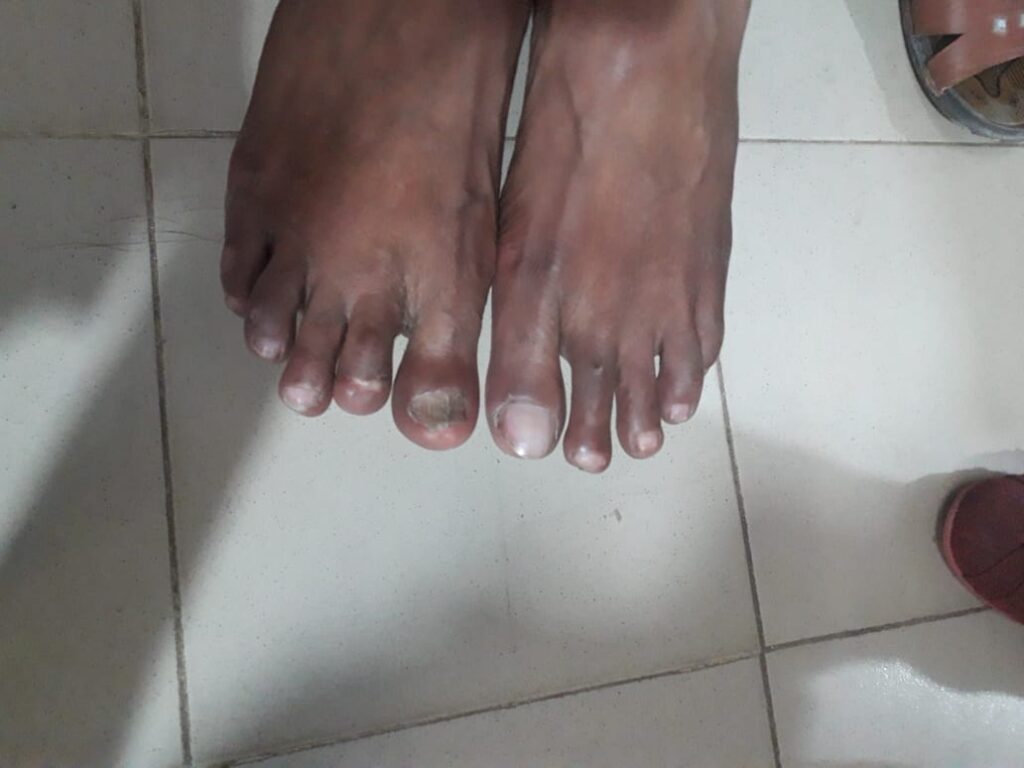
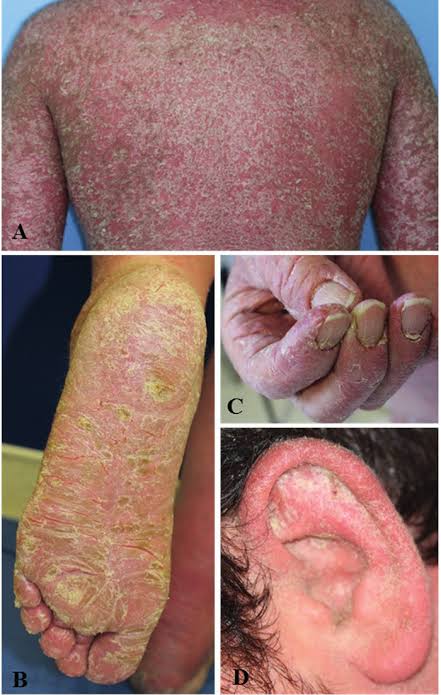
PSORIASIS
Modified napsi score
onycholysis or oil-drop dyschromia
0 No onycholysis or oil drop dyschromia present
1–10%
2 11–30%
3 > 30%
Pitting
0 0
1 1–10
2 11–49
3 > 50
Score Percent of nail with crumbling present
0 No crumbling
1 1–25%
2 26–50%
3 > 50%
Following findings can be graded as
0 absent
1 present
Leukonychia:
Splinter hemorrhages:
Red spots in the lunula:
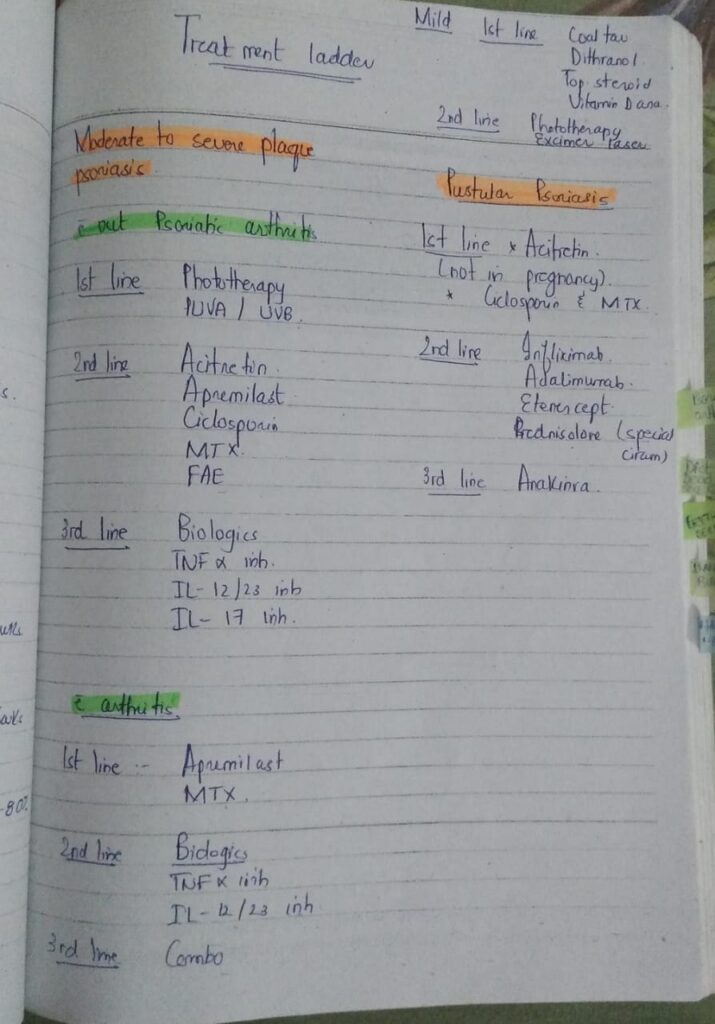
Topical preparations for psoriasis
Psoriatic ointment
Clobetasol 25%
Salicylic acid 3%
Liquor pices carbonis 5%
WSP 67%
Lassar paste
Zinc oxide 24%
Starch 24%
Salicylic acid 2%
WSP 50%
Topical retinoids
Topical calcineurin inhibitor
Comparison of topical therapies
Combination therapy

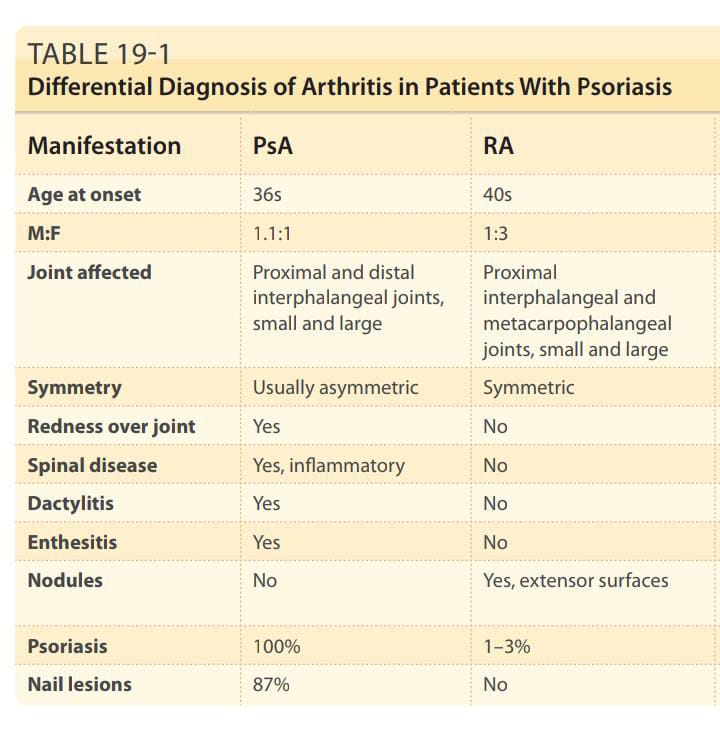
Joint involvement in Psoriasis


Treatment of patients with TB along with psoriasis
ATT give 1 month of ATT followed by both ATT and immunosuppressive therapy or biologics with close monitoring
Preferred treatment is
Phototherapy
Acitretin
Apremilast
Secukinumab
Treatment options in patients of hiv with psoriasis..
Antiretroviral therapy
Topical therapies with following
Retinoid
Phototherapy
Apremilast
Secukinumab
Less favourable options MTX, Cyclosperin, TNF inh and ustekinumab
Treatment options in hep b/c patients with psoriasis
Systemic therapy
Acitretin
Ciclosporin
Apremilast
Biologics esp etenercept
Ustekinumab, secukinumab, ixekizumab and brodalumab
Do not prescribe MTX
Treatment of Psoriasis and malignancy
TNF inh
Ustekinumab
Apremilast
Acitretin
Treatment options in children
Topical calcineurin inh for face and intertriginous areas
Vit D analogues +/- mid potency steroids
Mtx
Ciclosporin
Etanrecept greater then 5 yr children
Ustekinumab greater then 12 yr old child
Treatment options in pregnancy
NB UVB Phototherapy
Ciclosporin (Category C drug)
TNF inh (discontinue at 30 weeks of gestation).live vaccine to infant is postponed till 7th month of age
Topical agents
Systemic steroid only in pustular psoriasis
History
Examination
Important additions
Spesolimab , sold under the brand name Spevigo, is a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of generalized pustular psoriasis. It is an interleukin-36 receptor (IL-36R) antagonist.
Certolizumab and golimumab are licensed for psoriatic arthritis, not for cutaneous psoriasis
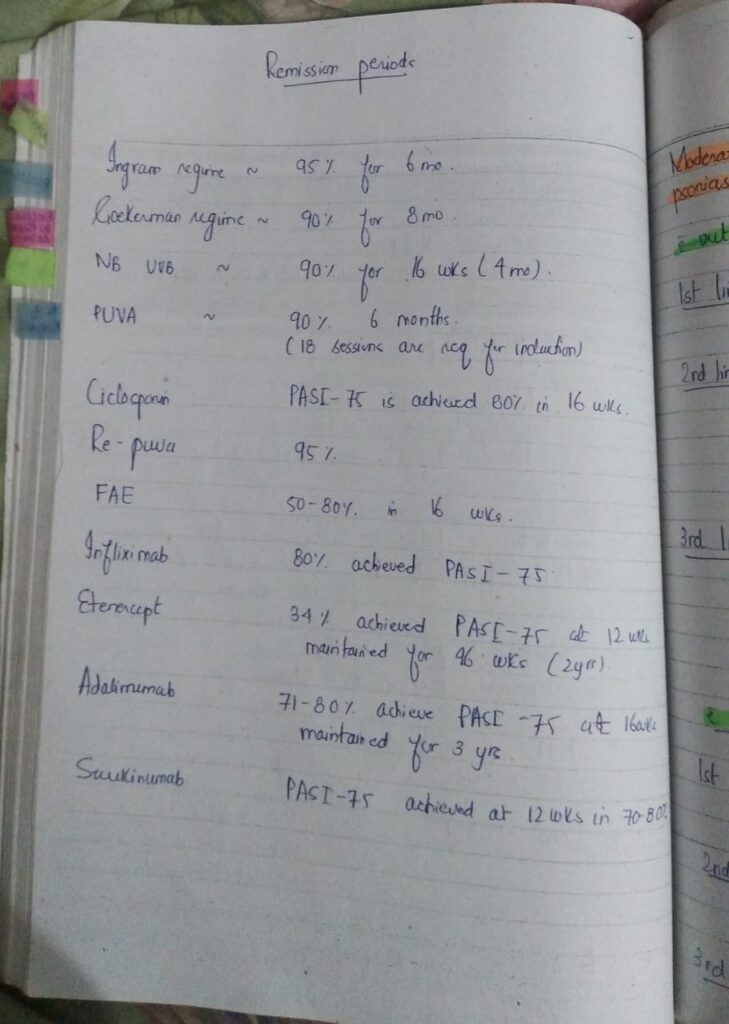

Phototherapy
Important note
Phototherapy is an important modality of treatment and hence very important for theory as well as clinical exam.
U must have a clear concept of every single step regarding phototherapy, how to begin, indications, MED calculation, adverse effects and contraindications.
Above shared voice note gives a concise yet easy understanding of how PUVA is used.
IMMUNOBULLOUS DISORDERS:
Intraepidermal blistering disorders
Pemphigus vulgaris
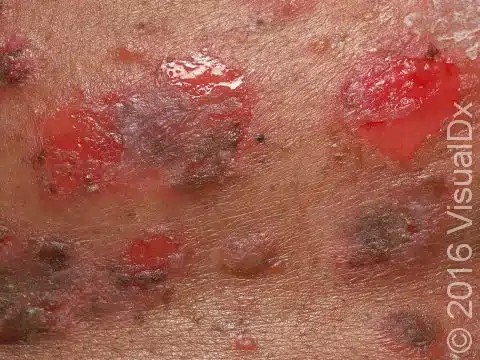
Pemphigus foliaceous
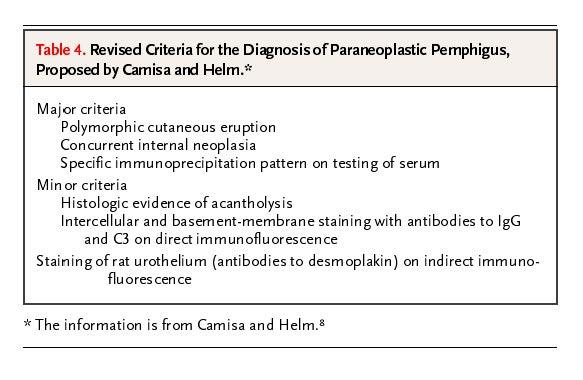
Paraneoplastic pemphigus
Pemphigus vegetans


Pemphigus herpetiformis

Pemphigus erythematosus
IgA pemphigus
Investigations
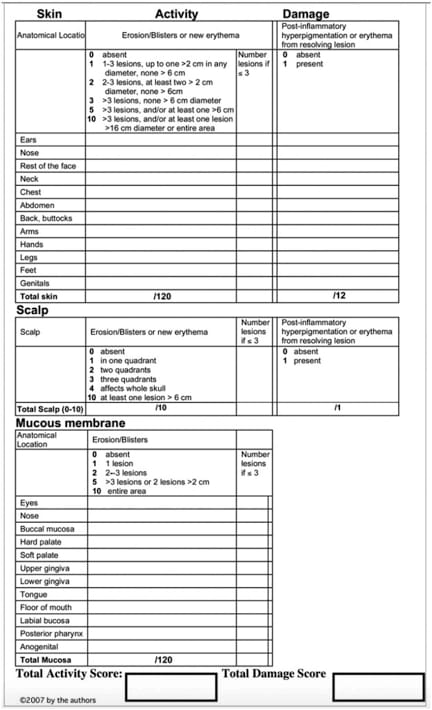
Severity indices
Pemphigus vulgaris in pregnancy
Childhood and juvenile PV
Bullous pemphigoid
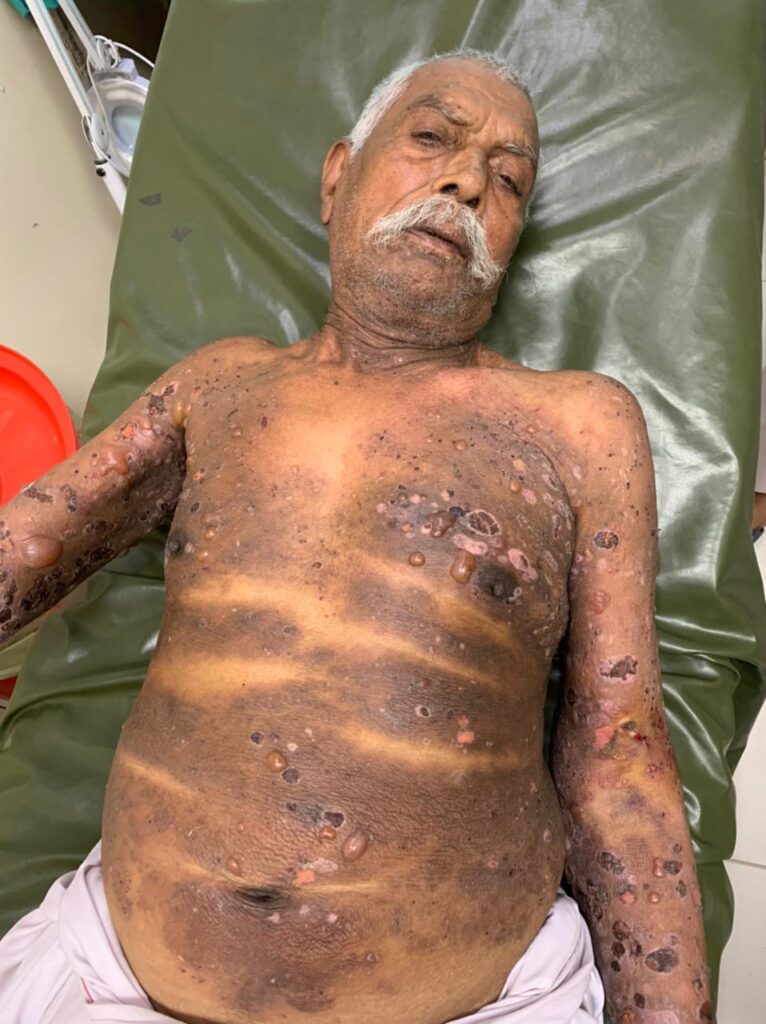





Linear IgA disease
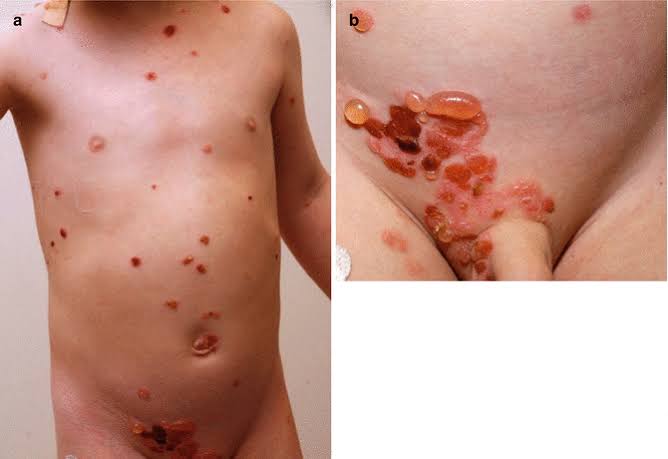
Bullous LP vs LP Pemphigoides
LP pemphigoides ⬇

Bullous LP ⬇

Bullous SLE
EBA
Dermatitis herpetiformis
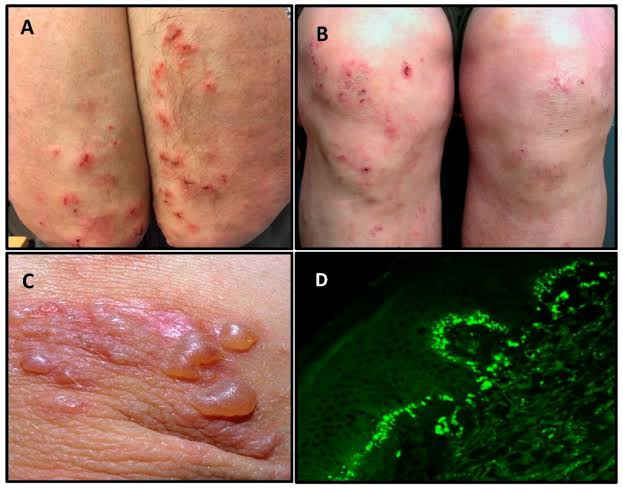
Immunofluorescence
Salt split skin
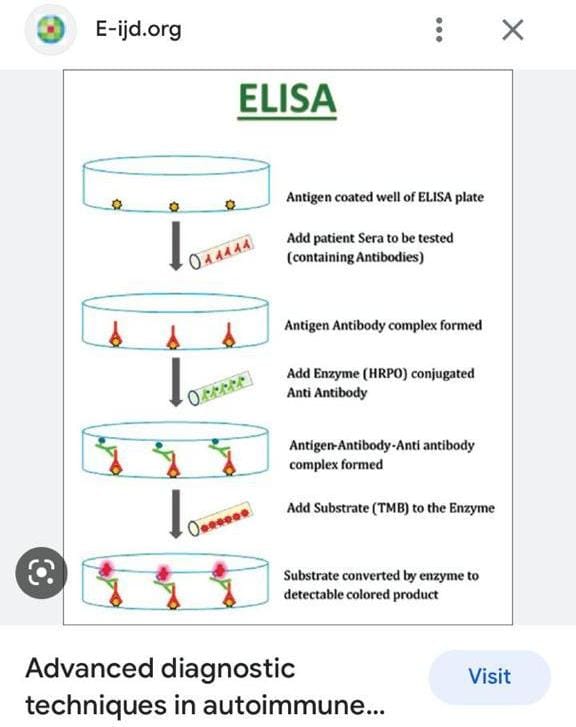
Management

Follow up
Discontinuation of treatment
Tapering of steroids
Viva questions
BP counselling


History
Examination
Classification of pemphigus vulgaris 👇🏻
Based on PDAI score
🔅Mild PDAI 0-15.
BSA <10%
🔅Moderate PDAI 16-45
BSA 10-30%
🔅Severe PDAI >45%
BSA >30%
🔰 Important note
In long case of Immunobullous which is a must to come always to most of the candidates, ua viva usually begins with present ua case and then how will u manage this case. In long case no 1 asks u about the types or classifiaction so dun waste ua time preparing tht.
U must know the S2 guidelines, rituximab protocol and dose, tapering of steroids, preferred choice of immunosuppressive therapy to be used.
In the end new advances will be ua last question for bonus marks


Direct and indirect immunofluorescence well explained by worthy Dr Saadat 👆🏻
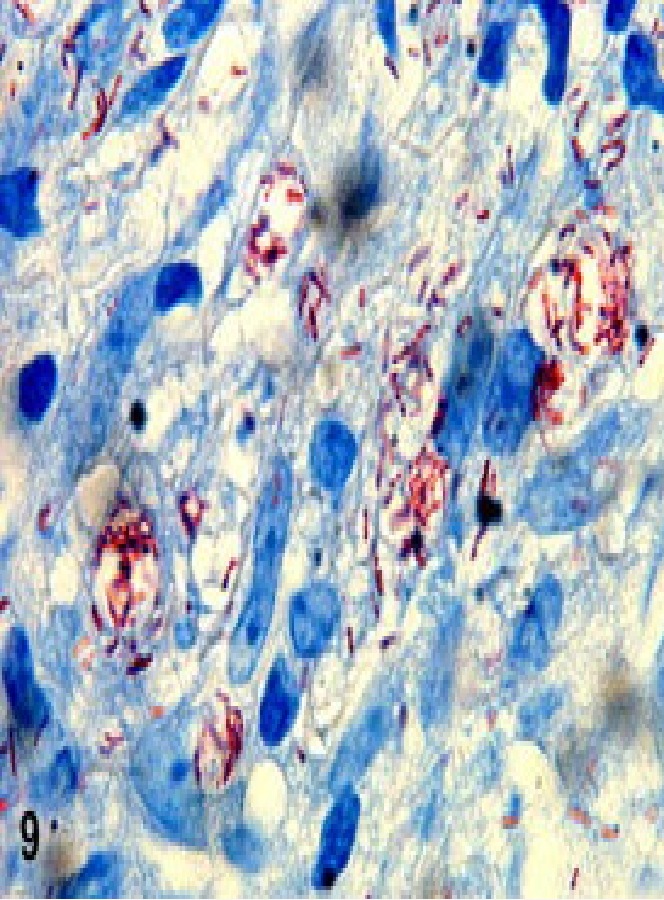
Leprosy
Diagnosis
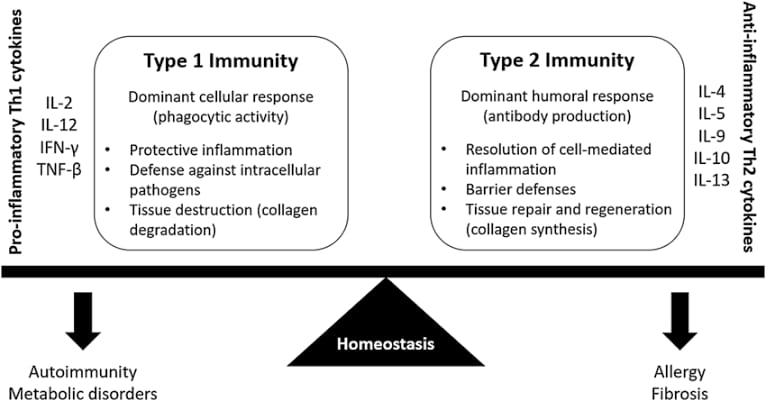
Immunology
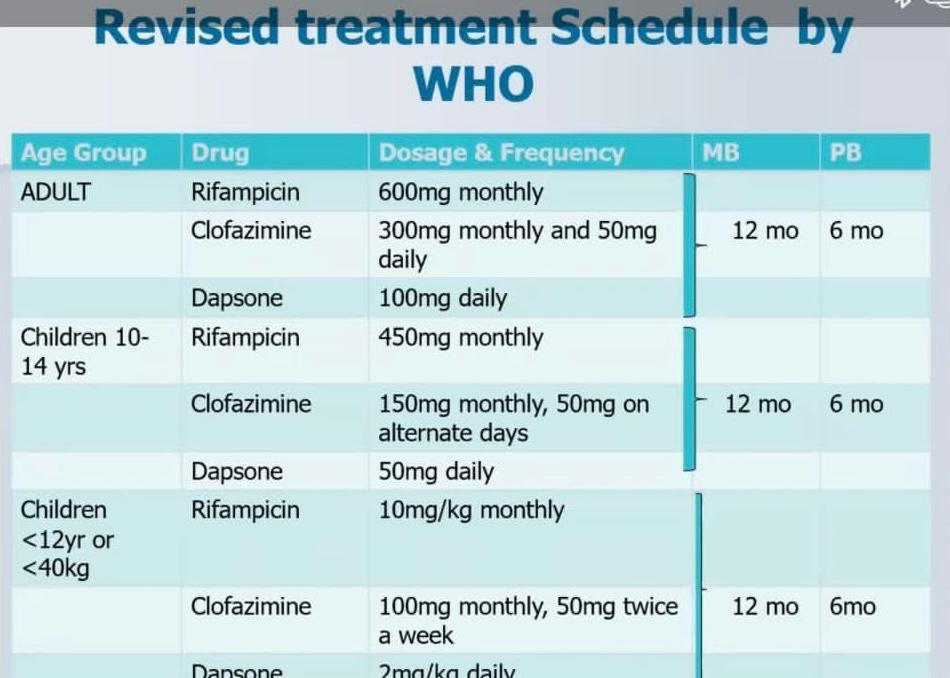
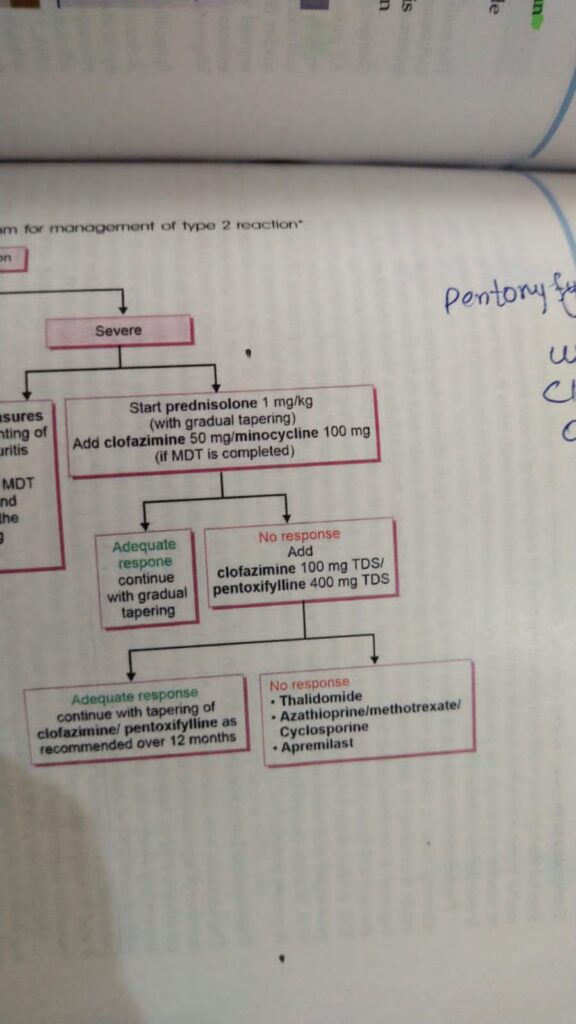
Treatment
Leprosy history
Leprosy examination
VIVA QUESTIONS👇🏻

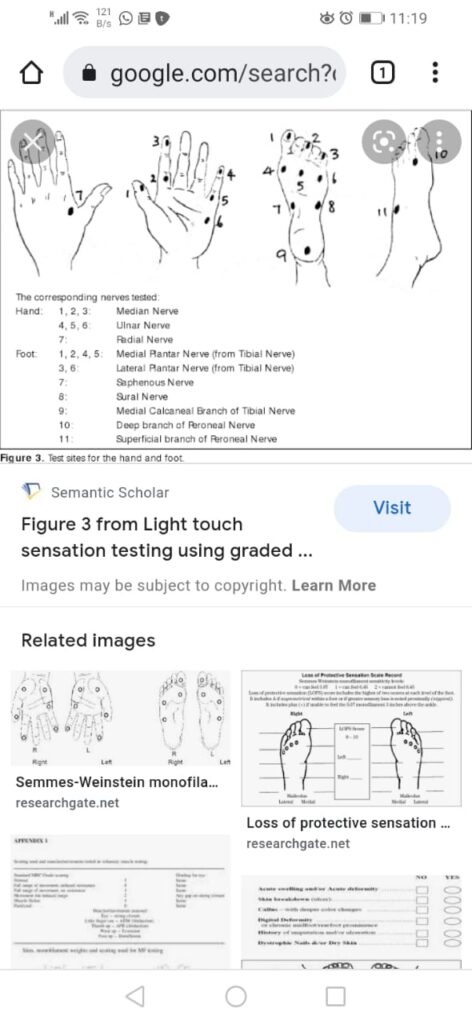

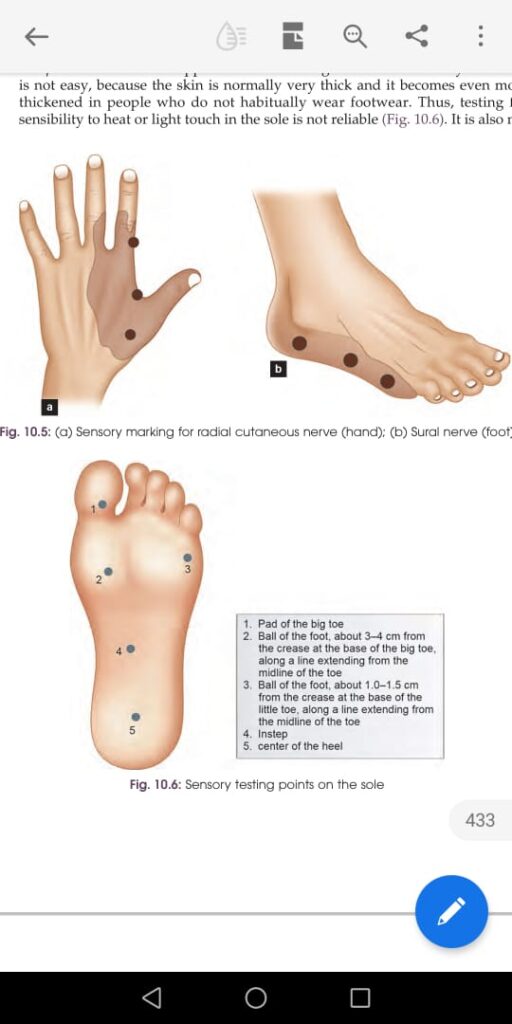

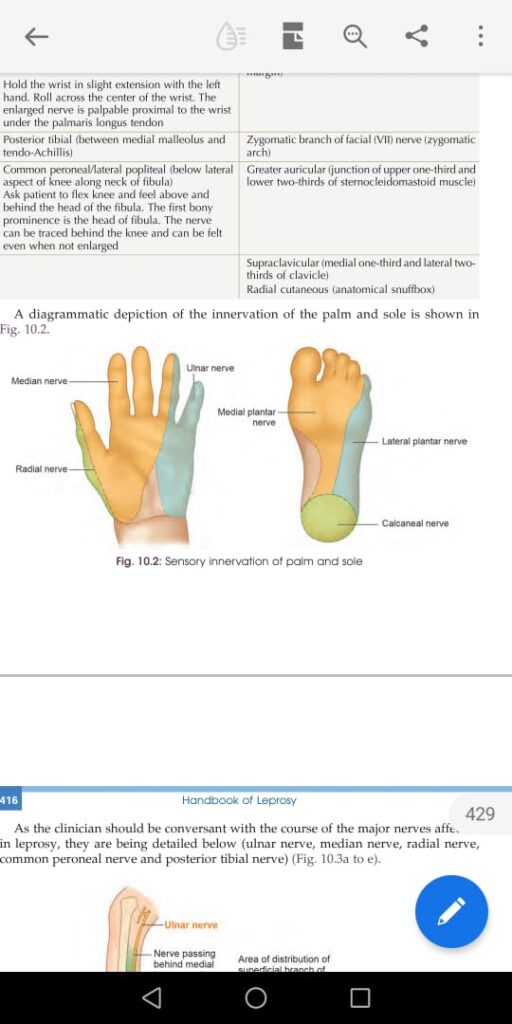
TT Th1 immune response
LL Th2 immune respone

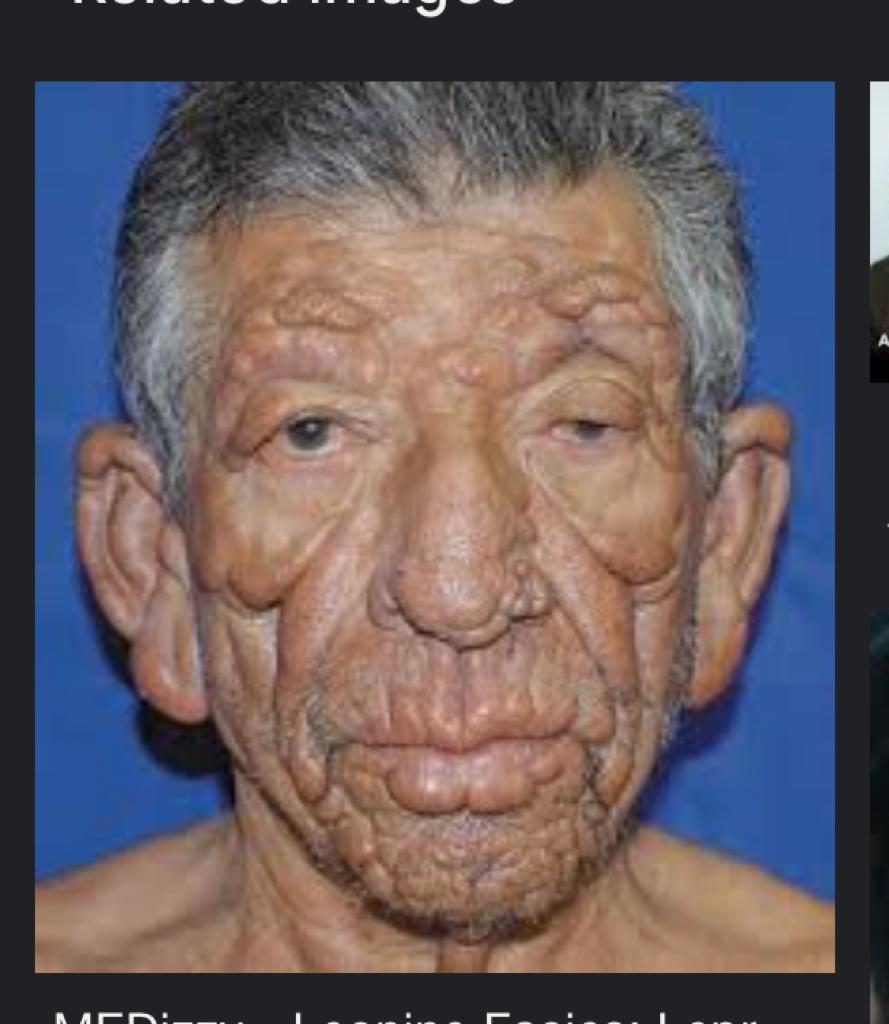





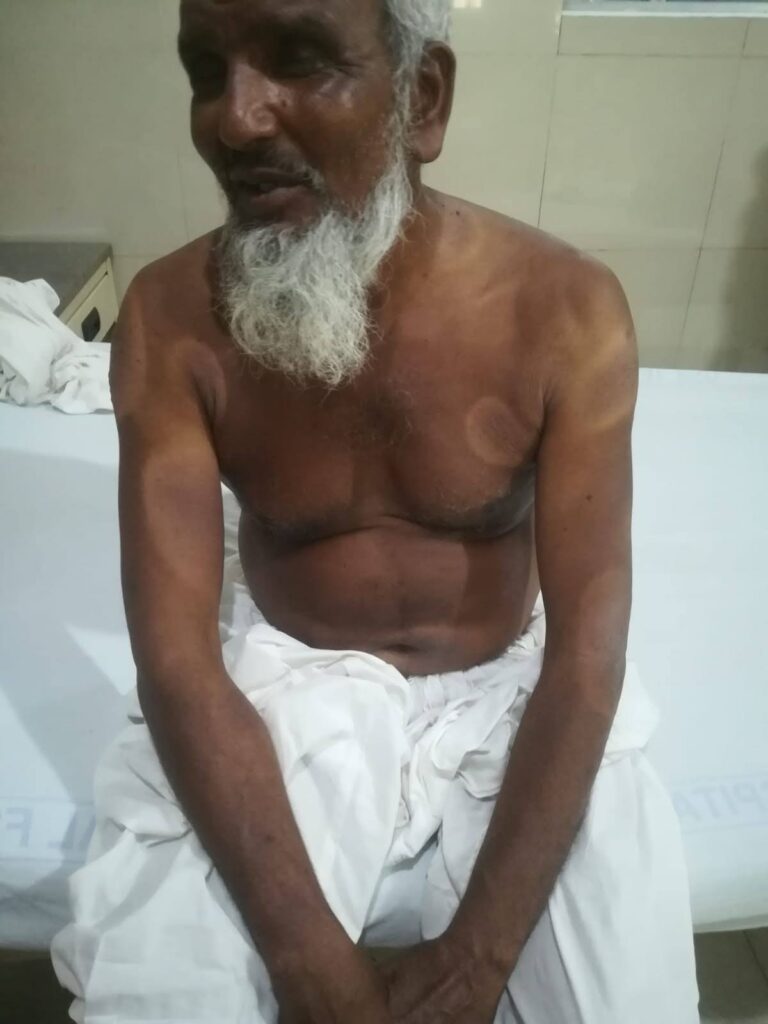
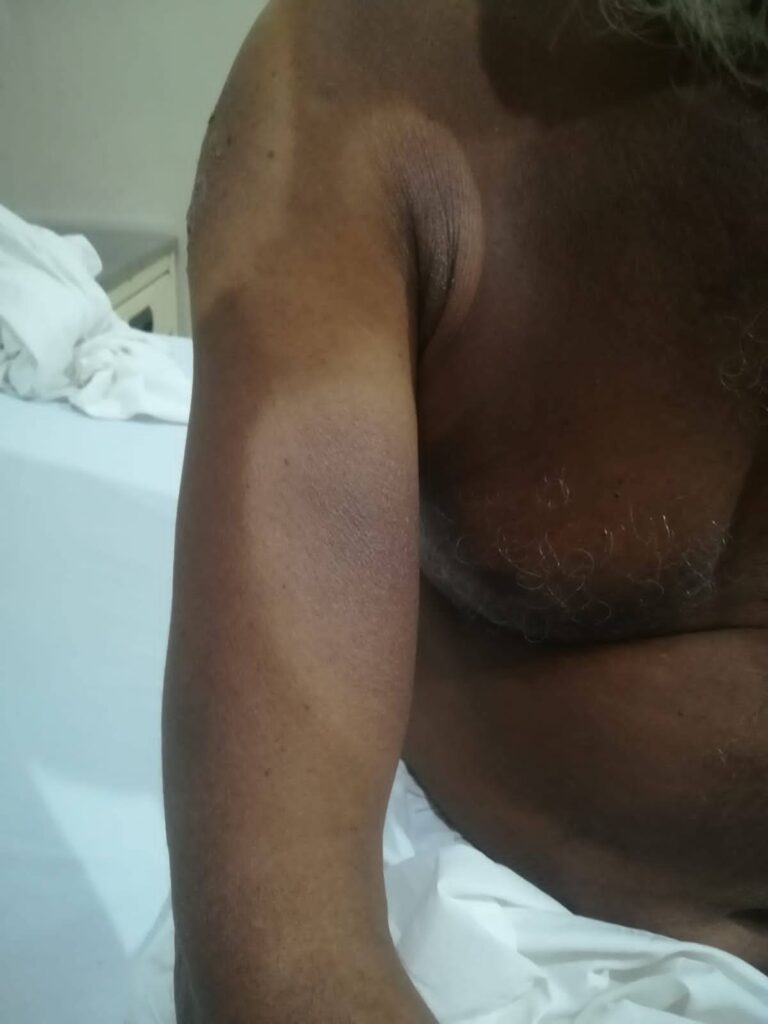
Clofazamine induced pigmentation👇🏻
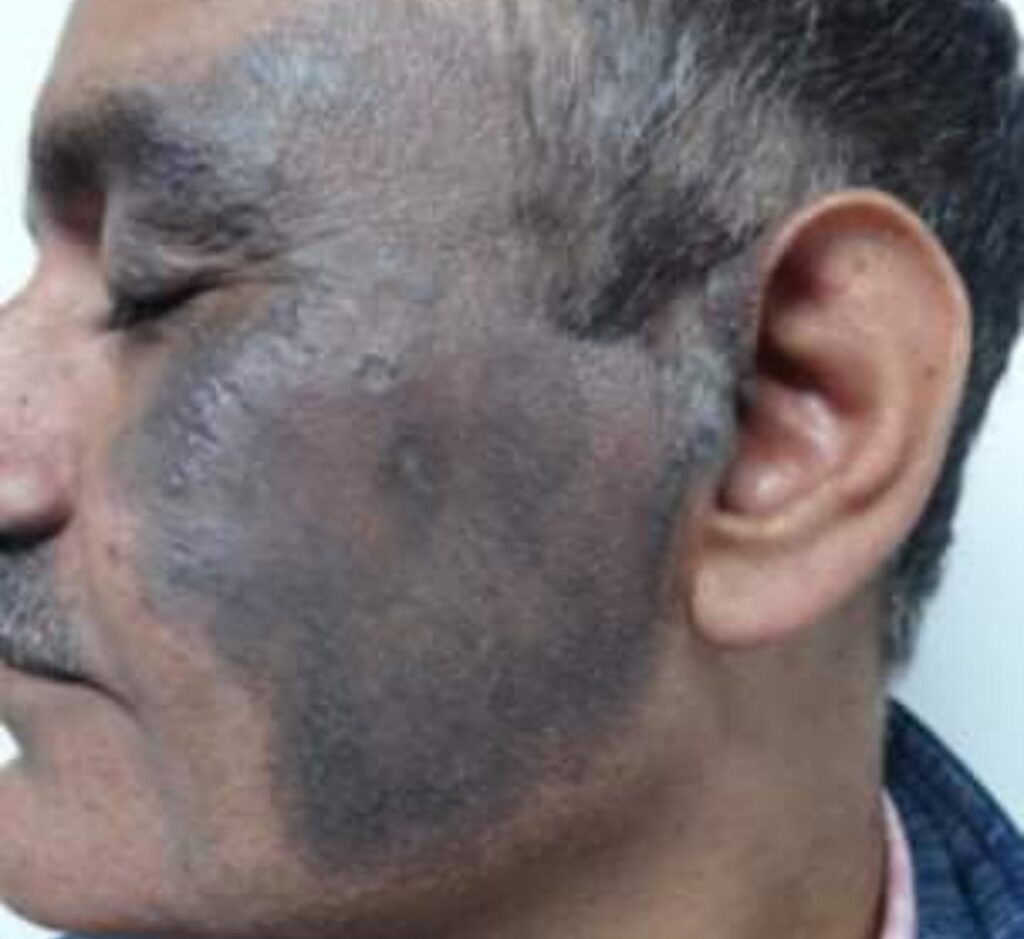

Difference between the clinical appearance of various types of leprosy👆🏻
🔅History and examination

Mouth aperture test range is 39 to 76mm
Modified rodnan skin score
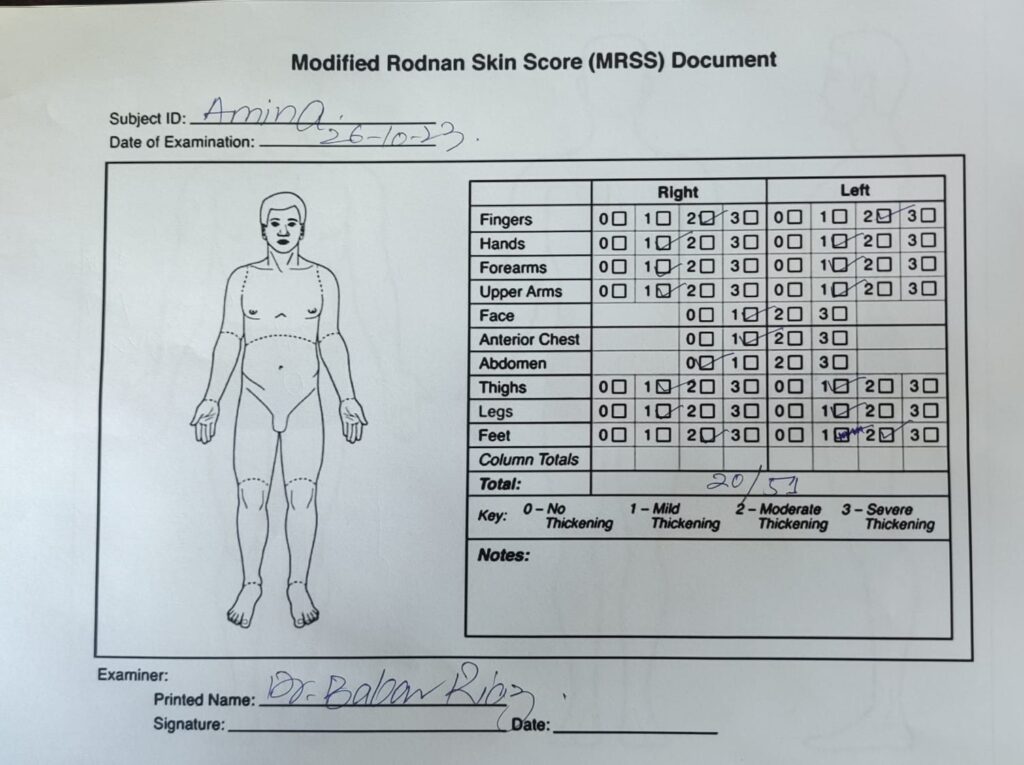
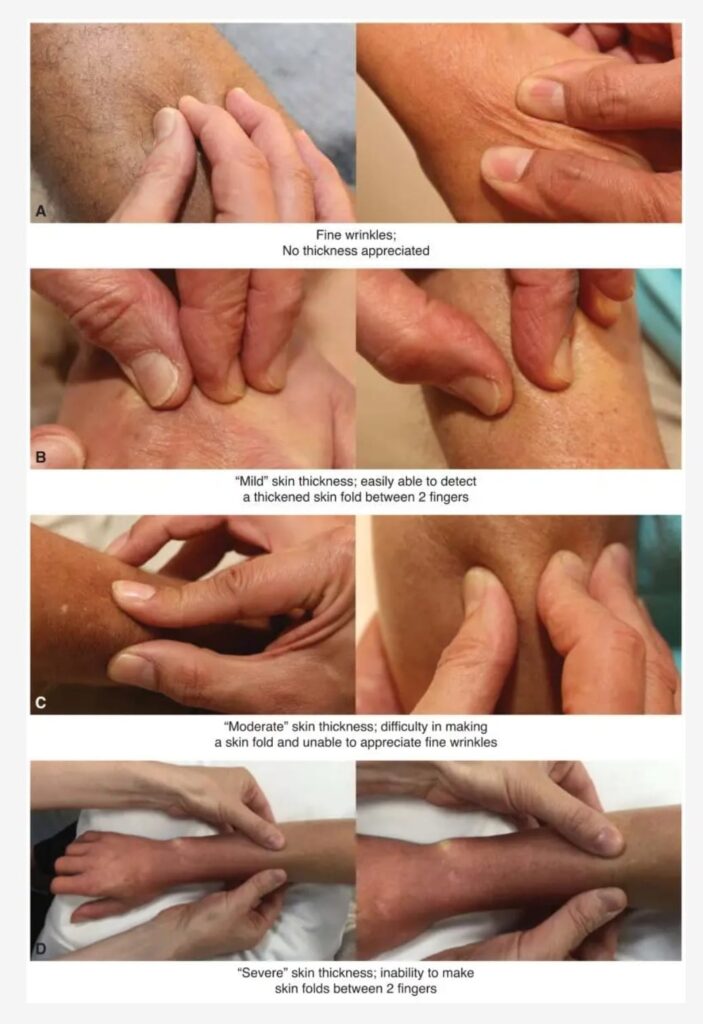
Viva questions 🔰

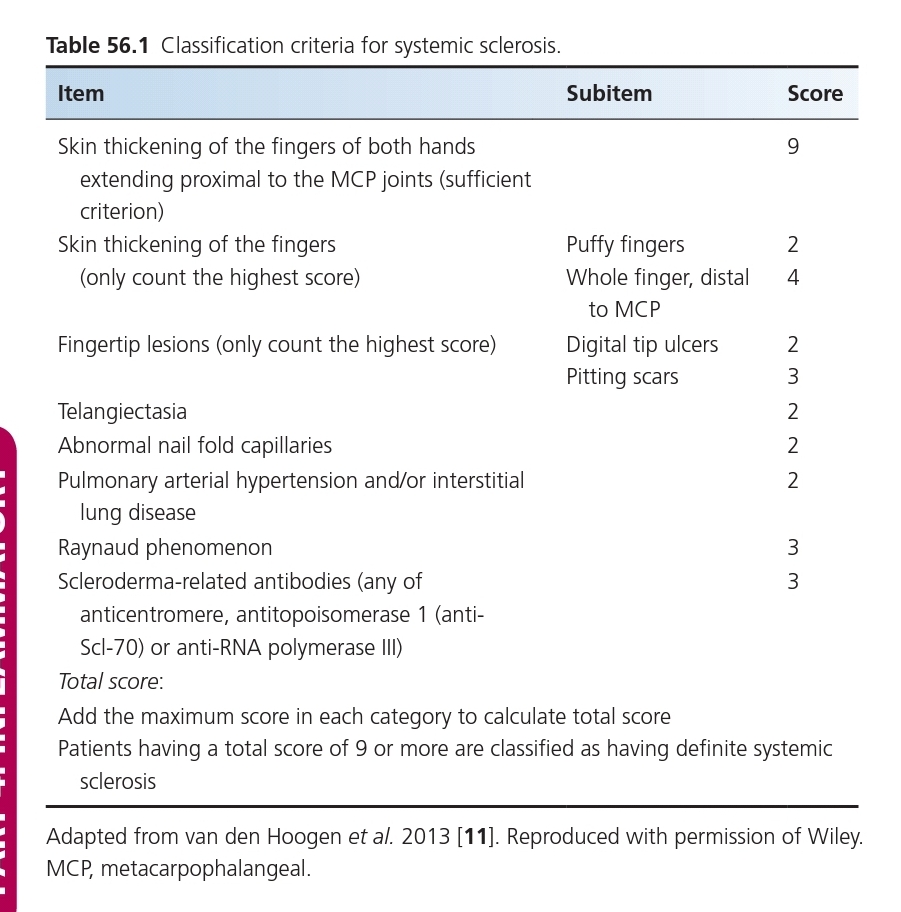
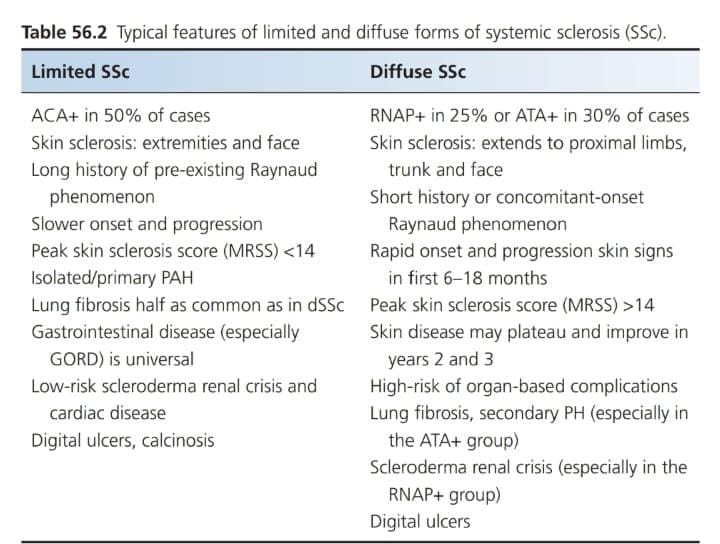
Investigtions
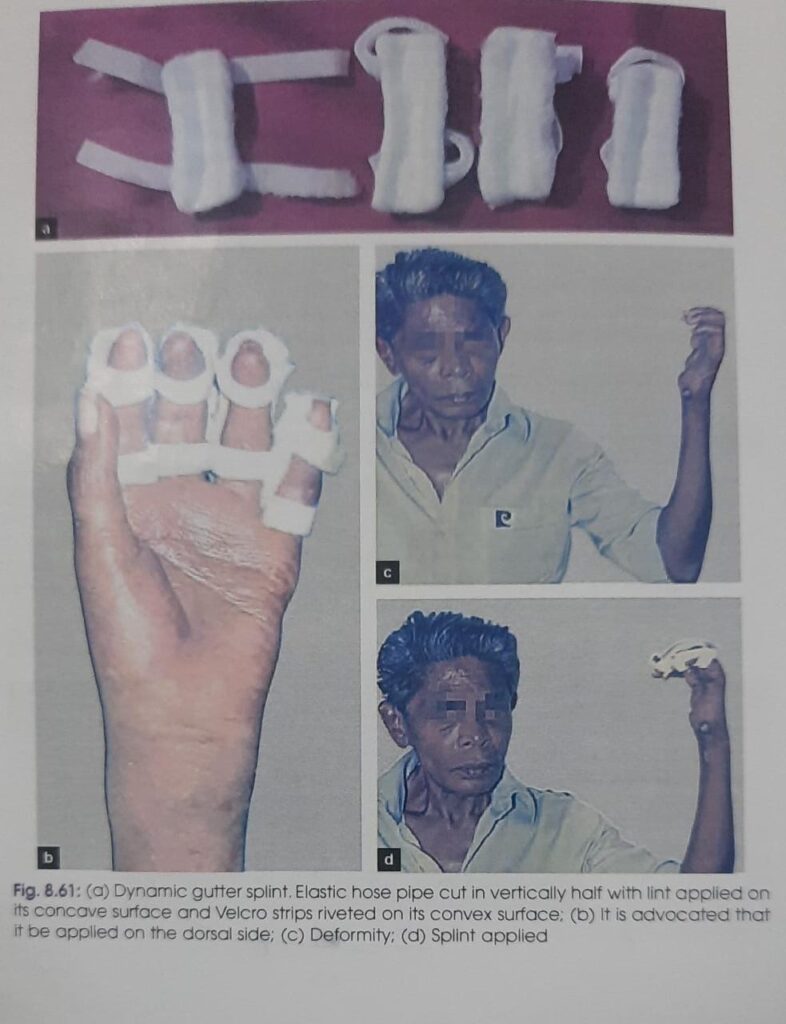
Treatment
Exercises
https://fb.watch/cR67OveY8U/
Refractory disease
Bad prognostic factors
Monitoring of disease
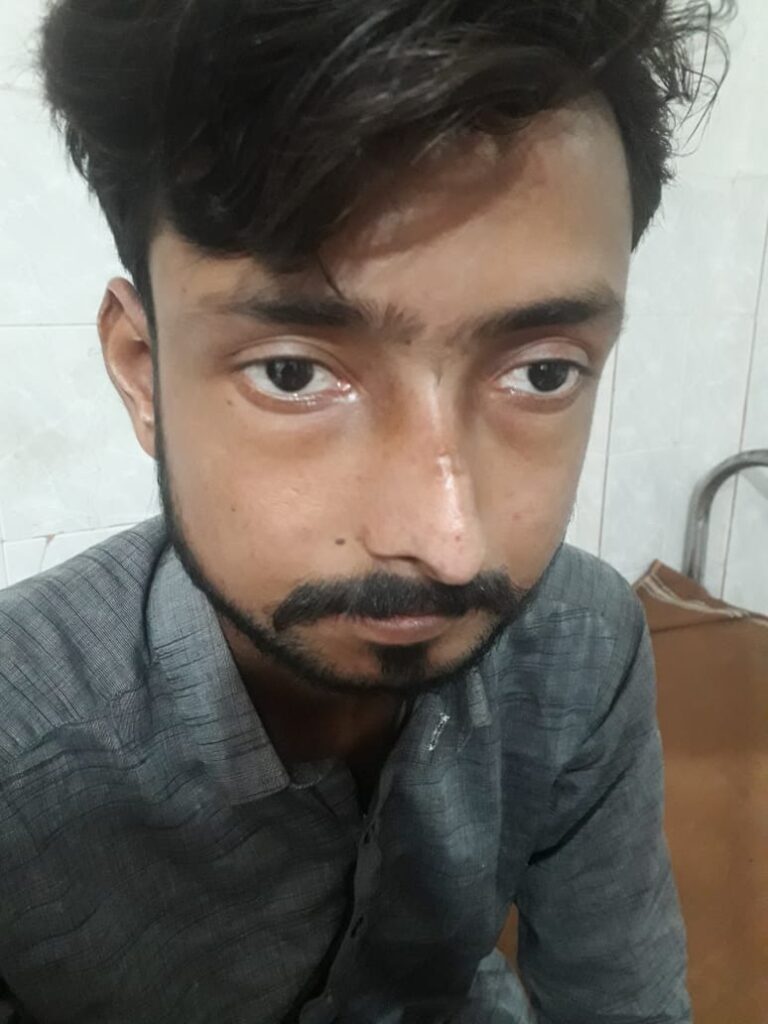
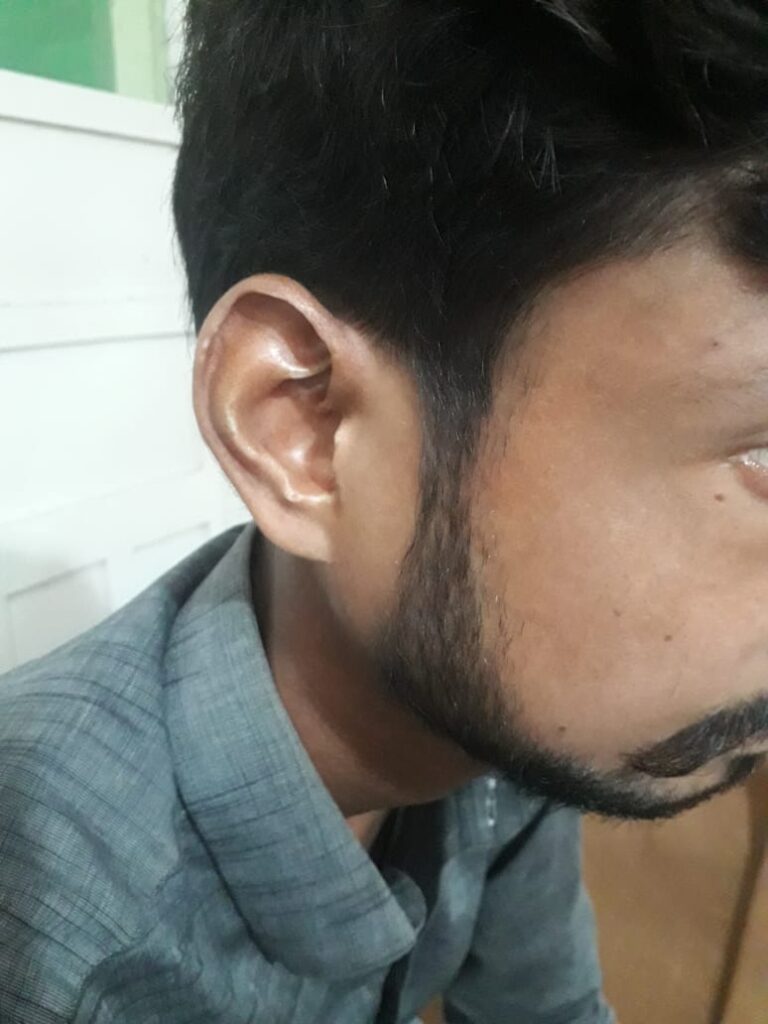


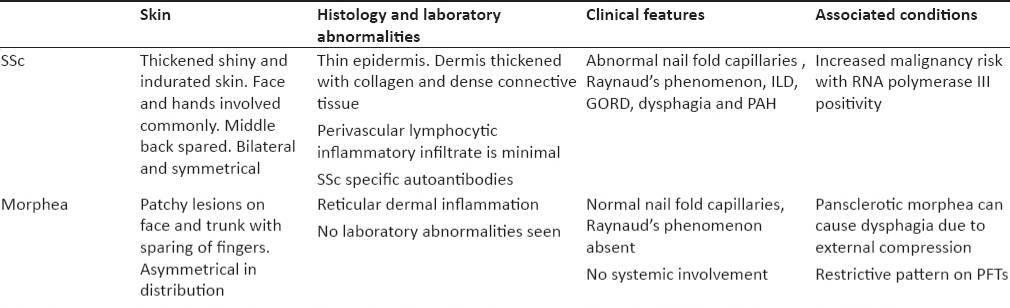






What are the eye changes in systemic sclerosis??*
– start from outside… eyelid stiffness, eyelid telengiectasis
– cataracts
– glaucoma
– keratoconjuctivitis sicca
– optic neuropathy
– orbital fat atrophy
What are the git findings ??
Remember findings from top to bottom, you will never forget
- Start from mouth i.e microstomia & icrocheilia ( this is dec in mouth width)
- Xerostomia
- Then comes teeth, enamel is damaged
- Dysphagia/ regurg
- Gastroparesis
- Small bowel dysmotility
- Large bowel diverticulosis
- Ano rectum… this is 2nd most common site affected after oesophagus, internal anal sphincter is involved
What are the bone changes in systemic sclerosis ?*
– phalangeal resorption
– erosive arthropathy ( pestle and mortar deformity)
– flexion deformities
– acro osteolysis
– joint space narrowing
-severe resorption of 1st carpometacarpal joint with radial subluxation and this is characteristic finding…
– calcinosis
What are soft tissue changes ?*
– subcutaneous and periarticular calcification
– atrophy of finger tips
What are the ecg findings in systemic sclerosis ?*
ST-T changes
– conduction abnormalities like LBBB, first degree AV block, prolonged QT, SVT, VT
What are the echo findings in systemic sclerosis?
*
diastolic dysfunction
valvular regurgitation
Right ventricular pathology
DETECT study
A non invasive method to tell us when to go for invasive right heart catheterization.
🔅Step 1
Calculate a score by measuring 6 parameters
-fvc predicted /dlco predicted
-telengiectasia yes or no
– anti centromere antibody yes or no
– right axis deviation on ecg yes or no
– serum urate level
– pro bnp level
( easy to remember 3 have yes or no, and 3 are values)
If the score is more than 300 then go for echo
🔅Step 2
You see right atrium area in cm2,
TRJ (tricuspid regurgitant jet) velocity in m/s and step 1 total risk score
If its more than 35, then right heart catheterization is recommended..
HSCT considered in SSc when 👇🏻
Disease is rapidly progressive
Severe visceral involvement esp pulmonary involvement
Unresponsive to treatment
🔰 IMPORTANT 🔰
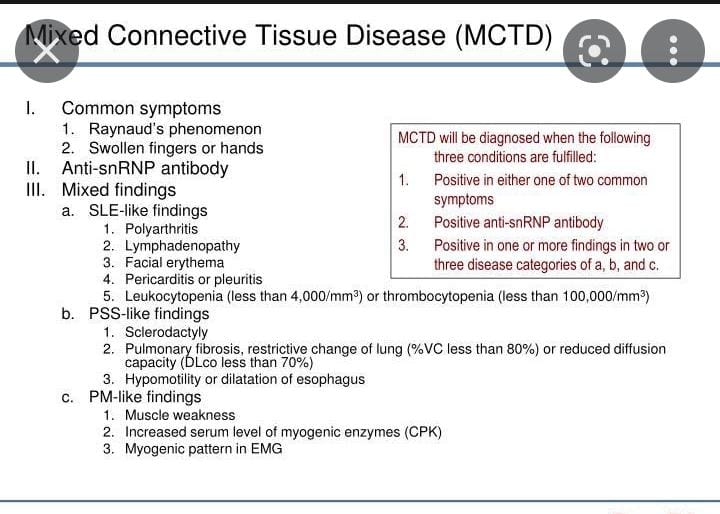
Systemic sclerosis is a very imp long case which always comes in exam, isolated or as a part of MCTD.
So its imp to know every aspect of it.
Like other long n short cases, examiner already makes his mind in the first 10mins after listening to ua history so its critically imp to have a firm grip over history taking and then on the examination.
Ua body language says it all about how many patients u have examined.
So practice as much as u can, ofcourse with a timer on ua bedside coz without time management even the best candidates face the bitterness if failure.
Happy learning😊
Dermatomyositis

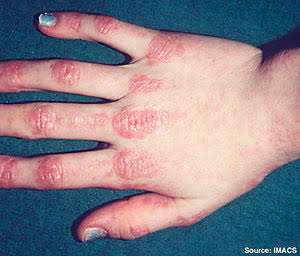
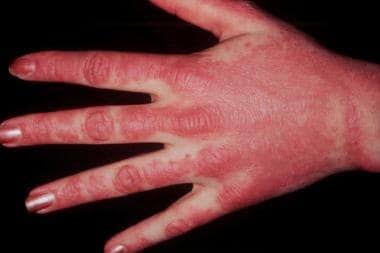
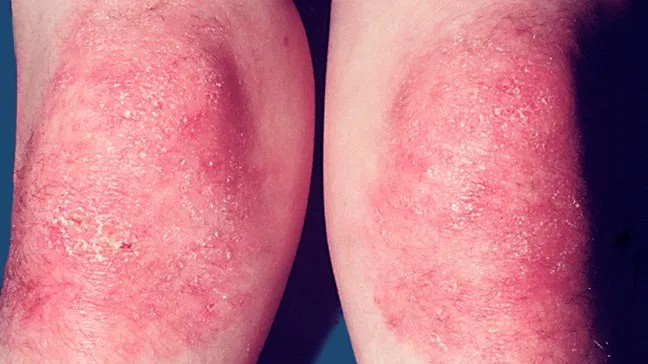
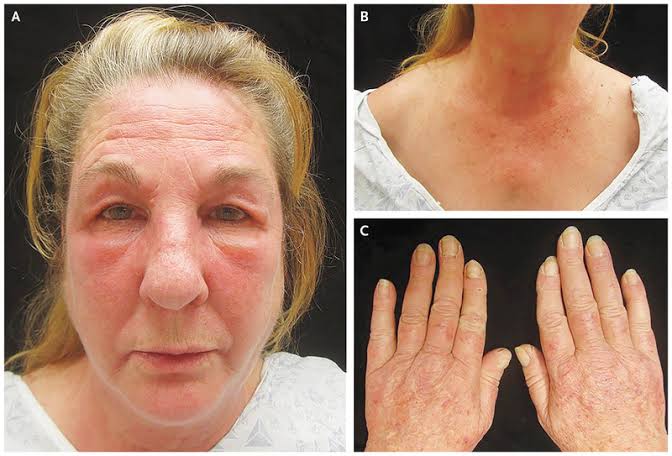
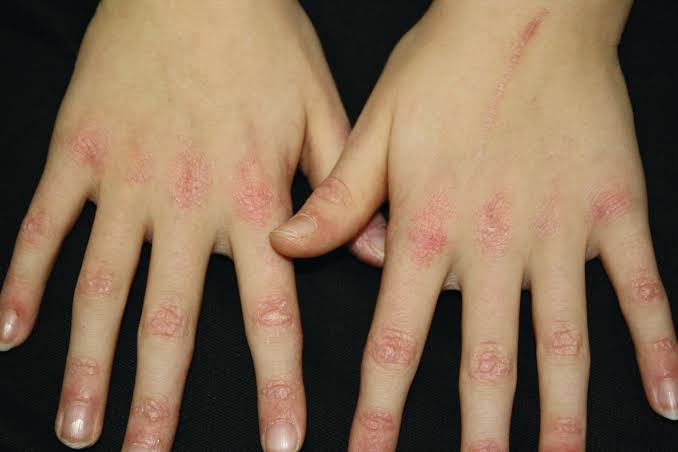


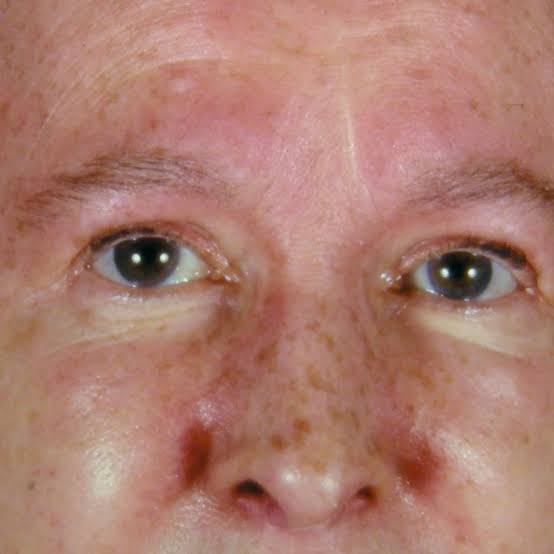
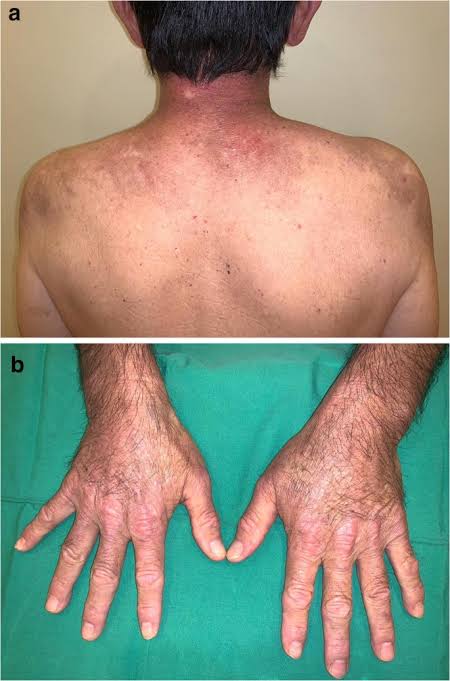

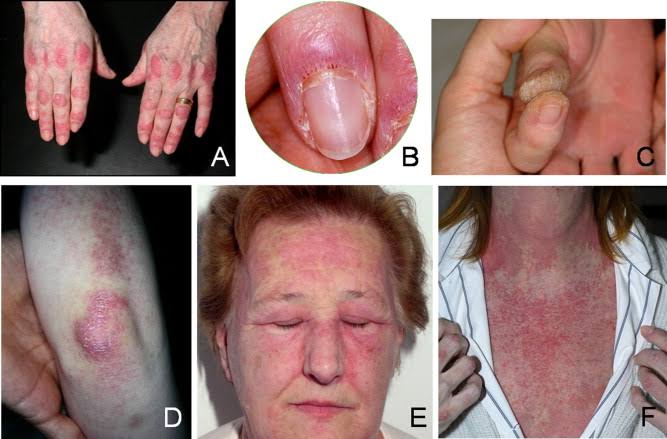
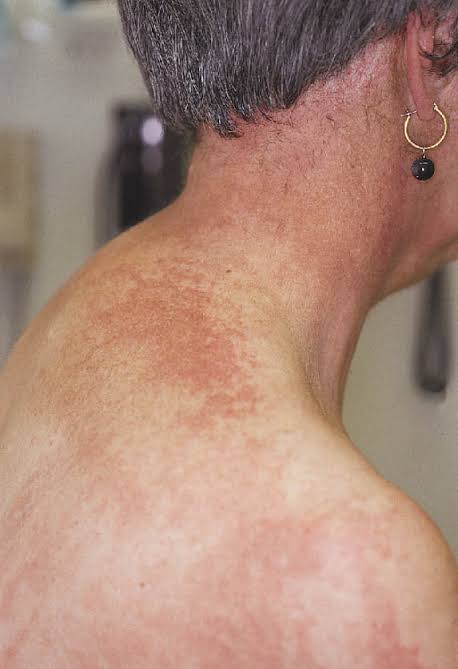

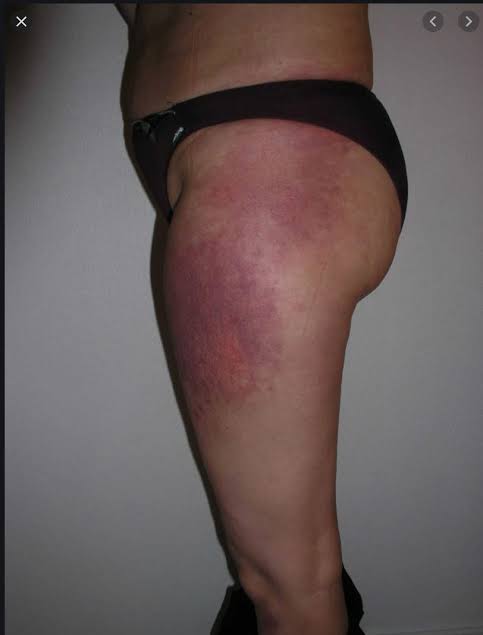
Juvenile DM👇🏻

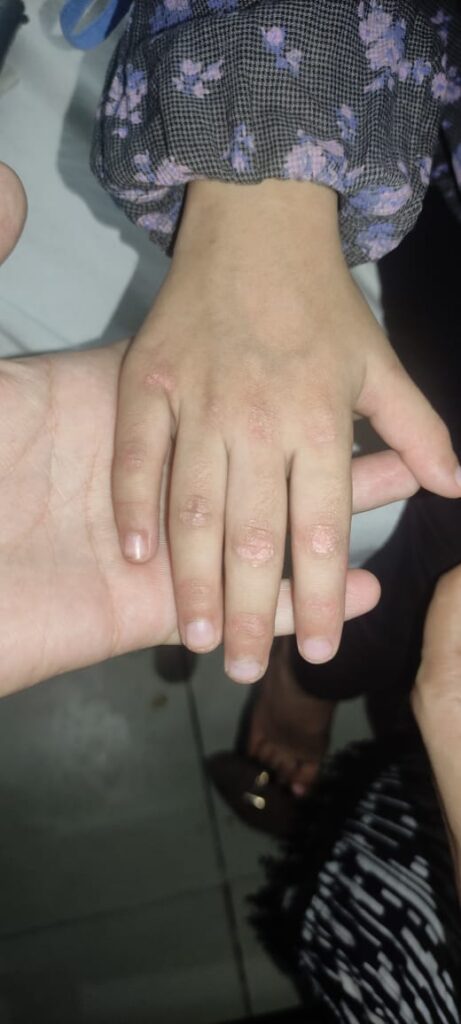
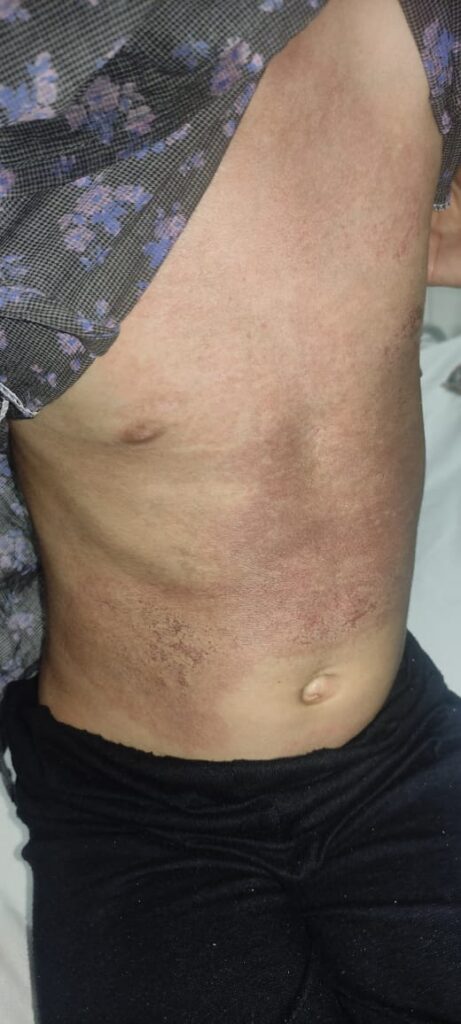
Adult DM👇🏻


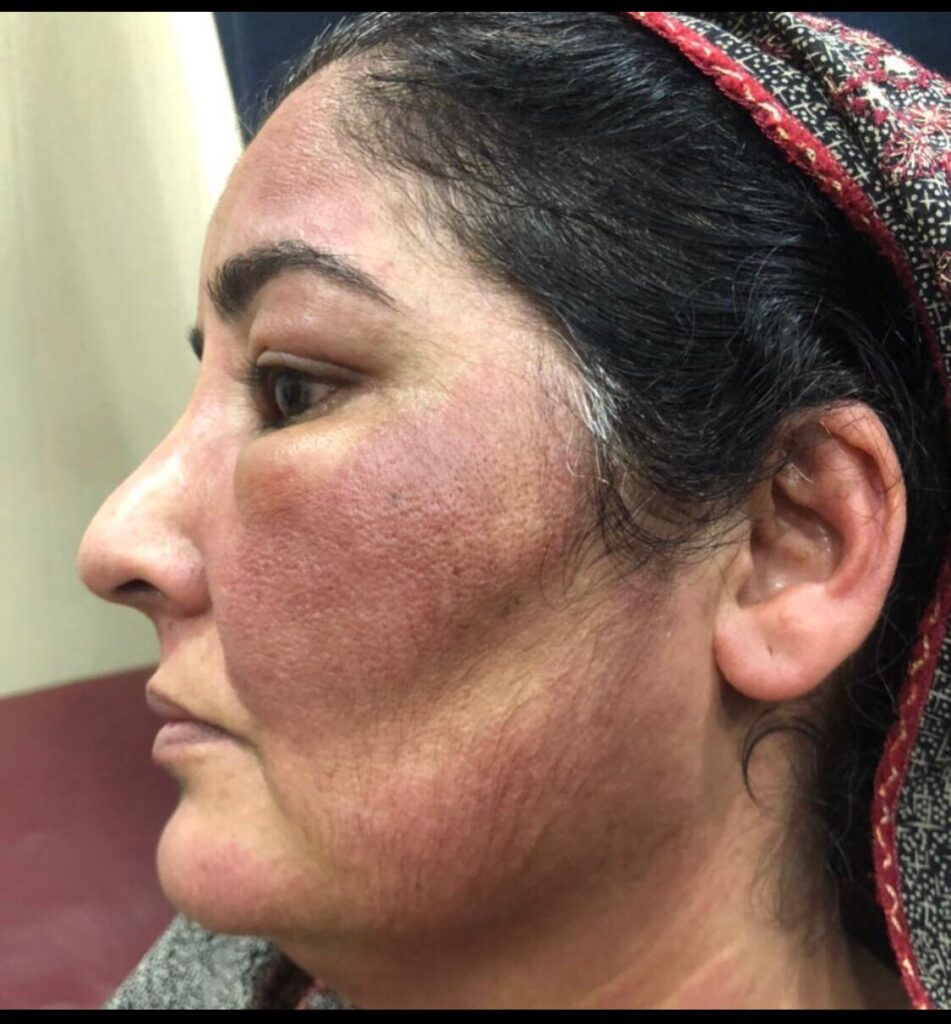



Management

New advances
ATE
Apremilast
Alemtuzumab
Abatacept
Anakinra
Tocilizumab
Eculizumab




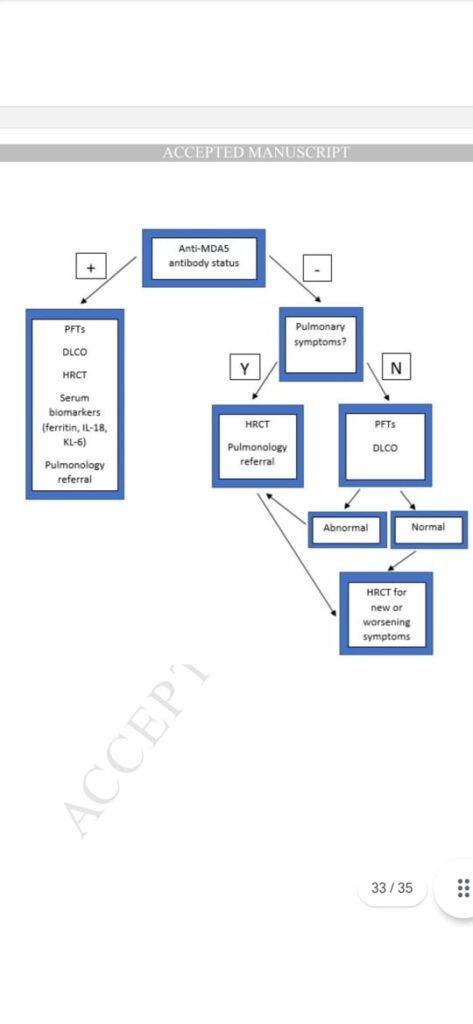

History
Examination
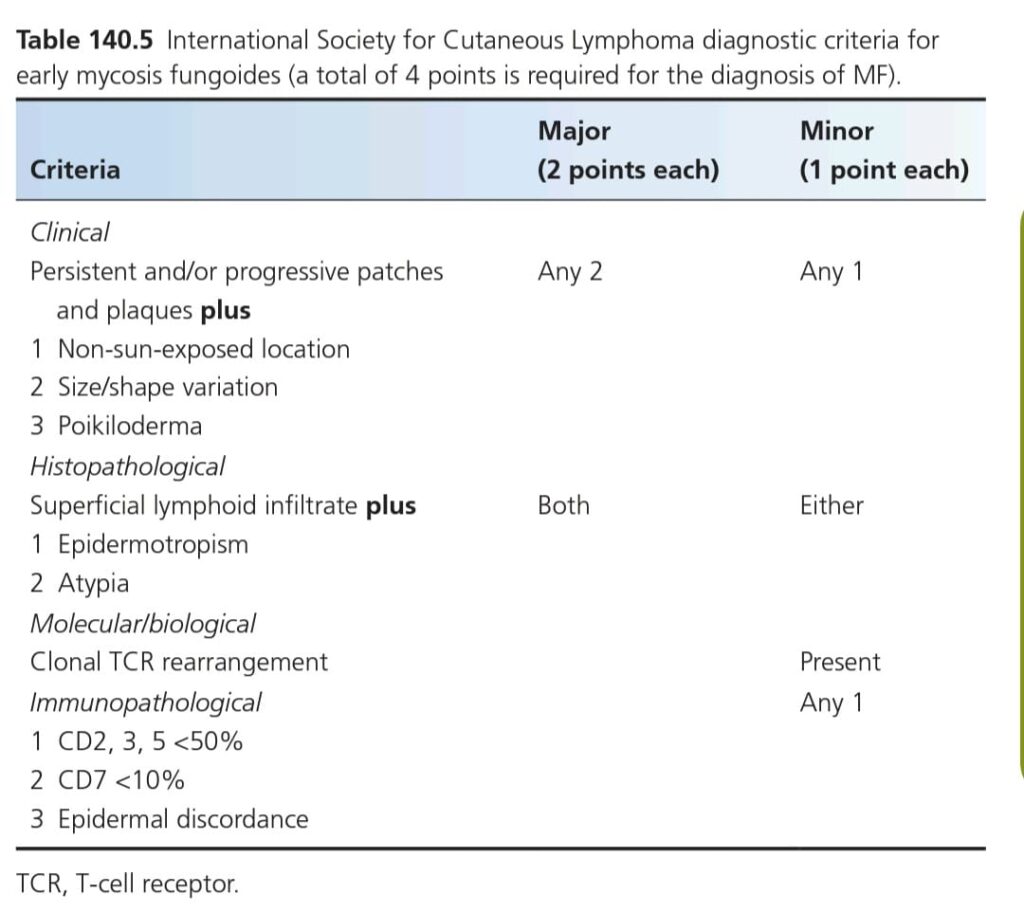
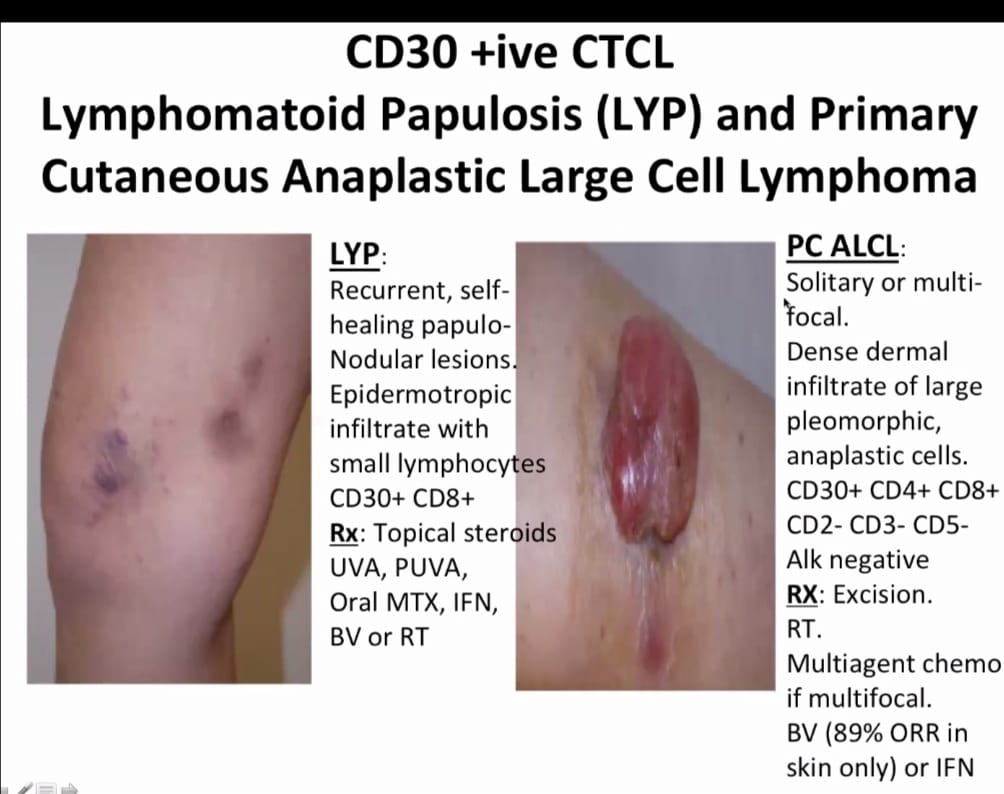
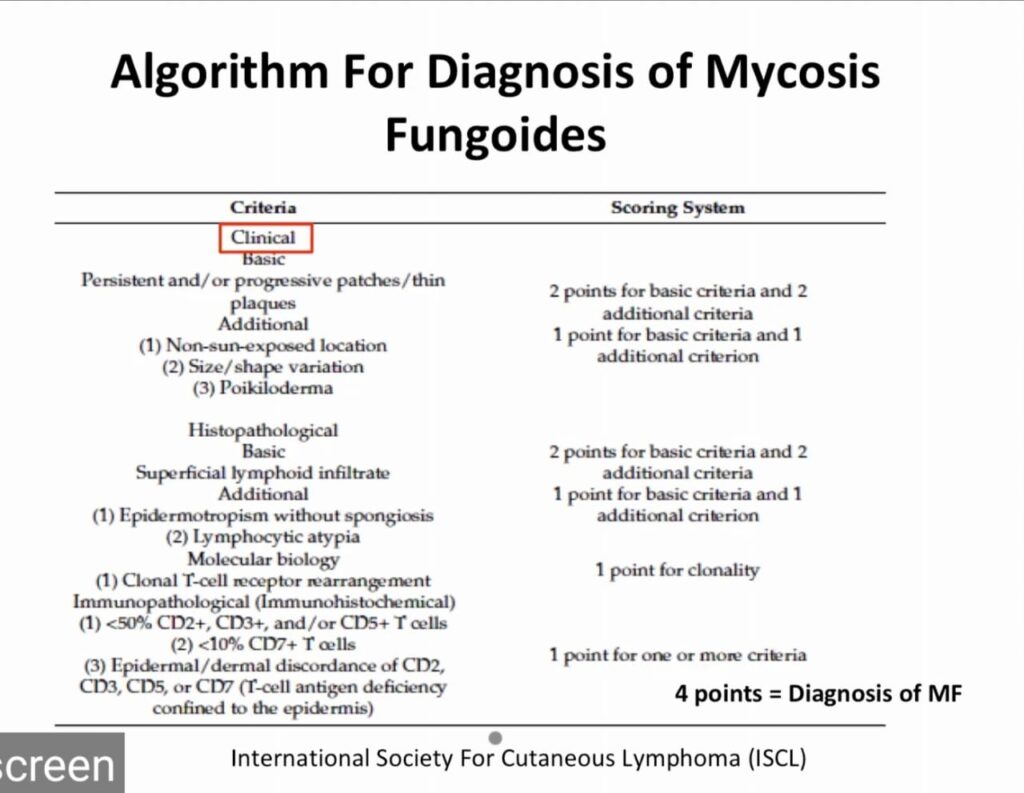
Diagnostic criteria
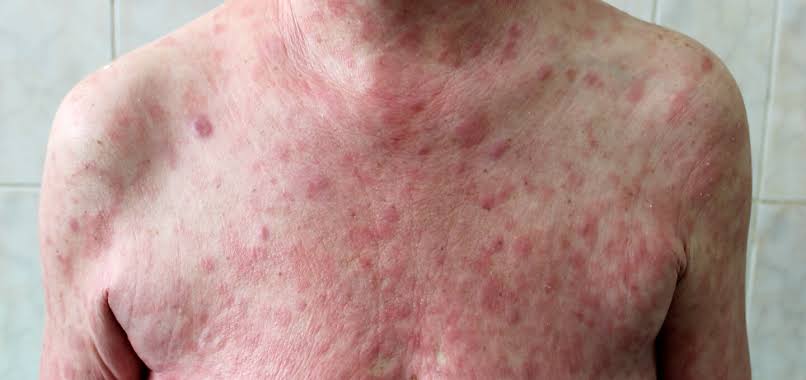
Clinical features

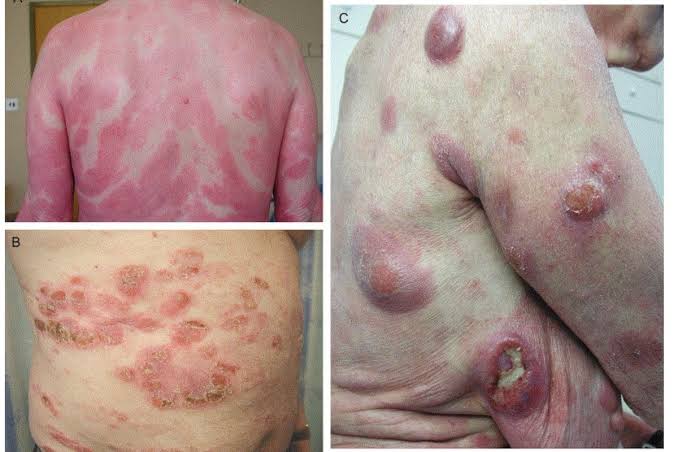
Clinical variants
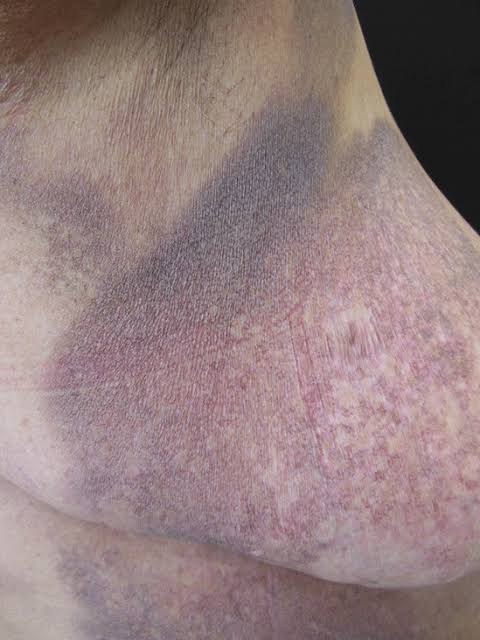
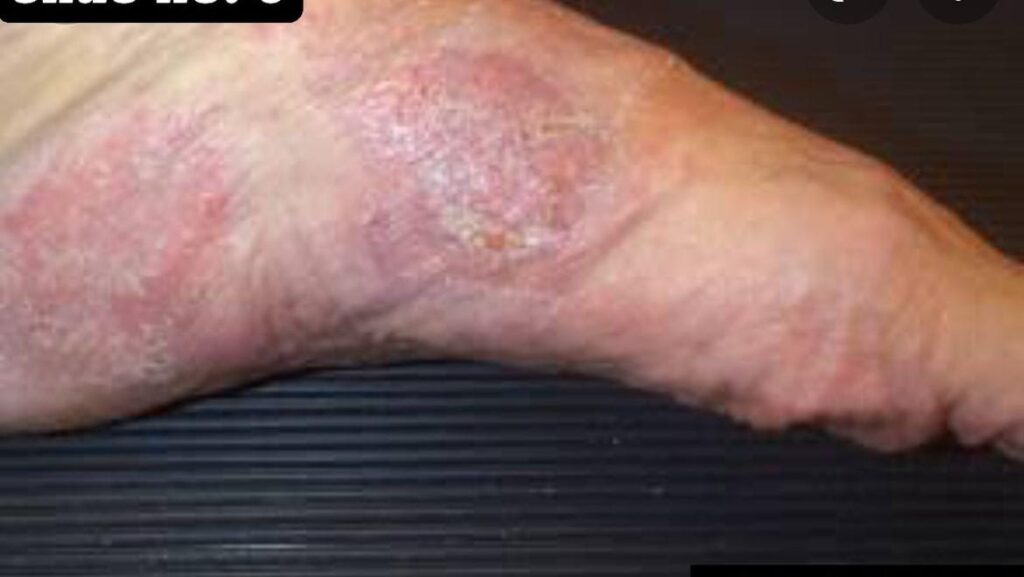
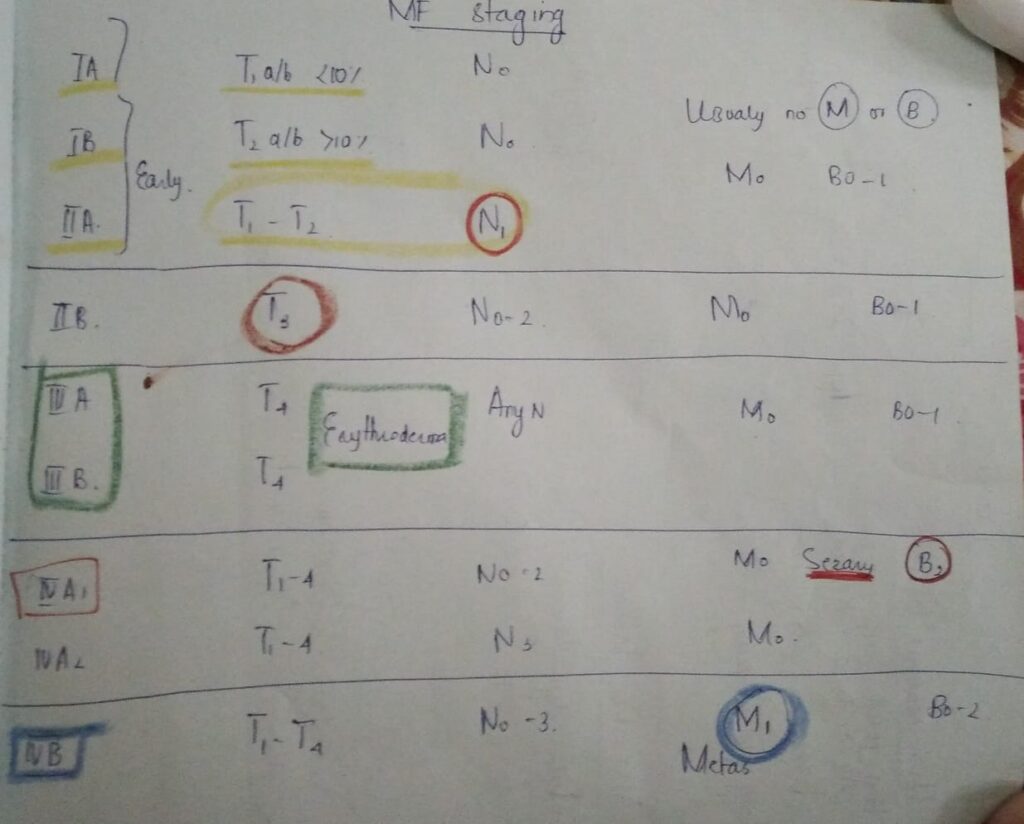
Staging

Investigations
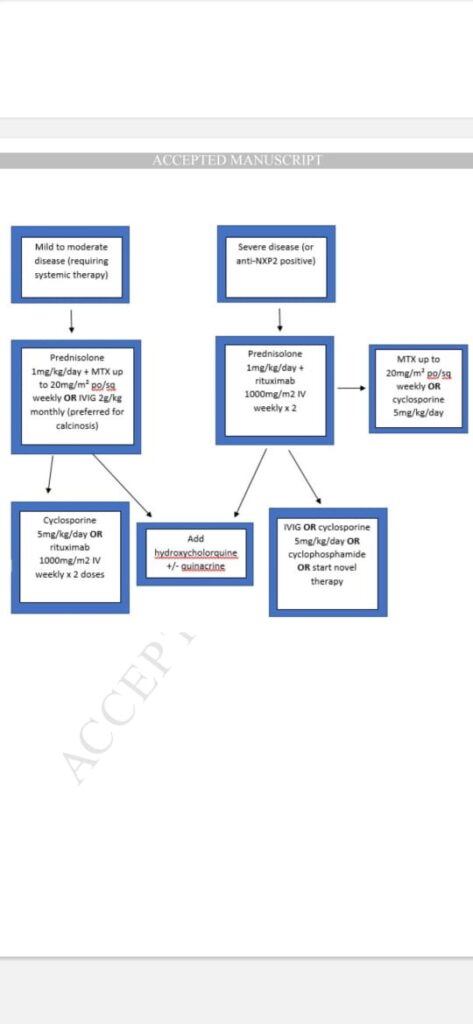
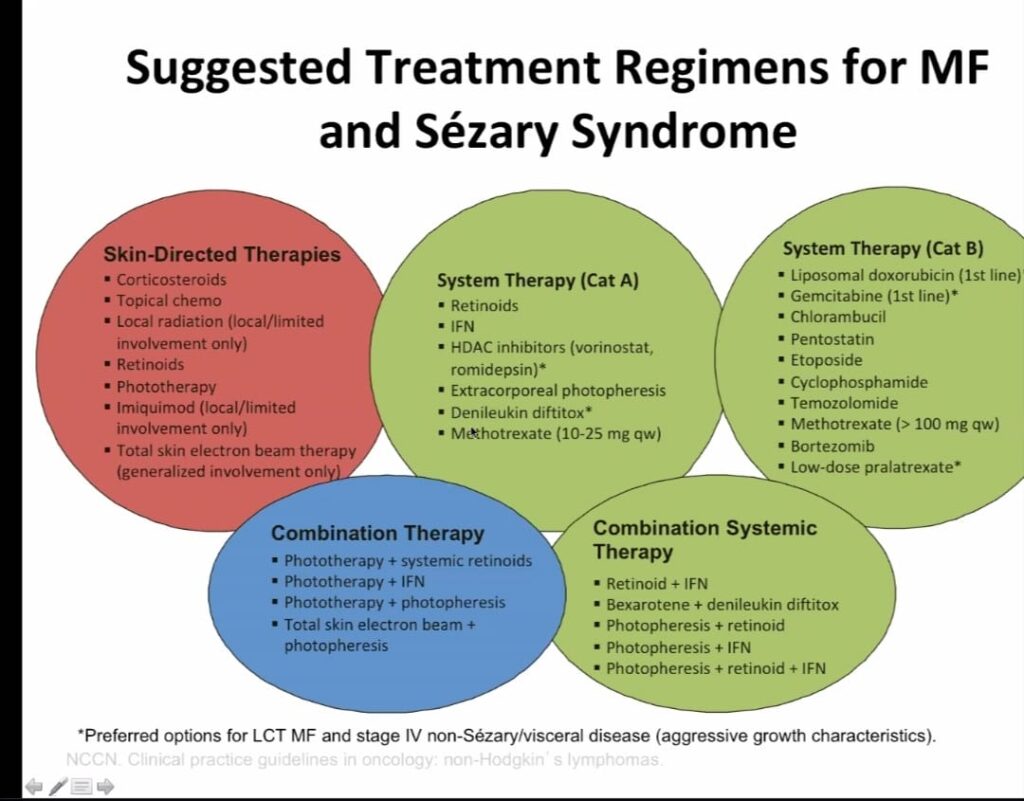
Treatment
Recent advances in MF treatment include:
– Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) like romidepsin and belinostat
– Immune checkpoint inhibitors like pembrolizumab and nivolumab
– Brentuximab vedotin (an antibody-drug conjugate)
– Mogamulizumab (a monoclonal antibody)
– Lenalidomide (an immunomodulatory agent
– zonalimunab (anti CD 4 antibody)
– alemtuzumab (anti CD 52)




Radiotherapy
Biological agents and new advances
BAM
BRENTUXIMAB
ALEMTIZUMAB
MOGAMULIZUMAB
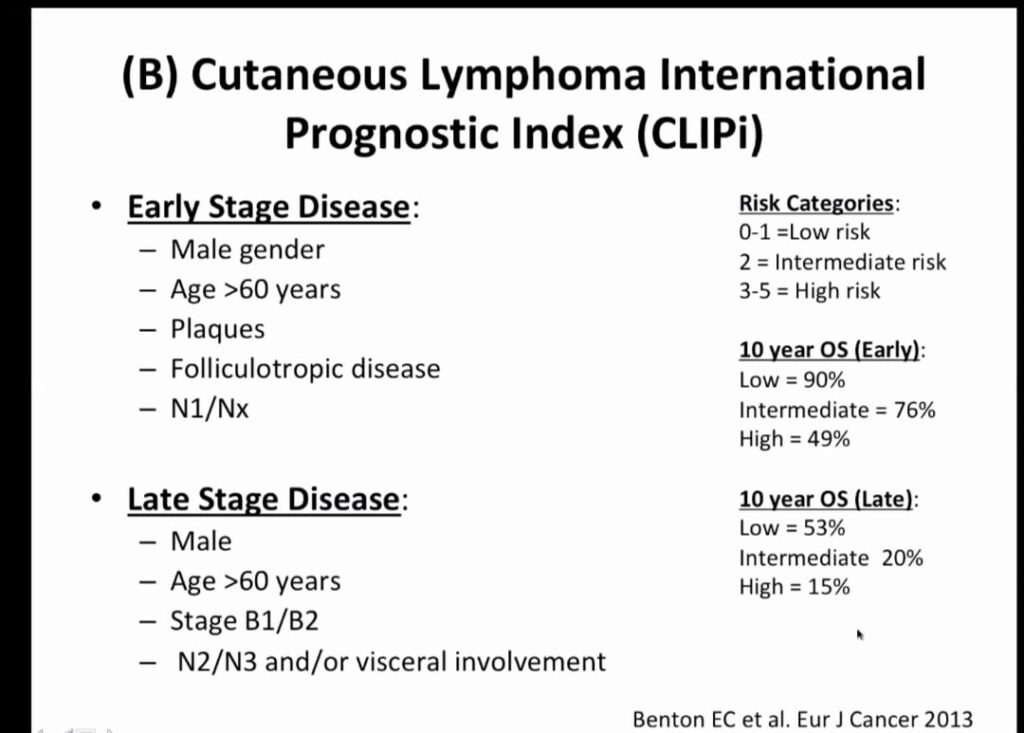
Prognosis
5 year survival rate 👇🏻
Stage I. 80-90%
Stage II. 47-78%
Stage III. 40-47%
Stage IV. 18-37%
Overall survival 68-80%
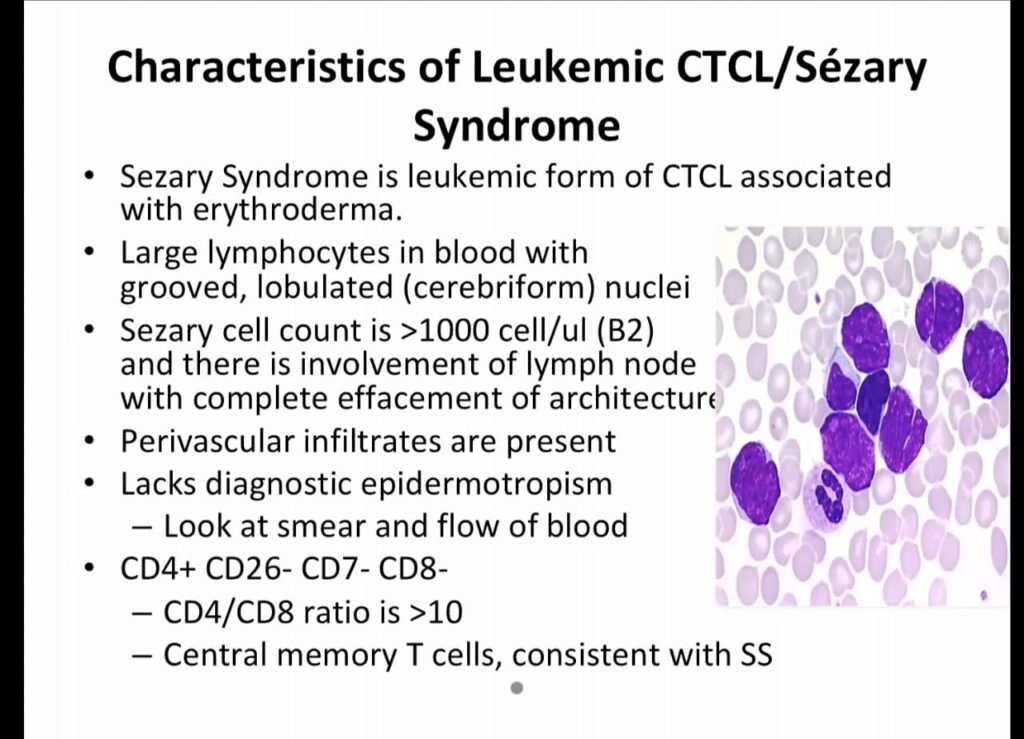
Sezary syndrome 32 months survival after diagnosis
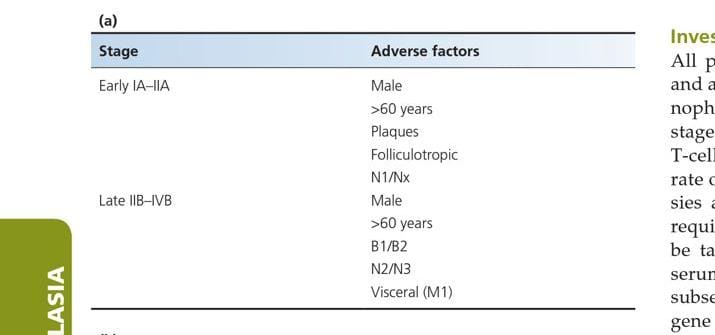
Viva questions👇🏻
Aggressive cd8 lymphoma Bf1 +ve
Gama delta – BF – ve CD8 -ve
Alpha beta – Bf1 +ve, Cd8 +ve
Pseudolymphoma – Bcl 2 – ve
Marginal Lymphoma – bcl2 +ve bcl 6 -ve
Follicular center lymphoma – bcl2 -ve bcl 6 +ve
Diffuse Large cell – bc2 +ve bcl6 +ve

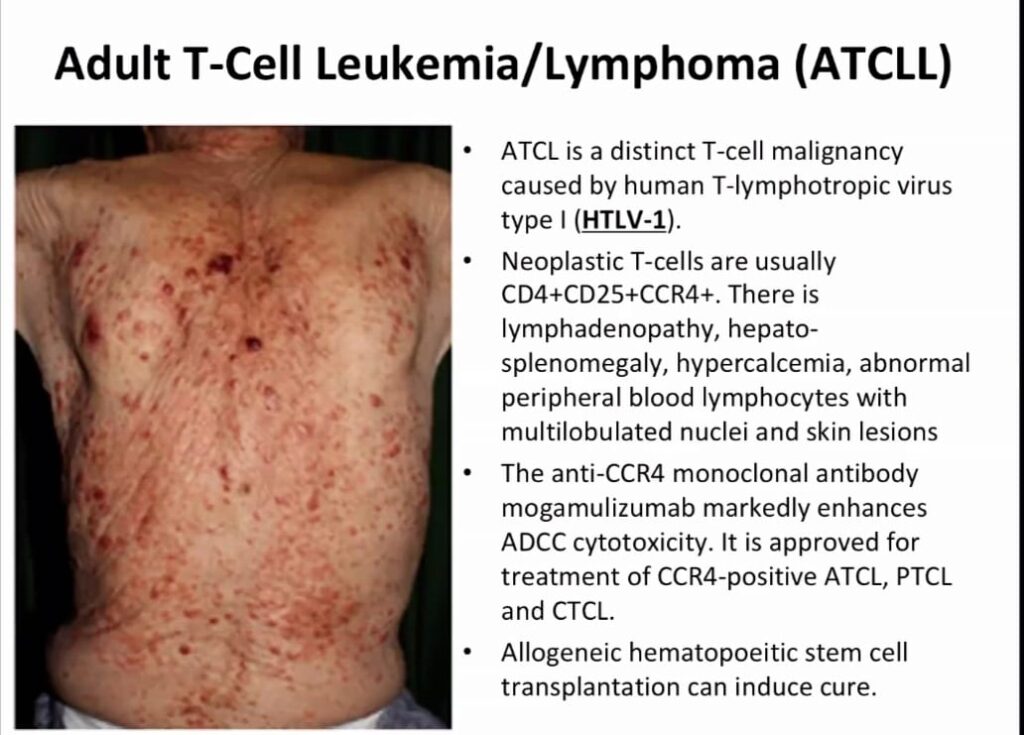
Important note
Mycosis fungoides is a very important long case
It must be kept in the dds of CAD,ABCD, psoriasis and leprosy, otherwise the examiner will already make his mind to fail the candidate.
Always ask questions specific for MF in above mentioned cases in history taking and palpate all the lymph nodes and liver spleen during examination, be it a long case or a short case to make sure it isnt MF.
Examiner will never spare u if u missed them.
If u did all these well then consider uaself in the safe zone after which ua viva will be easy in sha Allah.
Viva questions will be from the above voice notes and important tables which i have already shared.
Do not forget to mention the stage of the pt bcoz after mentioning MF in ua dds, nxt question will be why MF and what is the stage of MF in tht particular patient.
Rest of ua viva will be based on how will u manage this patient, investigations, IHC markers and treatment ladder.
🔰 Important 🔰
For revising MF for theory exam, revise from voice notes in long case grp
Its a summary and u l be able to revise imp points in an hour only
History
Examination

Investigations
Management
🔰 Cutaneous small vessel vasculitis
Erythema elevatum diutinum
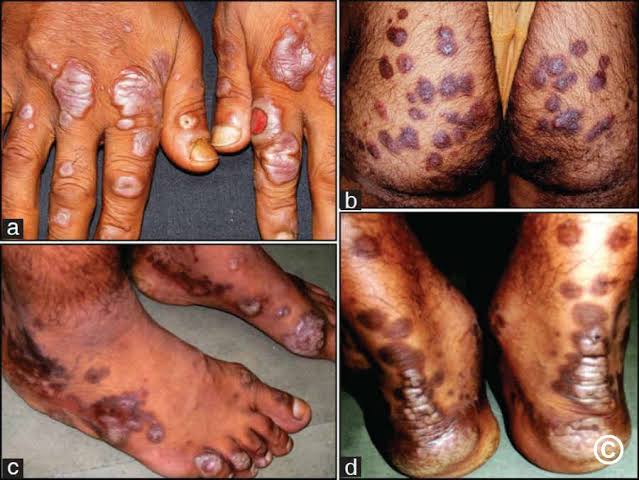
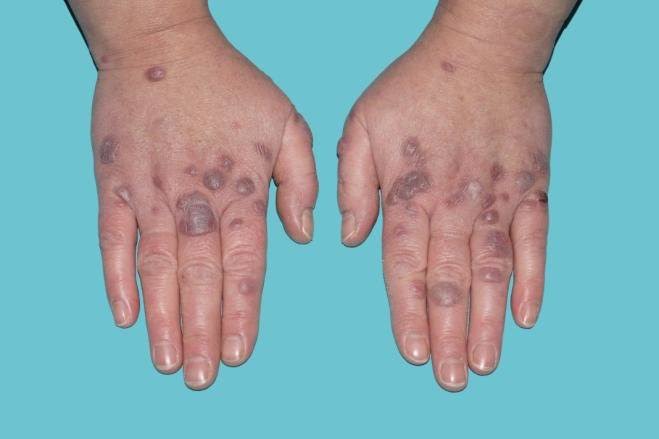
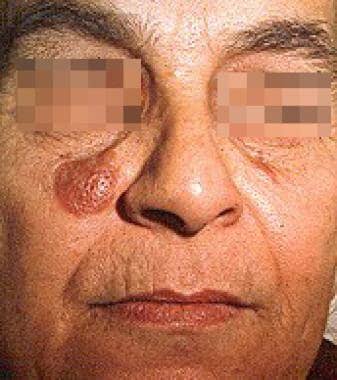
Granuloma faciale
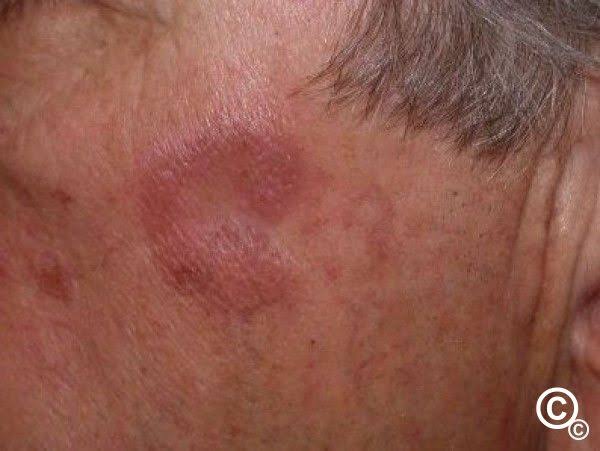
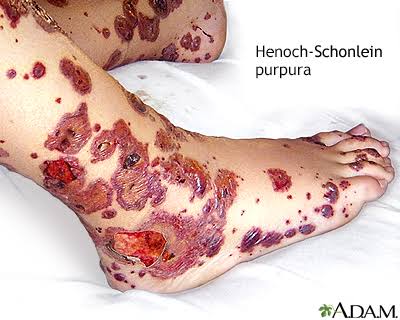
IgA vasculitis/ Henoch-Schonlein purpura

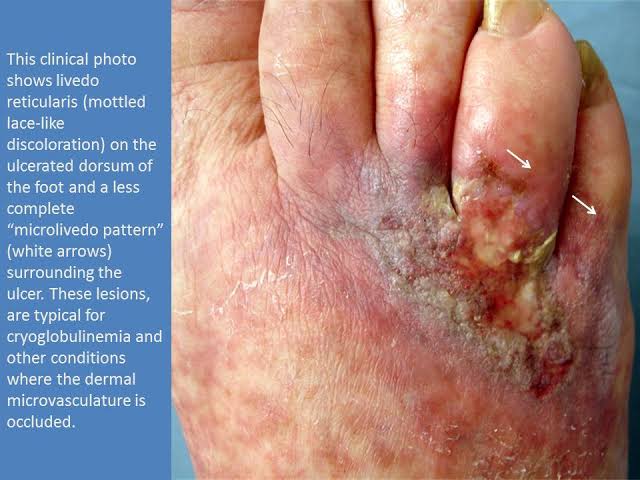
Cryoglobulinaemic vasculitis

Hypocomplementaemic urticarial vasculitis
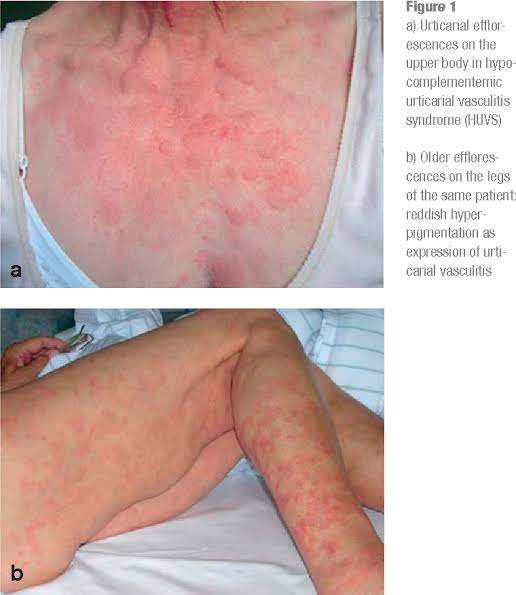
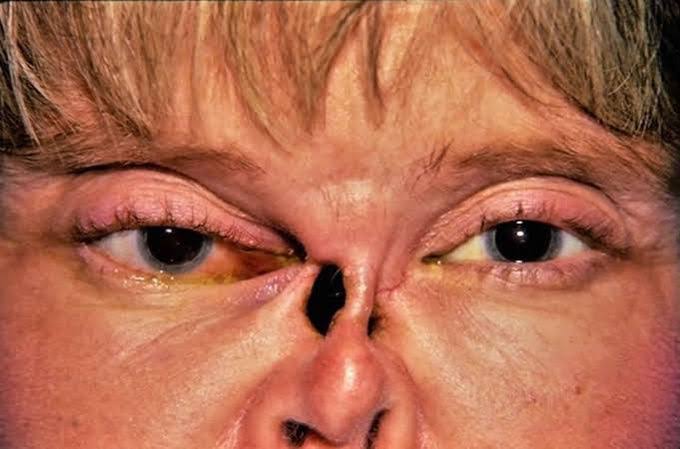
Anti GBM vasculitis/ Goodpasture syndrome
Small vessel ANCA associated vasculitis

Polyarteritis nodosa
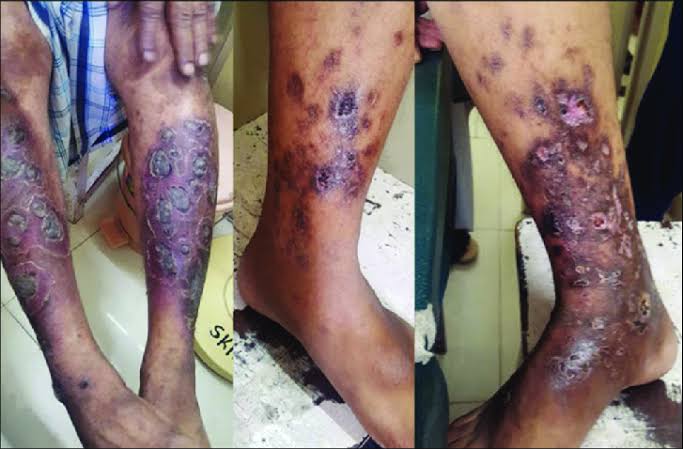
Large vessel vasculitis
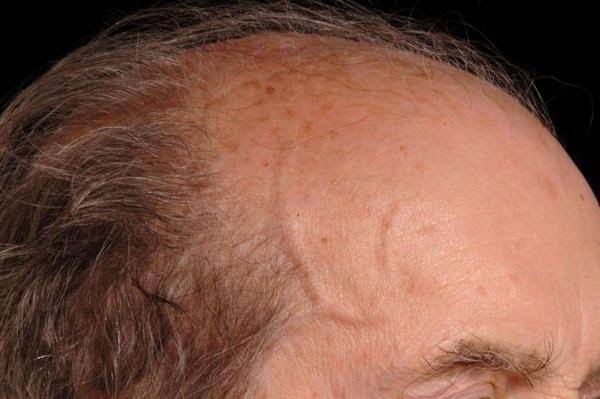

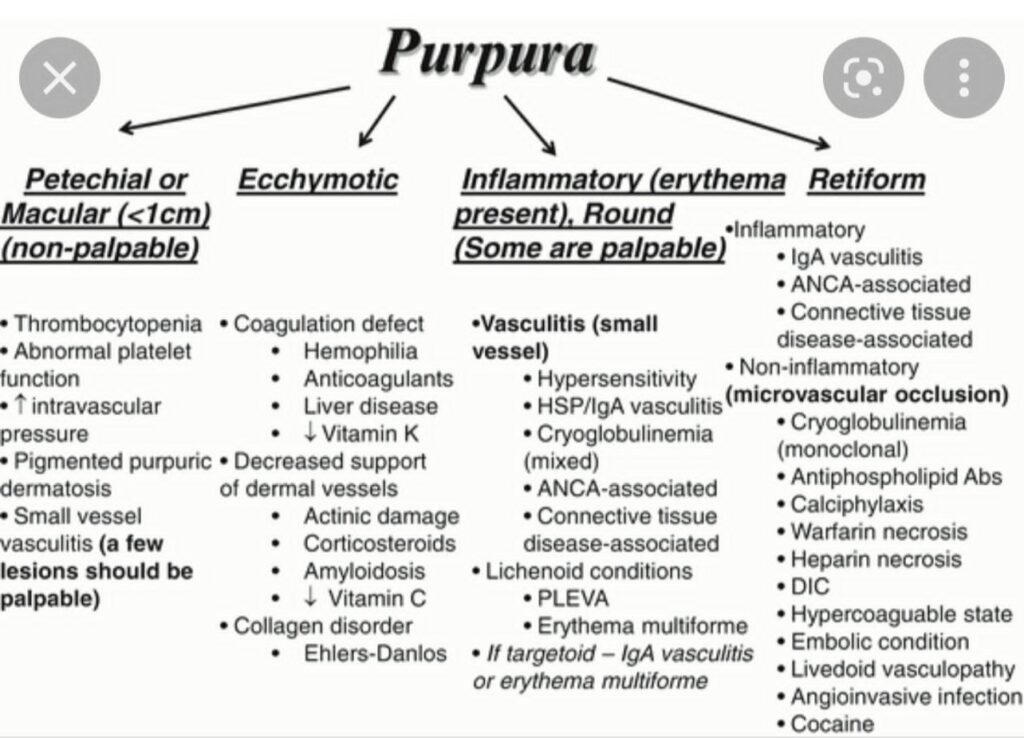
👆🏻vasculitis counselling
🔰 Important note
Vasculitis is a usual short case but can come as a long case too, atleast as a part of CTDs.
So u should prepare it for both short and long case.
🔰 For theory prep, revise this chapter from above voice notes, since i recorded them from rooks.
Listen, make concept and solve mcqs
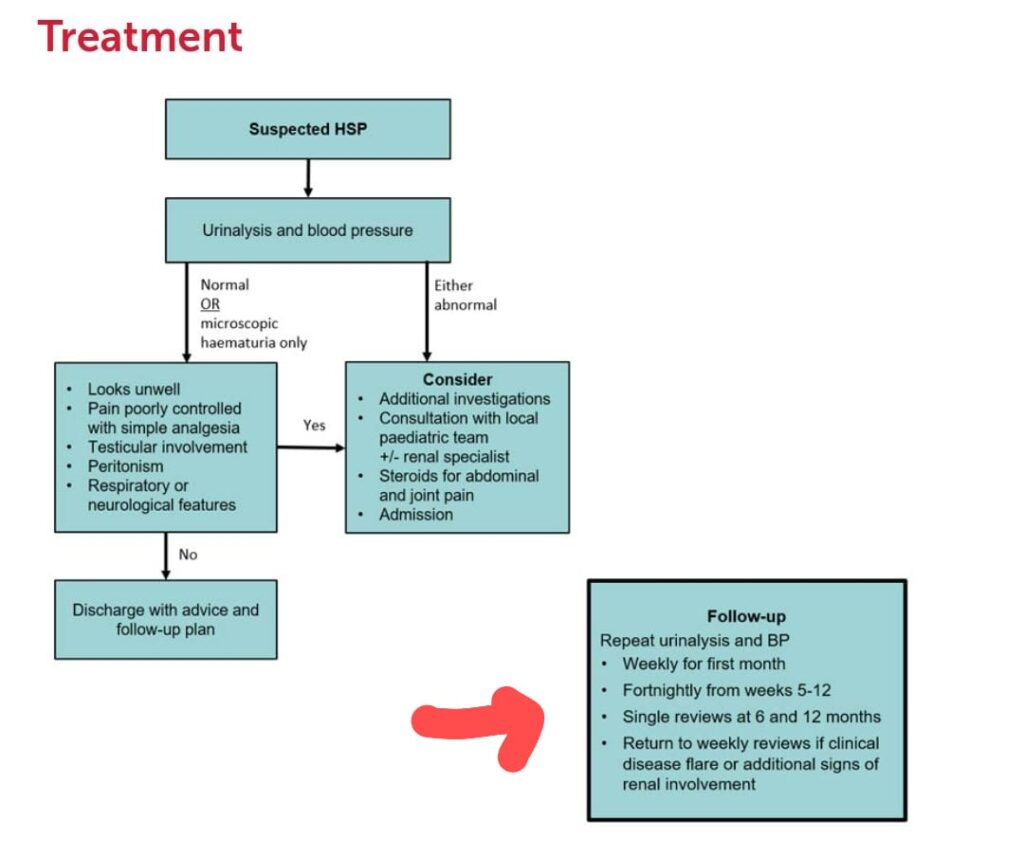
Investigations
Management
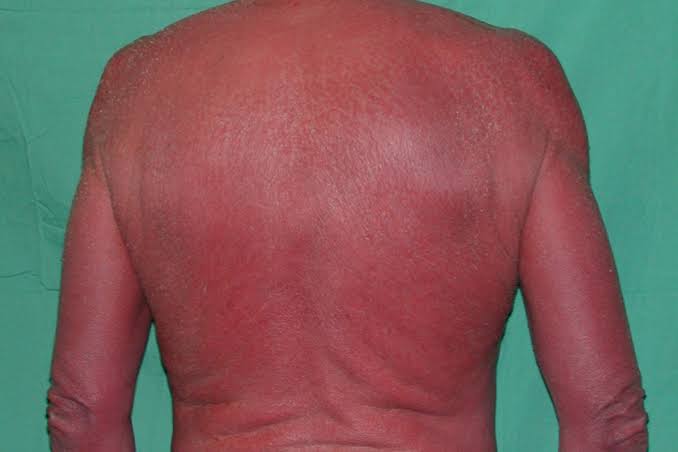
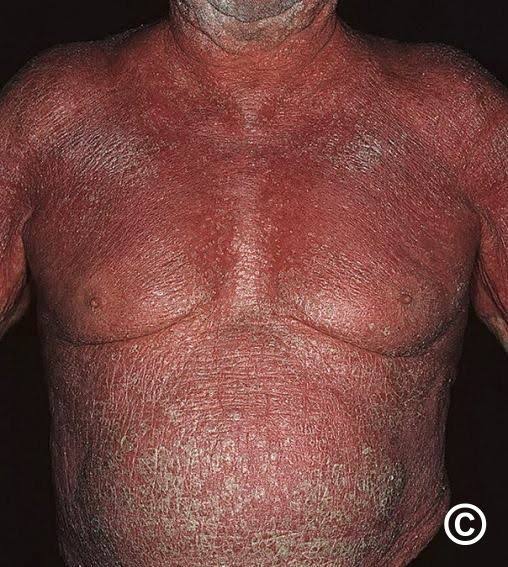
Causes of erythroderma
Eczemas 40%
Psoriasis. 25%
Lymphoma/leukemia 15%
Drugs 10%
Idiopathic. 8 %
CIE 1%
PRP. 1%
Pemphigus foliaceous 0.5%
Dermatophytosis 0.5%
Crusted scabies. 0.5%
Rare causes
Sarcoidosis
GVHD
HHD
LP
LE
HIV seroconversion
Transepidermal water loss
Normal 400ml/day
Increased to 3L/day in 50% skin involvement in erythoderma
Causes of glucosuria in erythroderma
Pancreatitis causing decreased insulin secretion
Peripheral insulin resistance
Stress
Infections

Investigations
Treatment
CLASSIFICATION OF PHOTODERMATOSIS
🟩Idiopathic
PLE
CAD
Juvenile spring eruption
Solar urticaria
Hydroa vacciniforme
Actinic prurigo
🟩Genodermatosis
XP
Bloom syndrome
Cockayne syndrome
🟩Endogenous photosensitizers
Porphyrias
🟩Exogenous photosensitizers
PABA
Naproxen
Diuretics
Tetracyclines
Sulphonamides
Retinoids
Dapsone
5 ALA
🟩Photoaggravated dermatosis
SLE and bullous SLE
Psoriasis
Photoaggravated eczemas
Rosacea
Acne vulgaris
Urticaria
Melasma
Lymphocytoma cutis
UVC 100-290nm
UVB 280 -320nm
NBUVB. 311-313nm
UVA 320 – 400nm
UVA1 340-400nm
Visible light 400-700nm
Infrared 700nm onwards
Grenz <100nm
X rays < Grenz rays
Effects of UVR on skin👇🏻
History
Examination
Viva questions
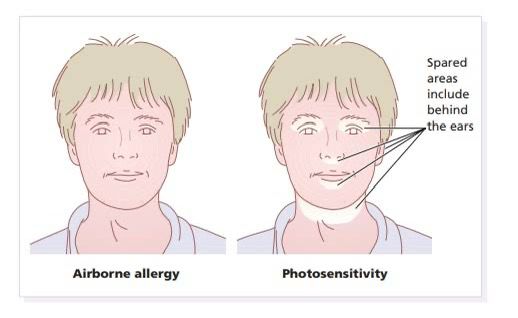

AIRBORNE CONTACT DERMATITIS👇🏻
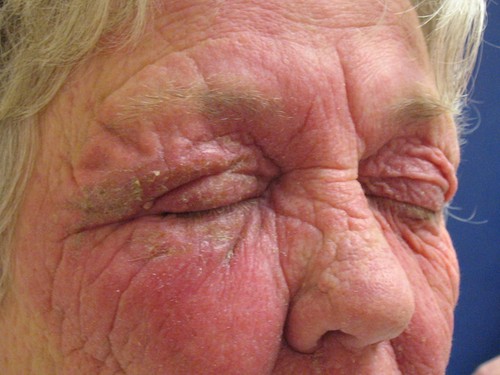
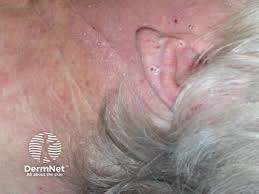
PHOTOTESTING
PHOTOPATCH TESTING
PATCH TESTING
Phototoxic vs photoallergic dermatitis
Management of Allergic contact dermatitis👇🏻
🔰 IMPORTANT
Patch testing and photopatch testing are imp.
Watch videos to clear the concept since it may come as a toacs station too.
Pathogenesis
Allergens
Dettol products 👇🏻
Chlorhexidine
Benzalkonium
Chloroxylenol
Dyes👇🏻
PPD
para phenylene diamine
Para toluene diamine
Ortho para phenylene diamine
Sunscreen👇🏻
Rubber👇🏻
Latex
Synthetic rubber – Nitrile/neoprene
Mercapto mix
Carba mix
Black rubber mix
Thiuram mix
Cosmetics, shower gels, bath oils and tooth paste👇🏻
Nail varnish👇🏻
tosylamide-formaldehyde resin.
Acrylates
ESCD baseline series 👇🏻
Following cosmetic allergens
FMI
FMII
balsam of peru
Lyral
Paraben mix
Quaternium 15
Formaldehyde
Ppd
Colophony
Applied medicaments👇🏻
🟩Local anaesthetics
Benzocaine
Lidocaine
🟩Neomycin
🟩Corticosteroid
Tixocortol pivalate
Budesonide
🟩lanolin
Metals
Nickel
Nickle sulphate
Nickle chloride
🟩 Chromium
Lead chromate
Zinc chromate
Clothing👇🏻
🟩Textile fibres
Natural – cotton, wool, silk, linen and rubber
Synthetic- rayon, nylon, polyester and acrylics
🟩Other allergens – nickel, chromate, rubber, formaldehyde resins
🟩 Textile dyes- azo dyes and anthroquinone
Shoes👇🏻
🟩Shoe series
Rubber. 43%
Chromate. 28%
formaldehyde 20%
Colophony. 9%
Ppd. 3.6%
Cobalt
Nickle
Epoxy resin
Biocides
Plants👇🏻
🔅Primula obconica
🔅Sesquiterpene lactone mix – Compositae asteraceae family
🔅Anacardiacae Family
🔅Garlic and onions
🔅Tea tree oil
🔅Chrysanthemum, sunflower, liliacea and P.abconica – Decorative plants
🔅lichens and liverworts
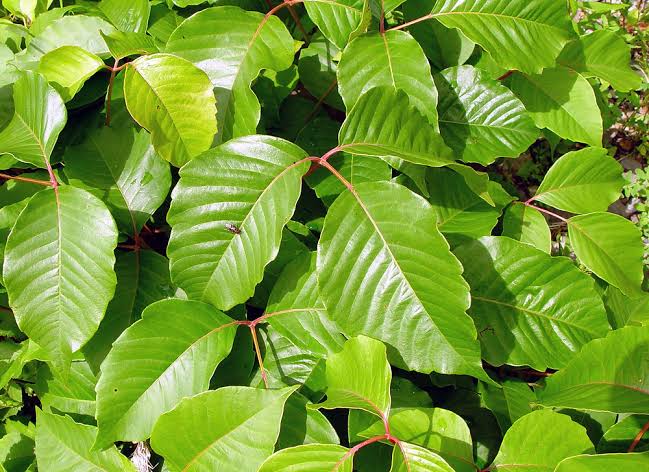
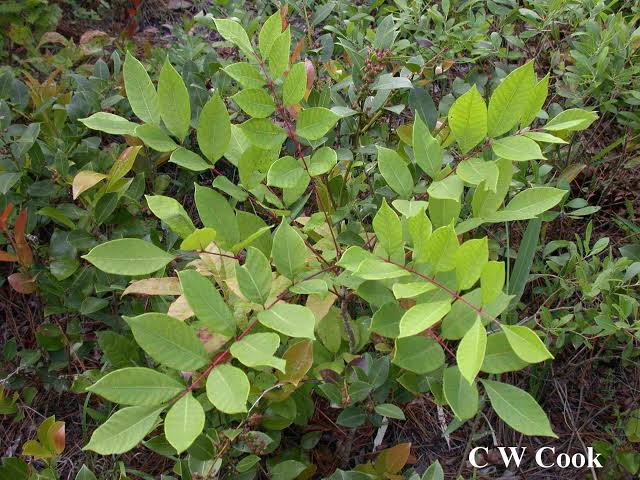
Anacardiacae toxicodendron 👇🏻



Compositae asteracae👇🏻






Decorative plants 👇🏻


Aliacae
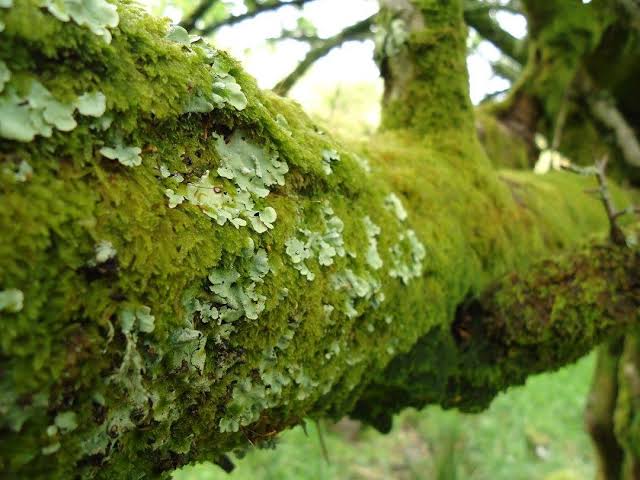
Lichen and liverworts👇🏻
Wood, colophony, turpentine, lanolin and propolis👇🏻
🟩Wood
Sawdust
🟩Colophony
Sap from pine
Flooring and floor polish
Cosmetics and mascara
Adhesive tapes
Glues
Topical medicaments
Chewing gum
Dental floss and dental materials
Adhesives in footwear
Paperwax
Paper dust
🟩 Turpentine
Pine trees
🟩Propolis
Resinous material from bee hives
🟩Lanolin
Natural product from sheep fleec/sebaceous sec of sheep
Found in medicaments, emollients, bath additives, cosmetics etc

IMPORTANT
Picture identification of plants and flowers associated with Allergic contact dermatitis is really imp since it may come in theory exam or toacs clinicals slides.
I have added few pictures but u must scroll through internet to look for more coz practice will definitely make things better.
Happy learning 😊
Ichthyosis vulgaris
ARCI
RXLI
Congenital reticular ichthyosiform erythroderma
Superficial epidermolytic ichthyosis
Bullosa of siemens
KID syndrome
Prognosis
History
Examination
Click here for Ichthyosis Syndromes and PPK
Investigations
Management of collodion baby
🔰 IMPORTANT NOTE
Although ichthyosis has least chances to come as a long case, but be prepared for the worse situation.
This ppt is the best 1 to memorize and revise ichthyosis.
History
Examination
Investigations
Management
Viva questions
Arterial ulcer
Venous ulcer
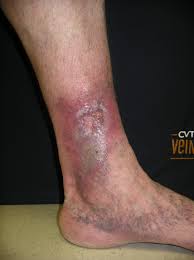
Neuropathic ulcer

Pyoderma gangrenosum
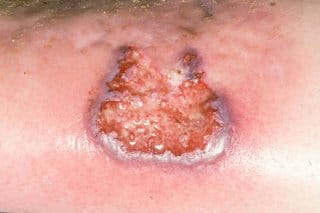
Hypertensive ulcer

Envitonmental triggers
Pruritis is caused by
Histamine
Substance P
Somatostatin
VIP
Abnormal response to ACH
Neuropeptide Y
Triggers in adults
Clinical features
Differential diagnosis
Complications
Course and prognosis
Classification of severity
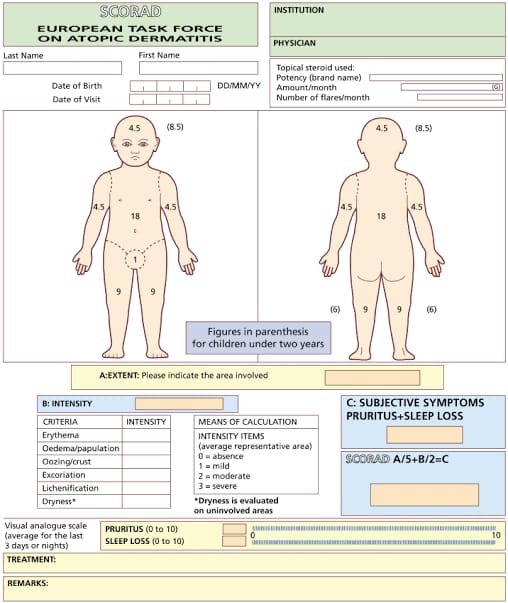

SCORAD assessment
Mild 《25
Moderate 25-50
Severe 》50
Investigations
Management
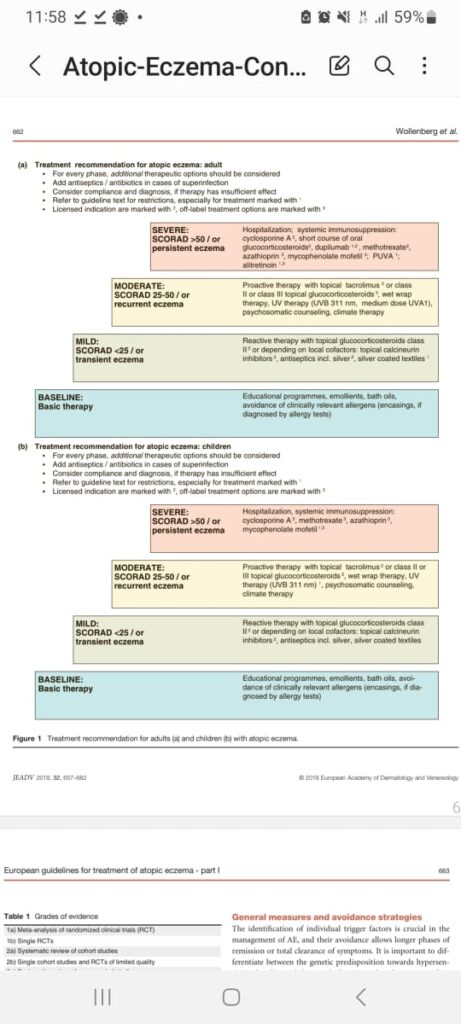
🔰 Important additions 👆🏻
Latest guidelines for AD.
Treatment plan is the same as mentioned earlier, juz given in a tabulated form.
History👇🏻
Examination
Investigations
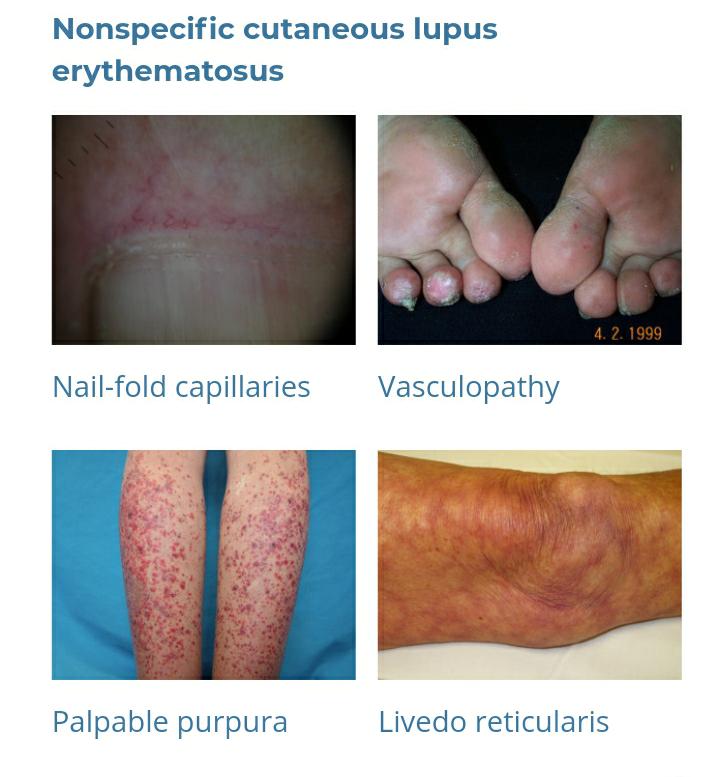
Systems involved in SLE 👇🏻
Mucocutaneous
Mulculoskeletal
Renal
Neurological
CVS
Pulmonary
Vascular
Hematological
General – fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, anorexia, nausea/vomiting.



SLEDAI
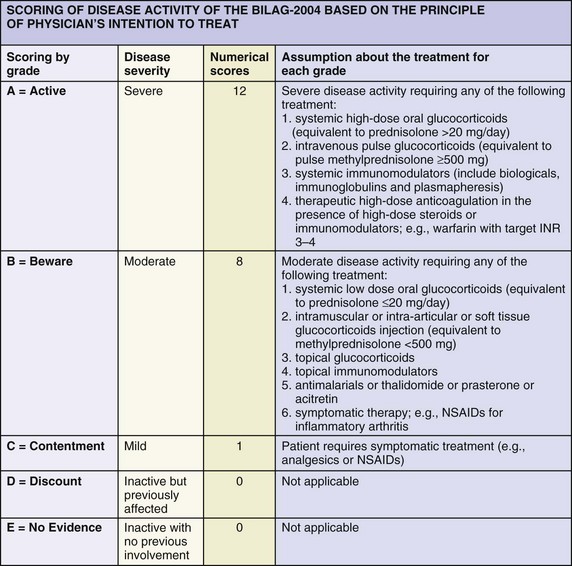
BILAG scoring👇🏻

Drugs causing SLE

Indications of renal biopsy👇🏻
ANA staining patterns👇🏻

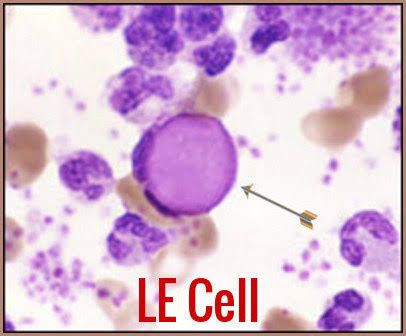
LE cell test👇🏻
Management
General measures
Specific management
Mild SLE activity👇🏻
Moderate SLE activity👇🏻
Severe SLE activity👇🏻
New advances in SLE👇🏻
Newer advances 👇🏻
Mneumonic. BARA TV📺
Belimumab
Abatacept
Rituximab
Anifrolumab
Tocilizumab
Volosporin
Lupus nephritis👇🏻
Prognosis
ANA negative SLE
Extra viva questions 👇🏻
DLE



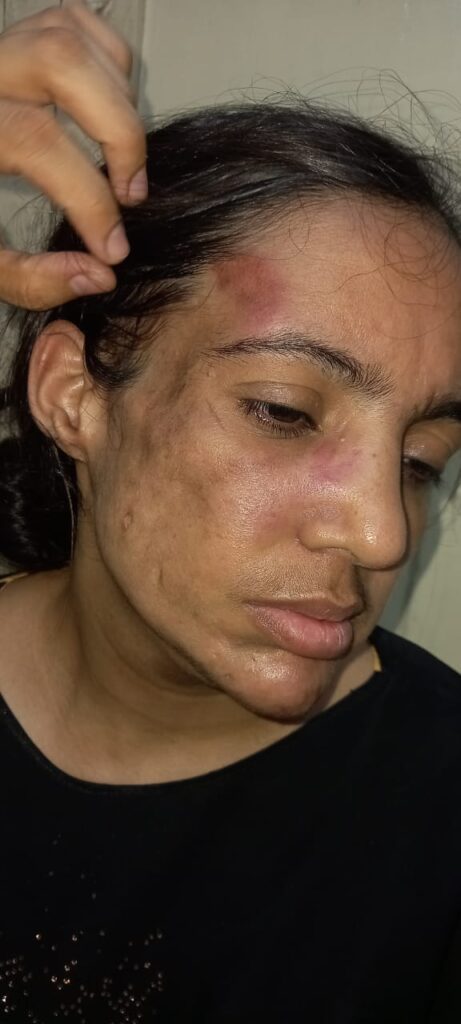
SCLE


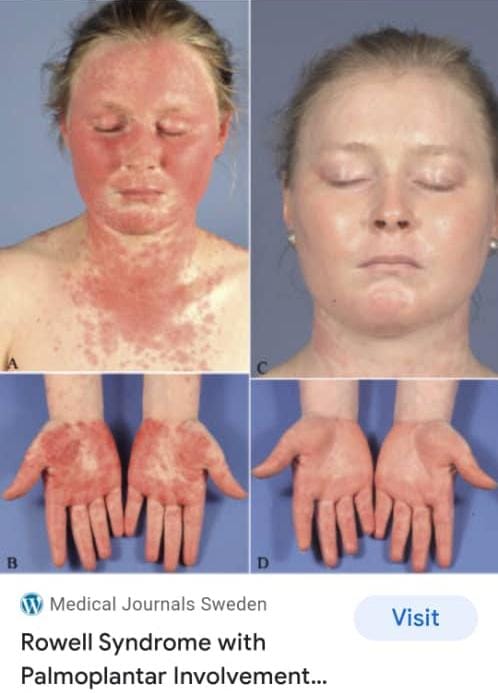
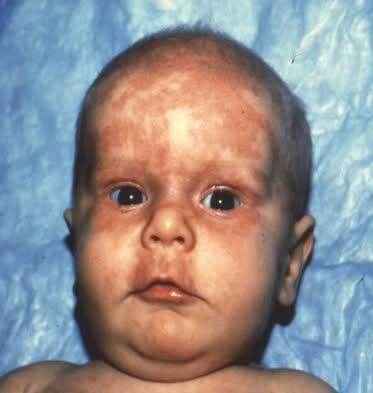
Neonatal LE
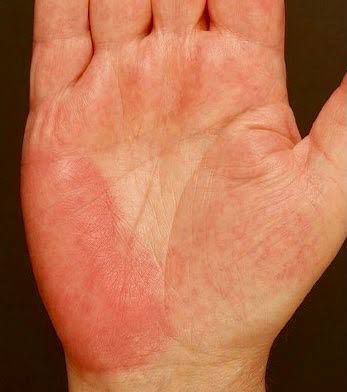
Palmer erythema in LE
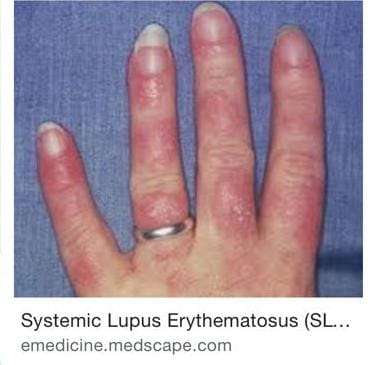
Knuckle sparing in LE
SLICC Criteria

EULAR ACR Criteria 2019